Massive tail and anti-tail jets reveal unexpected structure of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS

New images of the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS have captured an astonishing, multi-jet structure, with vast plumes extending millions of kilometers into space. The discovery, observed by Frank Niebling and Michael Buchner on November 9, 2025, reveals an unexpected scale and complexity far exceeding previous observations and raising fundamental questions about the object's origin, according to Harvard astronomer Avi Loeb on his Medium blog.
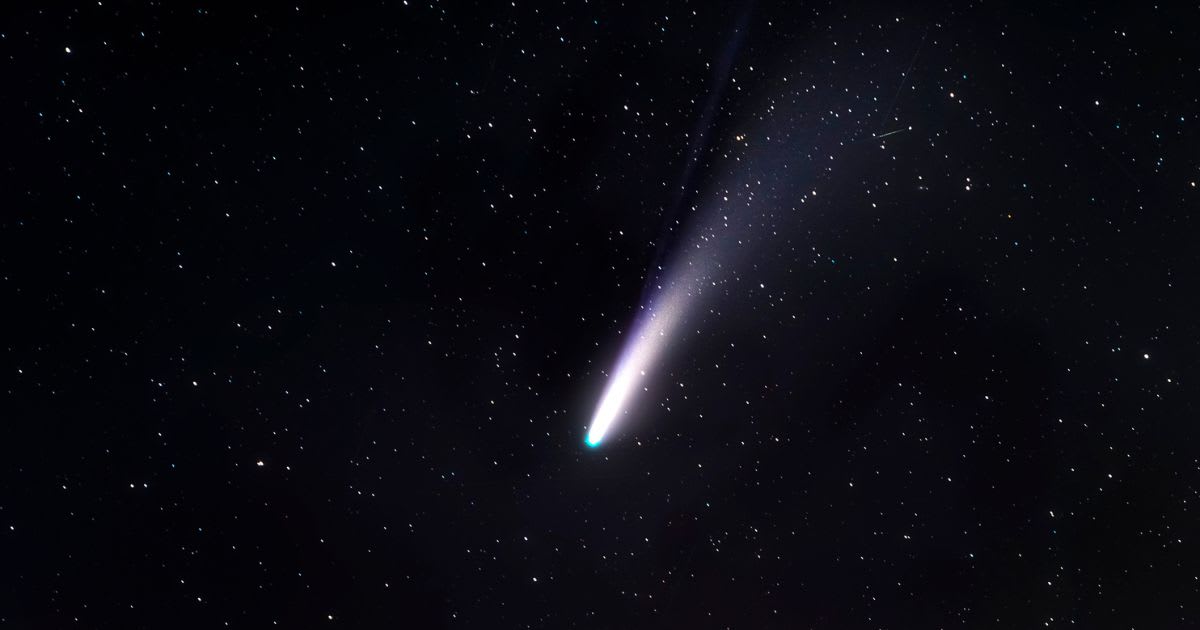

