Earth's 'wind' is causing the Moon to rust—but how is this possible?

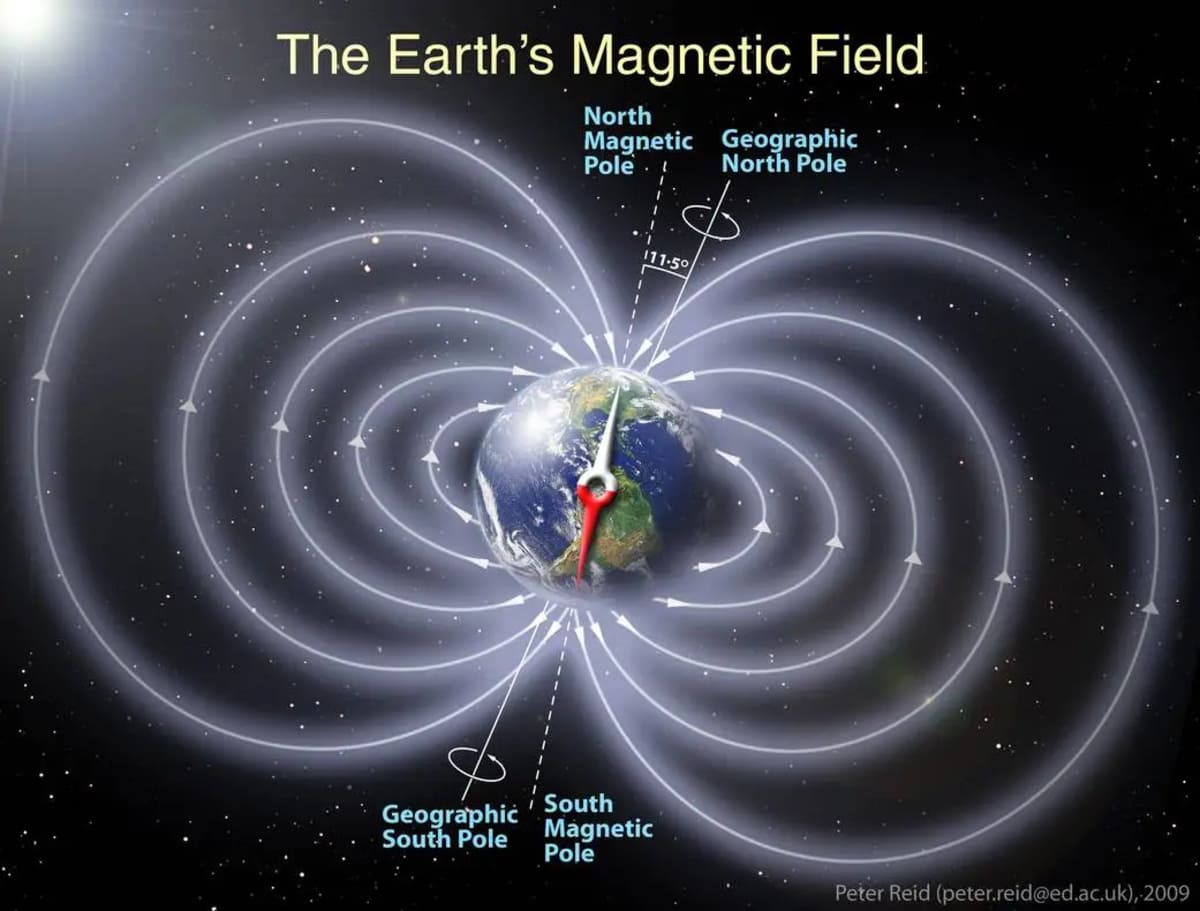
A new study has provided significant evidence for a surprising theory: that oxygen from Earth's atmosphere is being transported to the Moon, causing it to rust. The findings, published in Geophysical Research Letters, back up the idea that Earth's magnetic field acts as a shield, funneling oxygen ions from our planet's upper atmosphere toward the Moon during certain times of the month, as reported on Phys.org.
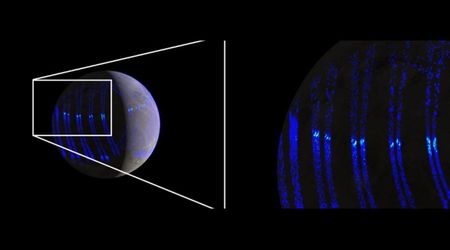
This phenomenon has been dubbed "Earth wind." The mystery of lunar rust, or hematite, began in 2020 when scientists discovered the mineral across the Moon's higher latitudes. The presence of rust was a major puzzle, as its formation requires oxygen, an element scarce on the Moon. While several theories for the origin of oxygen were proposed, the distribution pattern of the rust pointed to a connection with Earth. To test the "Earth wind" theory, researchers recreated lunar surface conditions in a lab. They exposed minerals found in lunar regolith (Moon dust) to oxygen and hydrogen ions at energy levels consistent with those from Earth's wind. The results showed that the oxygen ions effectively oxidized the iron-bearing minerals, creating hematite.

The study also addressed a critical counterpoint: the solar wind, which constantly bombards the Moon with hydrogen ions. Hydrogen is a reducing agent, meaning it should reverse the oxidation process and prevent rust from forming. The scientists found that while low-energy hydrogen from the solar wind had little effect, higher-energy hydrogen from Earth's wind was capable of reducing the hematite back to metallic iron.
According to the study's authors, this explains why rust can persist on the Moon. The retention of hematite depends on the delicate balance between the energy and volume of oxygen and hydrogen ions being blown over from Earth. The research suggests that while solar wind's low-energy hydrogen is largely ineffective, the higher-energy protons from Earth wind are a key factor in the lunar environment's chemical reactions.

The "Earth wind" model could also explain how rust forms on other airless celestial bodies, such as asteroids, per NASA. According to JPL scientist Abigail Fraeman, the impact of dust particles and small amounts of water could be allowing iron on these bodies to rust. These discoveries come at a time of renewed interest in lunar exploration. With nearly 50 years since the last Apollo landing, the Moon is once again a major destination for space agencies. NASA's Artemis program plans to send dozens of new instruments and technology experiments to study the Moon, with human missions to follow.
Among the upcoming missions, JPL is developing a new version of the Moon Mineralogy Mapper (M3) for the Lunar Trailblazer orbiter. One of its instruments, the High-resolution Volatiles and Minerals Moon Mapper (HVM3), will map water ice in the Moon’s permanently shadowed craters and may also reveal new details about lunar hematite. "I think these results indicate that there are more complex chemical processes happening in our solar system than have been previously recognized," said Shuai Li of the University of Hawaii. "We can understand them better by sending future missions to the Moon to test these hypotheses."
More on Starlust
How fast is the Moon moving away from Earth each year?
What would happen if Earth became tidally locked to the Moon?