New study identifies hundreds of previously undocumented satellite systems orbiting dwarf galaxies

A groundbreaking new study led by astronomers at Dartmouth has vastly expanded our knowledge of galactic ecosystems, identifying hundreds of potential satellite galaxies orbiting dwarf galaxies. The multi-institutional team's findings, published in The Astrophysical Journal, challenge existing assumptions about how these smaller galaxies are formed and how they interact with their environments, according to Dartmouth.
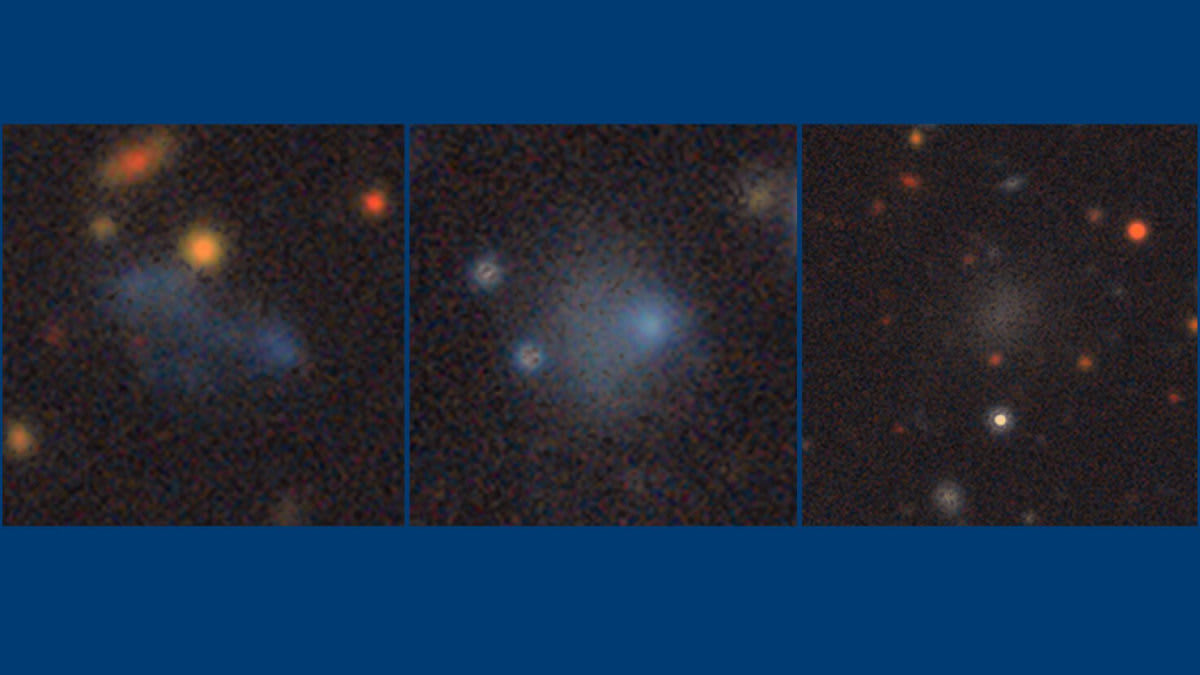

Traditionally, most research on galactic satellites has focused on large galaxies, such as the Milky Way. However, this new survey dramatically shifts the focus to dwarf galaxies, systems that are less than a tenth the size of our galaxy. The study nearly triples the number of dwarf galaxies that have been surveyed for satellites, providing a massive new dataset for astronomers to analyze.

The survey identified 355 candidate satellite galaxies, with 264 of these being previously uncatalogued. Researchers suggest that 134 of the candidates are highly likely to be true satellite galaxies. “This project fills a critical gap, offering fresh insights into the process of how galaxies form and their connection to dark matter," said author Burçin Mutlu-Pakdil, an assistant professor of physics and astronomy." Our goal is to build a statistical sample of the smallest galaxies in the universe, as they are the most dominated by dark matter and serve as clean laboratories for understanding its nature.”
The survey, led by postdoctoral fellow Laura Hunter, analyzed publicly available imaging data from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) Legacy Imaging Surveys. The team used an algorithm to identify potential satellites and then visually inspected each candidate to ensure accuracy. By studying these systems, the research aims to unlock clues about conditions in the early universe and how galaxies evolve. Previous studies of larger galaxies have suggested a correlation between a host galaxy's size and the number of satellites it possesses. The new data will enable scientists to test whether this principle applies to the much smaller dwarf galaxies.

