'Almost every area of astronomy': NASA's SPHEREx reveals universe's infrared secrets, week by week

NASA's cutting-edge SPHEREx space telescope, launched this past March, has commenced its ambitious mission to chart the cosmos, delivering an unprecedented all-sky map to a publicly accessible archive. This weekly release of data, available to researchers and enthusiasts alike, promises to revolutionize our understanding of the universe, according to NASA.
In March, NASA's SPHEREx telescope launched into orbit to create an all-sky map of the universe.
— NASA (@NASA) July 2, 2025
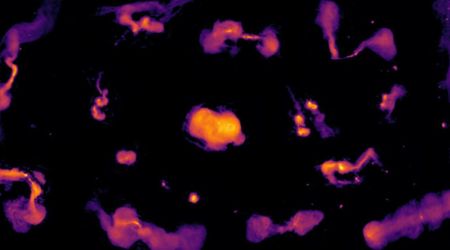
Now, it's returning its first results to the public—including this infrared image of the Vela Molecular Ridge: https://t.co/OrC0NCJ9Q2 pic.twitter.com/Oiy9Mg34ut
SPHEREx, or the Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization, and Ices Explorer, is now in low-Earth orbit, systematically scanning the heavens. Its primary objective is to create a comprehensive spectral atlas, providing a rich dataset for nearly every facet of astronomical inquiry. “Because we’re looking at everything in the whole sky,” stated Rachel Akeson, who leads the SPHEREx Science Data Center at IPAC, a renowned astrophysics and planetary science center at Caltech.
Building on the legacy of predecessors like NASA's retired Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE), SPHEREx significantly expands observational capabilities. While WISE mapped the sky in four infrared wavelength bands, SPHEREx boasts an impressive 102, enabling a far more detailed spectroscopic analysis. This enhanced spectral resolution allows scientists to identify the unique signatures of specific molecules. This mission's scientific team plans to leverage this technique to investigate the distribution of vital "building blocks of life" – frozen water and organic molecules – within our own Milky Way galaxy. Beyond molecular mapping, SPHEREx data will be instrumental in probing the early universe. Scientists will utilize the information to decipher the physics that governed the universe's rapid expansion after the Big Bang and to quantify the light output from galaxies across cosmic time.
In a move underscoring NASA's commitment to scientific transparency, SPHEREx data are entered into the public archive within 60 days of observation. This rapid release, following essential processing to ensure data quality and accuracy, is designed to foster widespread scientific collaboration. “By making the data public, we enable the whole astronomy community to use SPHEREx data to work on all these other areas of science,” Akeson emphasized. The team also publishes the detailed processing procedures, ensuring researchers have all the necessary tools for independent analysis.

Over its two-year primary mission, SPHEREx will complete four comprehensive all-sky surveys, with the first full-sky map across all 102 wavelengths anticipated after the initial year. The telescopes' data also holds immense potential when combined with other ongoing and upcoming missions. It can identify targets for the James Webb Space Telescope, refine exoplanet parameters from the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), and contribute to studies of dark matter and dark energy alongside the European Space Agency's Euclid mission and NASA's Forthcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope, as mentioned by NASA.

The NASA/IPAC Infrared Science Archive (IRSA), which hosts the SPHEREx data, offers a wealth of observational data from numerous past missions, providing a holistic view for astronomical studies. As Akeson aptly puts it, "Almost every area of astronomy can be addressed by SPHEREx data." The SPHEREx mission is managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). BAE Systems built the telescope and spacecraft. Scientific analysis involves a diverse team from 10 US institutions, two in South Korea, and one in Taiwan. Caltech in Pasadena managed and integrated the instrument, with the principal investigator holding a joint JPL appointment. Data processing and archiving are handled at IPAC at Caltech, and the entire SPHEREx dataset is publicly available via the NASA-IPAC Infrared Science Archive.