NASA's Hubble captures stunning image of Tarantula Nebula, brightest star-forming region in local universe
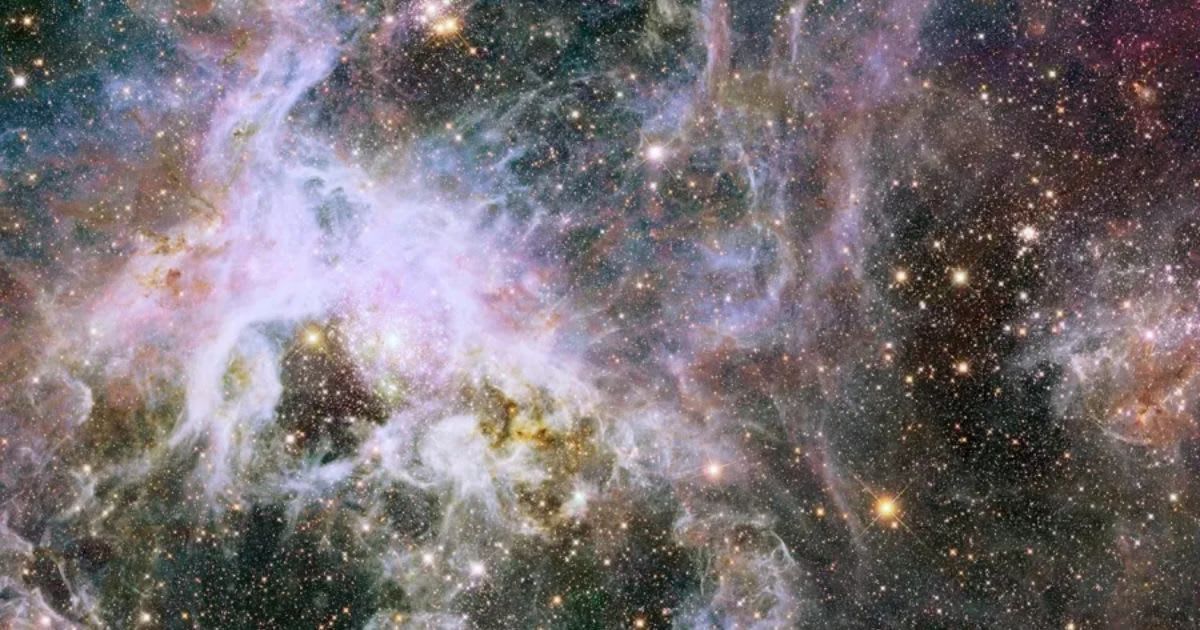

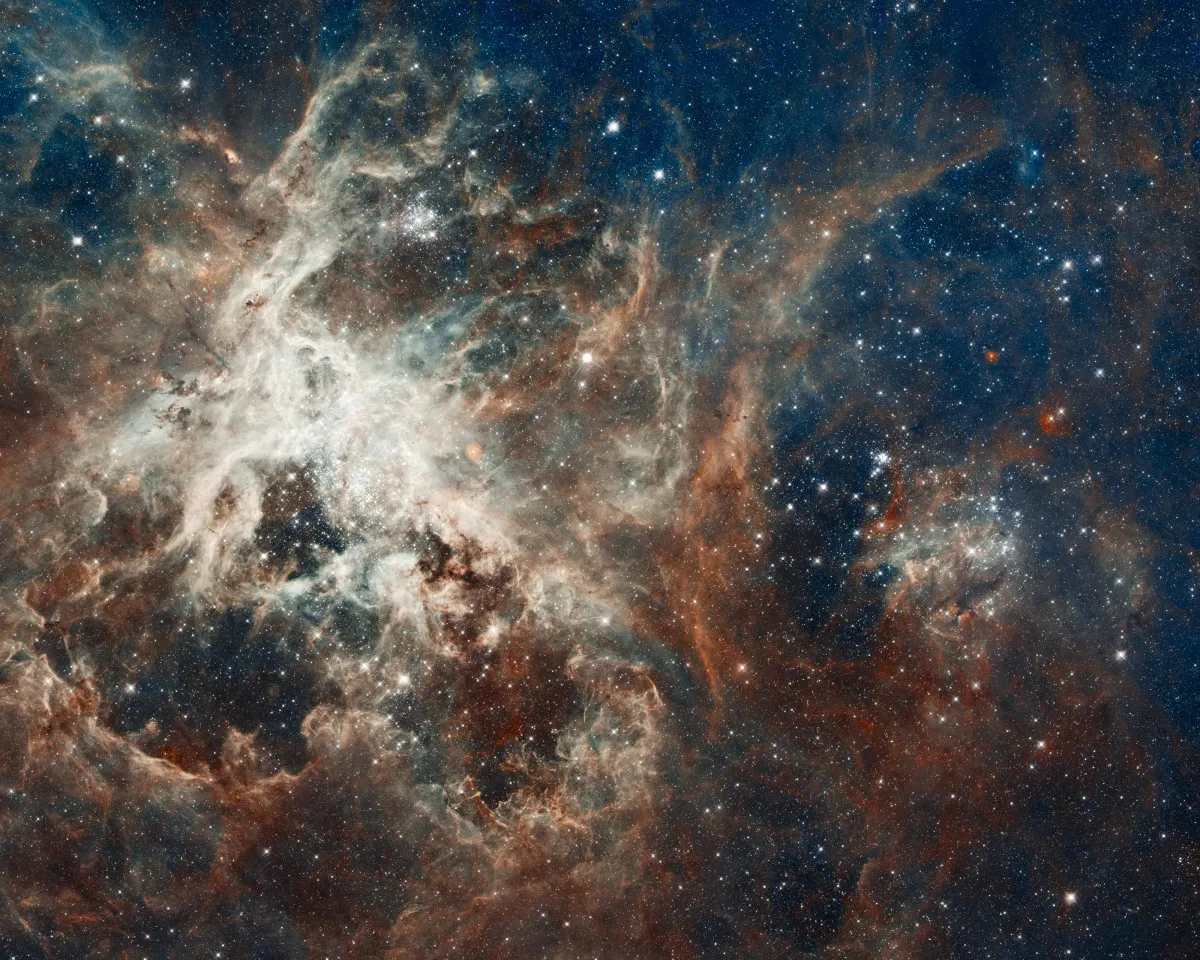
The Tarantula Nebula, the largest and brightest star-forming region in our galactic neighbourhood, has been recently captured in stunning detail by NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. This celestial nursery, which is not located in our galaxy but within the Large Magellanic Cloud, has long been a subject of fascination for astronomers. The Large Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf satellite galaxy orbiting the Milky Way, is situated approximately 160,000 light-years away, according to NASA.

The image, captured as part of a recent Hubble observing program, showcases the intricate, dusty structures within the nebula. The Tarantula Nebula is known for its colossal stars, some of which are up to 200 times the mass of our Sun. The captured view brings viewers remarkably close to a rare Wolf-Rayet star, a type of massive star that has shed its outer hydrogen layer. These stars are known for their extreme temperatures, high luminosity, and powerful stellar winds.
Creeping and crawling through the Tarantula Nebula! 🕷️⭐
— HUBBLE (@HUBBLE_space) August 8, 2025
Access more space-themed .gifs at our giphy page: https://t.co/oMHx7whFJ8 pic.twitter.com/kCp5U1ENLz
The observations are part of a program named Scylla, a nod to the multi-headed sea monster from Greek mythology. This initiative was designed to work alongside another program called ULLYSES, which studies young, massive stars. The Scylla program specifically focuses on examining the surrounding gas and dust structures that envelop these stellar giants. Hubble's multiwavelength capabilities are essential for piercing through the nebula's dense clouds and revealing these sculptural details.
First documented by astronomer Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille in 1751, the Tarantula Nebula is a sight that isn't reserved just for powerful telescopes. Despite its immense distance of 170,000 light-years, its impressive brightness gives it a magnitude of 4, making it visible to the naked eye, as mentioned on NASA's official site. The nebula's distinctive spider-like appearance, which gives it its name, becomes clear through medium to large telescopes. For the best chance to witness this cosmic arachnid, stargazers in the Southern Hemisphere should seek out the Large Magellanic Cloud in the constellation Dorado during the early months of the year, ensuring they are at a location with minimal light pollution.

