NASA's Parker Solar Probe confirms long-held theories about magnetic reconnection on the Sun
Data from NASA's Parker Solar Probe (PSP) has validated decades-old theoretical models of magnetic reconnection, a key driver of space weather phenomena like solar flares and coronal mass ejections. This groundbreaking confirmation comes from the only spacecraft to ever venture directly into the Sun's upper atmosphere, according to the Southwest Research Institute.
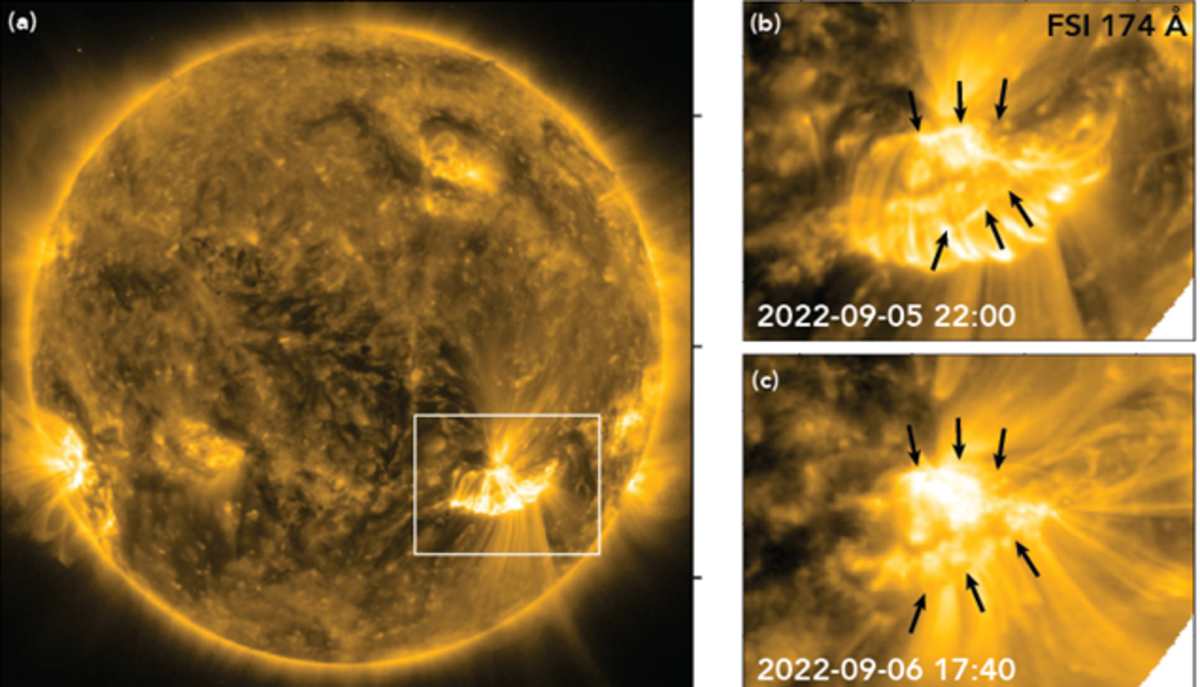
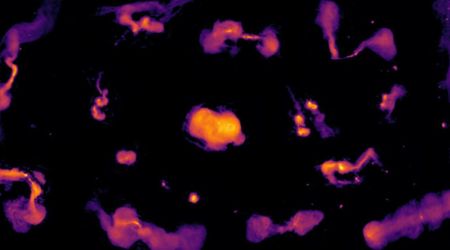
Led by the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), a new study utilized observations from PSP's September 2022 flyby, during which the probe passed through a massive eruption. This provided an unprecedented opportunity to measure the plasma and magnetic field properties within a reconnection zone for the first time. Magnetic reconnection is the process where magnetic field lines break and reconnect, releasing immense amounts of stored energy.

According to Dr. Ritesh Patel, a SwRI research scientist and the paper's lead author, this event finally allowed scientists to connect the dots between theoretical models and real-world observations. While previous missions, such as NASA's Magnetospheric Multiscale (MMS) mission, had studied reconnection in Earth's near-space environment, the PSP data provides the missing link to understanding these events on a solar scale.