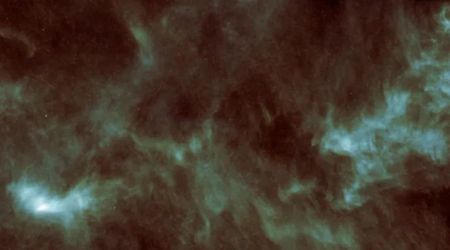
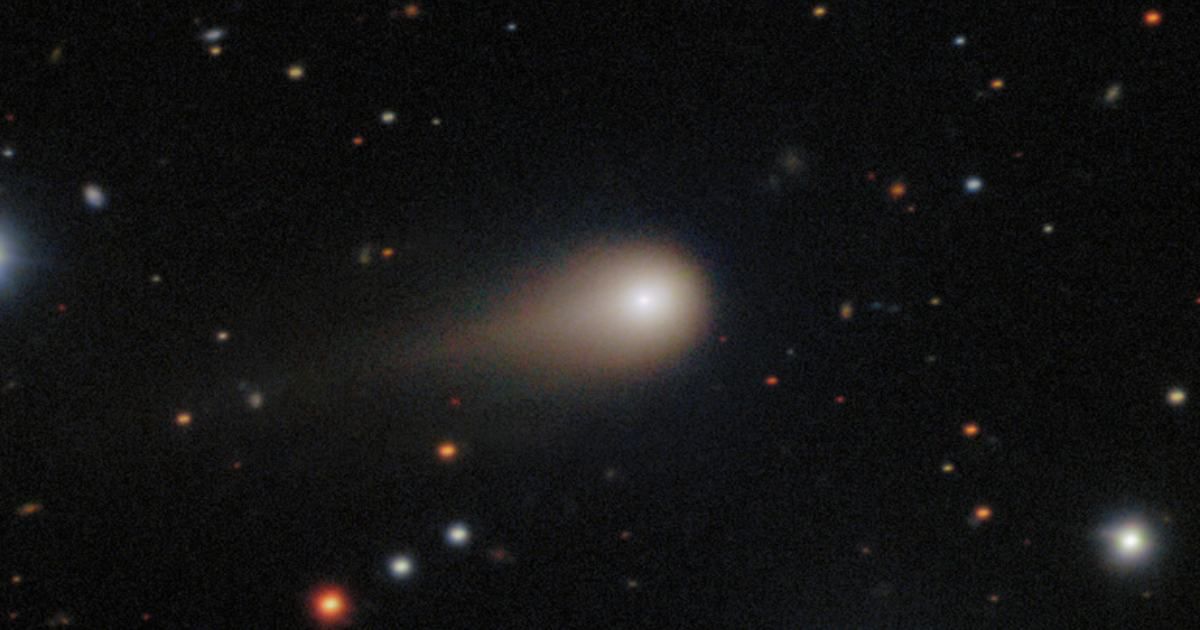
Stacked exposures from two separate telescopes documented two distinct anti-tail jets directed toward the Sun, stretching 0.95 million kilometers (0.59 million miles). Even more dramatic is a colossal, collimated tail jet extending 2.85 million kilometers (1.8 million miles) away from the Sun, an angular size of about 30 arcminutes, equivalent to the full diameter of the Sun or Moon as seen from Earth. This enormous scale is roughly a thousand times larger than the glowing halo seen around 3I/ATLAS in NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope images from July 21, 2025.
![Hubble captured this image of the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS on July 21, 2025, when the comet was 277 million miles from Earth. [Image Source: NASA, ESA, David Jewitt (UCLA); Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)]](https://de40cj7fpezr7.cloudfront.net/c49eeb4e-e60a-46c0-b39f-68fbb2ee9297.jpeg)
Astrophysicist Avi Loeb noted that if the object is a natural comet, the sheer size of these structures implies a phenomenal mass loss. Standard cometary outflow speeds suggest the tail jet has been active for about three months. To maintain such an expansive anti-tail against the solar wind, its mass density must be roughly a million times greater than the solar wind's, resulting in an estimated mass loss rate of 50 billion tons per month. This calculated mass loss is comparable to the object's minimum estimated total mass, which is approximately 33 billion tons, implying a nucleus diameter of at least 5 to 10 kilometers (3.1-6.2 miles).
The colossal size of 3I/ATLAS presents a significant statistical anomaly. At over 50 billion tons, it is at least a million times more massive than the first observed interstellar object, 1I/`Oumuamua. The probability of an object of this size randomly entering our solar system during the relatively short survey period is incredibly low, probably once per ten thousand years or longer. When combined with the object's rare retrograde trajectory, the odds of a natural cometary origin for 3I/ATLAS drop to as low as one in a hundred million, according to Loeb's analysis.

The alternative hypothesis suggests the jets could be a product of technological thrusters. Human-made chemical and ion thrusters have exhaust speeds 10 times higher than typical cometary sublimation. This higher velocity could reduce the required fuel, and thus the implied mass loss by one to two orders of magnitude, making the required "fuel" less than one percent of the object's total mass.
While the object will pass closest to Earth on December 19, 2025, at a distance of 269 million kilometers (167 million miles), the jets are unlikely to be intercepted by Earth-based or deep-space particle probes like NASA’s Juno or ESA’s Juice spacecraft. The most crucial data will come from upcoming spectroscopic observations, which are expected to measure the velocity, composition, and mass flux of the jets, potentially determining once and for all if 3I/ATLAS is a gigantic natural comet or a piece of advanced interstellar technology.