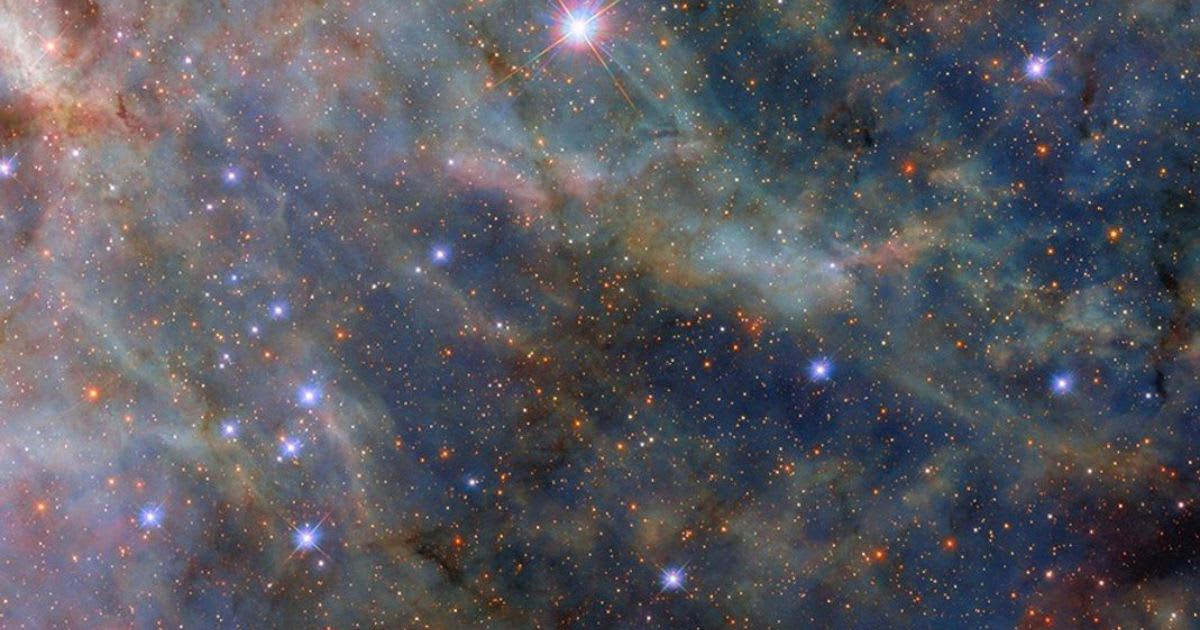
The Hubble Space Telescope continues to provide vital insights into how galaxies evolve, highlighting both active star-forming regions and more quiescent environments. A prime example is the dwarf galaxy NGC 4449, a "starburst galaxy" located a mere 12.5 million light-years away in the constellation Canes Venatici. Despite its smaller size, NGC 4449 is an incredibly active stellar factory, with new stars forming not just in its core but throughout its entire structure. Scientists believe this widespread star formation is triggered by gravitational interactions with nearby galaxies.
This is the nearby dwarf galaxy NGC 4449, which is punching above its weight when it comes to star formation! It is forming new stars much faster than expected for its size, making it a starburst galaxy 🌟 1/3 pic.twitter.com/zrsLXETaAY
— HUBBLE (@HUBBLE_space) June 19, 2025
Due to its relative closeness, NGC 4449 is an invaluable cosmic laboratory for understanding how galactic collisions and near-misses influence stellar birth. Hubble's recent observations, combining data from multiple programs, have helped to map its star formation history and identify its most massive stars. Further enhancing our view, the James Webb Space Telescope has also peered into NGC 4449, using its infrared capabilities to reveal dusty tendrils of gas glowing with the light of newly formed stars. These combined efforts are providing a comprehensive picture of the dynamic processes that drive star formation across the universe.