Hunter explains, “Astronomy is a field where you can’t run experiments; all you can do is observe and make as many measurements as you can," and "then put that data into a simulation and see whether it reproduces your observations. If it doesn’t, that tells us that there’s something wrong with our assumptions or our model of the universe.” This new survey is the initial phase of a broader effort. The research team is currently conducting a follow-up campaign to confirm the candidates and analyze their properties, such as size, gas content, and star formation rates. This work is expected to have a significant impact on our understanding of dark matter and the formation of galaxies on the smallest scale.
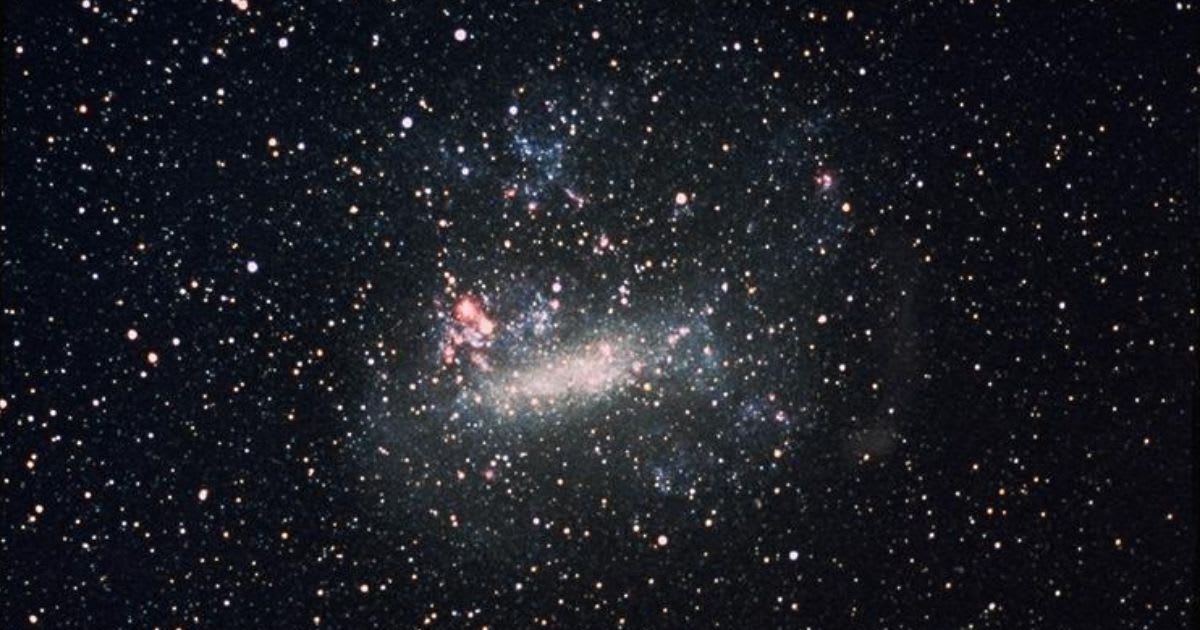
The Dartmouth team's work to understand how galactic interactions influence satellite formation is complemented by detailed observations of individual systems. A prime example is the dwarf galaxy NGC 4449, which the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope recently focused on. Located just 12.5 million light-years away in the constellation Canes Venatici, this small but mighty galaxy is a prime example of a "starburst galaxy," a system undergoing an extraordinary period of star creation. The dwarf galaxy's proximity to Earth makes it an ideal cosmic laboratory for studying how these gravitational encounters fuel the creation of new stars and shape galactic evolution, providing a valuable case study for the statistical data gathered by the Dartmouth team.