How far away is Venus

How far away is Venus now?
Last Updated: Today
On 2026-03-03, the distance between Venus and Earth is 247268283 kms, with a range-rate of -3.8316036 km/s, indicating that Venus is moving slightly closer to Earth at that moment.

Where does this distance data come from?
I source Venus's distance from Earth via the Horizon JPL API. It is a free service provided by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) that offers access to ephemeris (positional) data and related information for celestial bodies, such as planets, asteroids, and comets. The system can be accessed through various interfaces, including a web interface, a telnet interface, and an email interface. This API contains the precise distance between Venus and Earth for each day of the next few hundred years. So, I simply created a system to check for today's date, then go retrieve the accurate distance value directly from NASA's database. The up-to-date value is then displayed on this page.
How do scientists calculate the real-time distance between Venus and Earth?
Scientists calculate live distance between Venus and Earth using a combination of mathematics, astronomical data, and the principles of celestial mechanics. The positions of Earth and Venus in their respective orbits are constantly changing due to their elliptical orbits and different orbital periods around the Sun.

Venus' orbital parameters
Orbital parameters describe the way objects move around in space, such as planets, moons, and satellites. These parameters include the size, shape, and tilt of the orbit, as well as the object's position and speed within the orbit. They help scientists understand and predict the paths of celestial bodies, which is crucial for planning space missions, observing astronomical phenomena, and monitoring satellites.
| Orbital Property | Explanation | Venus | Earth | Ratio (Venus/Earth) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Semimajor axis (106 km) | Avg. distance from the Sun | 108.210 | 149.598 | 0.723 |
| Sidereal orbit period (days) | Time for one orbit relative to fixed stars | 224.701 | 365.256 | 0.615 |
| Tropical orbit period (days) | Time for one orbit relative to the vernal equinox | 224.695 | 365.242 | 0.615 |
| Perihelion (106 km) | Closest distance to the Sun | 107.480 | 147.095 | 0.731 |
| Aphelion (106 km) | Farthest distance from the Sun | 108.941 | 152.100 | 0.716 |
| Synodic period (days) | Time to return to the same position relative to the Sun | 583.92 | - | - |
| Mean orbital velocity (km/s) | Avg. speed while orbiting the Sun | 35.02 | 29.78 | 1.176 |
| Max. orbital velocity (km/s) | Highest speed in the orbit | 35.26 | 30.29 | 1.164 |
| Min. orbital velocity (km/s) | Lowest speed in the orbit | 34.78 | 29.29 | 1.187 |
| Orbit inclination (deg) | Angle between the orbital plane and the ecliptic plane | 3.395 | 0.000 | - |
| Orbit eccentricity | Deviation of orbit shape from a perfect circle | 0.0068 | 0.0167 | 0.407 |
| Sidereal rotation period (hrs) | Time for one rotation relative to fixed stars | -5832.6 | 23.9345 | 243.690 |
| Length of day (hrs) | Time for one rotation relative to the Sun | 2802.0 | 24.0000 | 116.750 |
| Obliquity to orbit (deg) | Angle between the equatorial plane and orbital plane | 177.36 | 23.44 | - |
| Inclination of equator (deg) | Axial tilt of the planet | 2.64 | 23.44 | 0.113 |
Venus' greatest elongations (list for the next few years)
Greatest elongation is the term used in astronomy to describe the maximum angular separation of a planet from the Sun as viewed from Earth. In simpler terms, it refers to the point at which a planet appears farthest from the Sun as seen from our perspective on Earth. Venus is sometimes referred to as the "Morning Star" or the "Evening Star" due to its appearance in the sky during different times of the day. This phenomenon occurs because of the relative positions of Venus, Earth, and the Sun as they orbit the Sun. As an inferior planet (meaning it orbits closer to the Sun than Earth), Venus goes through phases similar to the Moon, as well as various positions relative to Earth and the Sun. These positions include inferior and superior conjunctions and greatest elongations.
- Inferior Conjunction: Venus is between the Earth and the Sun, and not visible from Earth.
- Superior Conjunction: Venus is on the opposite side of the Sun from Earth, and not visible from Earth.
- Greatest Western Elongation: Venus is visible in the eastern sky just before sunrise, making it the "Morning Star."
- Greatest Eastern Elongation: Venus is visible in the western sky just after sunset, making it the "Evening Star."
| Greatest Elongation West (Evening | Time | Angle |
|---|---|---|
| August 15, 2026 | 06:59 | 45.9° |
| March 22, 2028 | 11:50 | 46.1° |
| October 27, 2029 | 10:05 | 47° |
| Greatest Elongation East (Morning) | Time | Angle |
|---|---|---|
| June 12, 2026 | 02:45 | 46° |
| January 3, 2027 | 17:57 | 47° |
| August 10, 2028 | 16:00 | 45.8° |
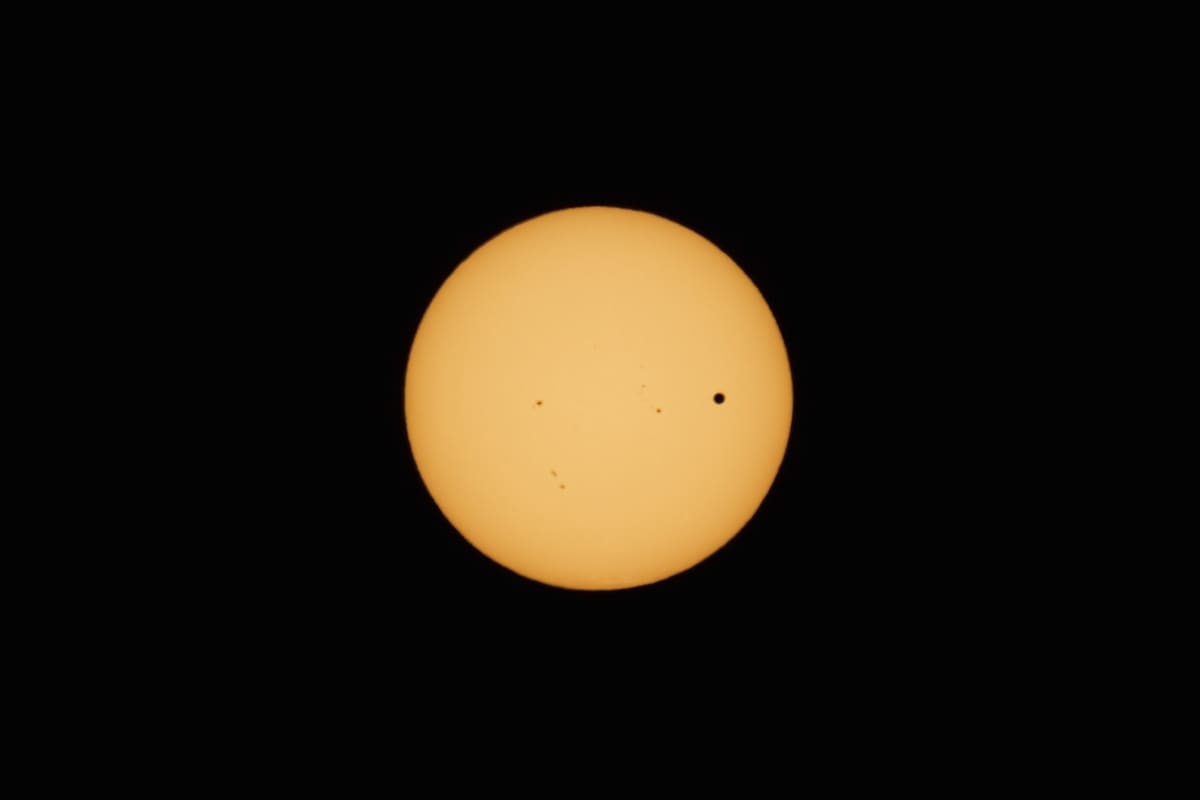