The findings, published in the journal Nature Astronomy, not only confirm the validity of long-standing numerical simulations but will also serve as a crucial benchmark for future models. A more accurate understanding of solar reconnection could significantly improve predictions for space weather events that can disrupt satellites, communication systems, and power grids on Earth. Researchers now plan to investigate if turbulence or other magnetic field fluctuations are present in these active reconnection zones, a step that could further refine our understanding of how energy is transferred and particles are accelerated on the Sun.
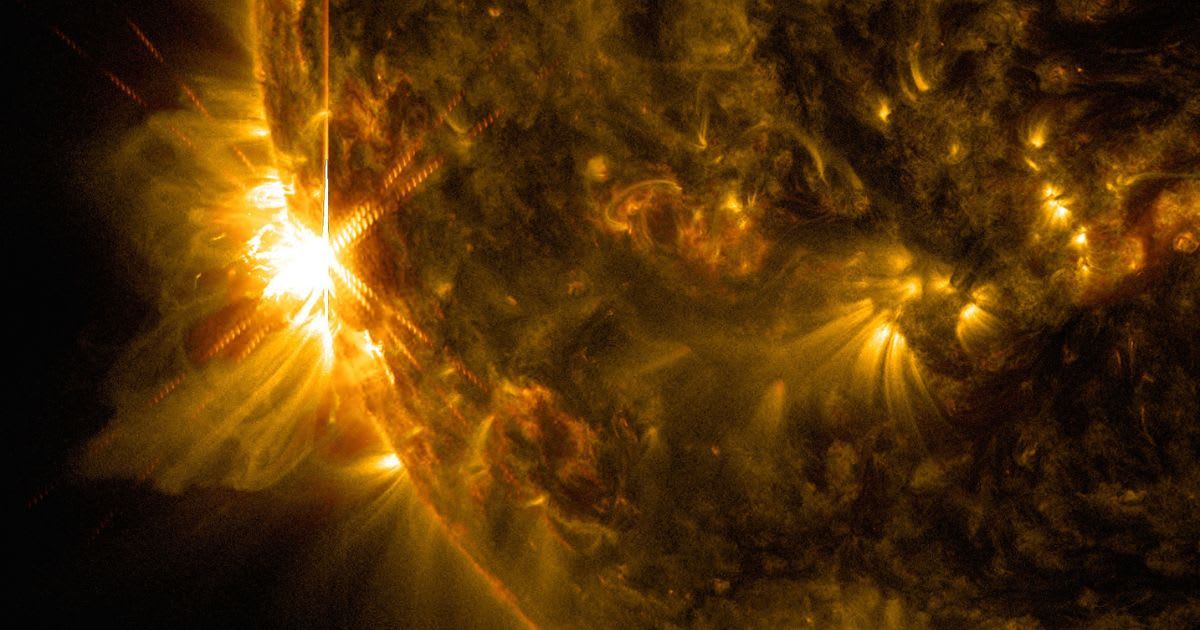
While the Parker Solar Probe is validating long-held theories, it has also released stunning, never-before-seen images captured from within the Sun's atmosphere, offering the closest views ever recorded of our star. These unprecedented visuals, obtained during a record-setting flyby in late 2024, are providing scientists with direct observations of the origins of space weather.
This is the view from WITHIN the Sun’s atmosphere! ☀️👀🛰️
— ARCHIVED - NASA Sun & Space (@NASASun) July 10, 2025
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe just released imagery from its closest-ever flyby of the Sun, revealing details in the solar atmosphere that scientists will be studying for years.
More: https://t.co/ZDyJ1ReiWC pic.twitter.com/fuEVAy55mk
Nicky Fox, associate administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, emphasized the significance of these images. “We are witnessing where space weather threats to Earth begin, with our eyes, not just with models," she said. "This new data will help us vastly improve our space weather predictions to ensure the safety of our astronauts and the protection of our technology here on Earth and throughout the solar system.”
During its December 24, 2024, approach, the probe came within just 3.8 million miles of the solar surface. Using its Wide-Field Imager for Solar Probe (WISPR) instrument, it captured intricate details of the Sun's outer atmosphere, known as the corona, and the solar wind. The imagery provides a detailed look at the heliospheric current sheet, where the Sun's magnetic field changes direction, and also captures high-resolution collisions of multiple coronal mass ejections (CMEs), the powerful bursts of charged particles that profoundly influence space weather.

The Parker Solar Probe's historic journey began in 2021 when it became the first spacecraft to fly directly through the Sun's corona. On its mission to "touch the Sun," the probe endures brutal heat and radiation, getting closer with each orbit, per NASA. These daring flybys provide humanity with an unparalleled opportunity to study our only star up close, offering insights that are impossible to obtain from Earth.