NASA’s Roman Space Telescope survey aims to discover 100,000 star explosions and feeding black holes

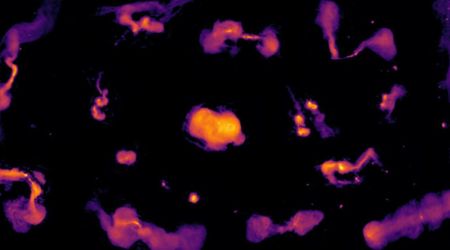
A single, sweeping survey by NASA's upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope is projected to uncover an unprecedented 100,000 cosmic explosions, from the final moments of stars to the chaotic feeding of black holes. The "gold mine" of data, as described by a lead scientist, promises to open new windows into some of the universe's most profound mysteries, including the nature of dark energy, the mysterious pressure accelerating the expansion of the cosmos, as per NASA.

The planned two-year observing program, dubbed the High-Latitude Time-Domain Survey, will repeatedly scan the same vast patch of the sky, allowing scientists to stitch together a time-lapse cosmic movie. This dynamic view will capture a dazzling array of celestial fireworks, chief among them a special class of stellar detonation known as type Ia supernovae. These exploding stars are crucial for cosmological studies because they consistently reach a peak brightness, allowing astronomers to use them as "standard candles" to measure cosmic distances and map the universe's expansion, per NASA.

A new study, published in The Astrophysical Journal, simulated Roman's planned survey and suggests the telescope could discover approximately 27,000 type Ia supernovae, a tenfold increase over all previous surveys combined. The dramatic leap in sample size will allow scientists to peer further back in time, with Roman expected to detect thousands of these supernovae from more than 10 billion years ago. This will fill in a critical gap in our understanding of how the cosmos has evolved.
“Whether you want to explore dark energy, dying stars, galactic powerhouses, or probably even entirely new things we’ve never seen before, this survey will be a gold mine,” said Benjamin Rose, an assistant professor at Baylor University and the study's lead author. “Evidence is mounting that dark energy has changed over time, and Roman will help us understand that change by exploring cosmic history in ways other telescopes can’t.” Beyond its primary mission of charting the universe's expansion, Roman's wide field of view will capture a significant amount of cosmic "bycatch." The study estimates the telescope will spot around 60,000 core-collapse supernovae, which are the violent deaths of massive stars. It may also unearth extremely rare phenomena, including tidal disruption events — where black holes shred a star with their immense gravity — and superluminous supernovae, which can outshine a typical supernova a hundredfold.

Even rarer and more sought after are kilonovae, the powerful blasts created by the collision of two neutron stars. To date, only one such event has been definitively observed. The Roman telescope could potentially detect five more, which would provide crucial data for understanding these enigmatic events and their final products, which could be either a single neutron star or a black hole. Perhaps most thrilling is the possibility that Roman will find evidence of the universe's very first stars. These primordial giants were so massive that they are thought to have self-destructed in powerful "pair-instability" supernovae, leaving nothing behind. “I think Roman will make the first confirmed detection of a pair-instability supernova,” Rose stated.“They’re incredibly far away and very rare, so you need a telescope that can survey a lot of the sky at a deep exposure level in near-infrared light, and that’s Roman,” as mentioned on NASA.
The immense volume of data from the survey will require innovative solutions. “With the dataset we’ve created, scientists can train machine-learning algorithms to distinguish between different types of objects and sift through Roman’s downpour of data to find them,” stated Rebekah Hounsell, a co-author of the study. “Roman’s going to find a whole bunch of weird and wonderful things out in space, including some we haven’t even thought of yet. We’re definitely expecting the unexpected.”