NASA is tracking asteroid more than twice the size of Empire State Building as it approaches Earth

NASA has its eye on a huge asteroid that is more than twice the size of the Empire State Building (1,454 feet) as it approaches our planet for a close encounter. The space rock has a formal name, 162882 (2001 FD58), and it is categorized under the "Potentially Hazardous Asteroids" umbrella because of its proximity to Earth’s orbit.

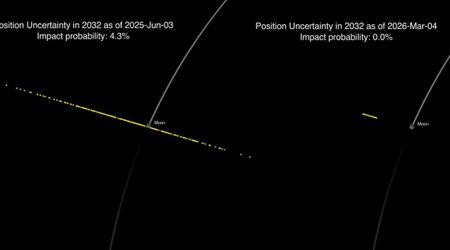
The asteroid, according to the latest tracking data of the Center for Near-Earth Object Studies (CNEOS), will come close to Earth on February 14, 2026. Given that it could be around 2,411 feet in size, the damage would be significant if it hit Earth. Fortunately, data indicates it won't. On the day of its close approach to Earth, the asteroid will be over 4 million miles away. For perspective, the distance between our planet and the Moon is around 239,000 miles, and the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS was around 167 million miles away on the day of its closest approach. However, while the asteroid poses no danger to us, it has been assigned a rarity of 2 by CNEOS, which means that a close approach by an asteroid of this size is not that common and happens roughly once a year.
The precise asteroid was originally recognized in March 2001, which was a time of intense sky surveys, per Space Weather. In a very short span of time, experts recorded several notable Earth-approaching asteroids, among them 2001 FE90 and 2001 FO32. Keeping an eye on these objects is a standard operation under the planetary defense plan by NASA. By keeping close tabs on 2001 FD58 and similar rocks, researchers not only gain insights into the population of debris in our solar system but also secure early warning of any threats posed by them.

The February flyby of 2001 FD58, although the most important one, is not the only celestial object to skim past Earth in the next few weeks. Just before that, five smaller asteroids will safely approach our planet throughout the first week of January 2026, according to the data shared on NASA JPL.
In fact, the first day of the New Year is going to see two flybys taking place. The first, an asteroid called 2025 YL4, will come within 903,000 miles of Earth. It will have the company of 2025 XC7, which is an airplane-sized object that will stay at a larger distance of 2.12 million miles. January 2 will see two more visitors: the small asteroid 2025 YZ, which is only 28 meters wide, will pass at a distance of 3.36 million miles, and another small asteroid, 2025 YT2 (which is the size of a bus), will also pass at a distance of 3.54 million miles. The week of early encounters will end on January 3 with a relatively close pass of about 1.04 million miles by another bus-sized object, 2025 YV6.
More on Starlust
January 2026: Quadrantids meteor shower and more skywatching events to start the new year