Venus' Inferior Conjunctions (for the next 4 years)
An inferior conjunction is an astronomical event that occurs when a Venus passes between the Earth and the Sun, and is therefore at its closest point to Earth. During an inferior conjunction, the planet appears as a dark silhouette against the bright disk of the Sun, and is usually difficult or impossible to observe.
| Inferior Conjunction | Time (GMT) |
|---|---|
| October 24, 2026 | 3:44 GMT |
| June 1, 2028 | 10:00 GMT |
| January 6, 2030 | 13:18 GMT |
| August 11, 2031 | 3:01 GMT |
Venus' Superior Conjunctions (for the next 4 years)
A superior conjunction is an astronomical event that occurs when Venus is on the opposite side of the Sun as seen from Earth, and is therefore at its greatest distance from Earth. During superior conjunction, the planet is not observable.
| Superior Conjunction | Time (GMT) |
|---|---|
| January 6, 2026 | 16:35 GMT |
| August 12, 2027 | 0:21 GMT |
| March 23, 2029 | 20:12 GMT |
| October 20, 2030 | 11:13 GMT |
Just for fun, how long would it take to reach Venus via different transportation means
The average distance between Earth and Venus is 67 million miles (108 million km), so based on that distance, I have calculated the time it would take to reach the Earth's sister planet at the speed of different means of transportation.
- On foot (3 mph): 2,549 years
- Bicycle (15 mph): 510 years
- Horse (galloping at 25 mph): 306 years
- Motorbike (average speed of 70 mph): 109 years
- Boat (cruising speed of 20 knots): 332 years Car (60 mph): 127 years
- High-speed train (322 km/h): 38 years
- Commercial Airplane (575 mph): 13 years
- Concorde supersonic jet (1,350 mph): 5.7 years
- SpaceX Starship (projected average speed of 16,777 mph): 0.46 years
Bonus Fact: On average, it takes about 6 minutes for light from Venus to reach Earth.
How far away are the other planets of the solar system?
I have developed a webpage that monitors the real-time distances between Earth and each planet of the solar system (work in progress):
- Real-time distance between the Moon and Earth
- Real-time distance between Mercury and Earth
- Real-time distance between Mars and Earth
- Real-time distance between Jupiter and Earth
- Real-time distance between Saturn and Earth
- Real-time distance between Uranus and Earth
- Real-time distance between Neptune and Earth
- How Far Away Is Earth From The Sun?
Learn more about Venus!
This page is part of our collection of astronomy articles. If you enjoyed the read, then you'll love the following articles.

Why is Venus hotter than Mercury?
It would make sense that the closer an object is to the Sun, the hotter it would be. So why is Venus hotter than Mercury?

Although there are more than 210 known moons in our solar system, there are a couple of planets that have no moons at all: Mercury and Venus.

How to observe Venus with a telescope
I have compiled a comprehensive guide to help you observe planet Venus through your home telescope.