3I/ATLAS update: First X-ray detection suggests the comet behaves like its solar system counterparts
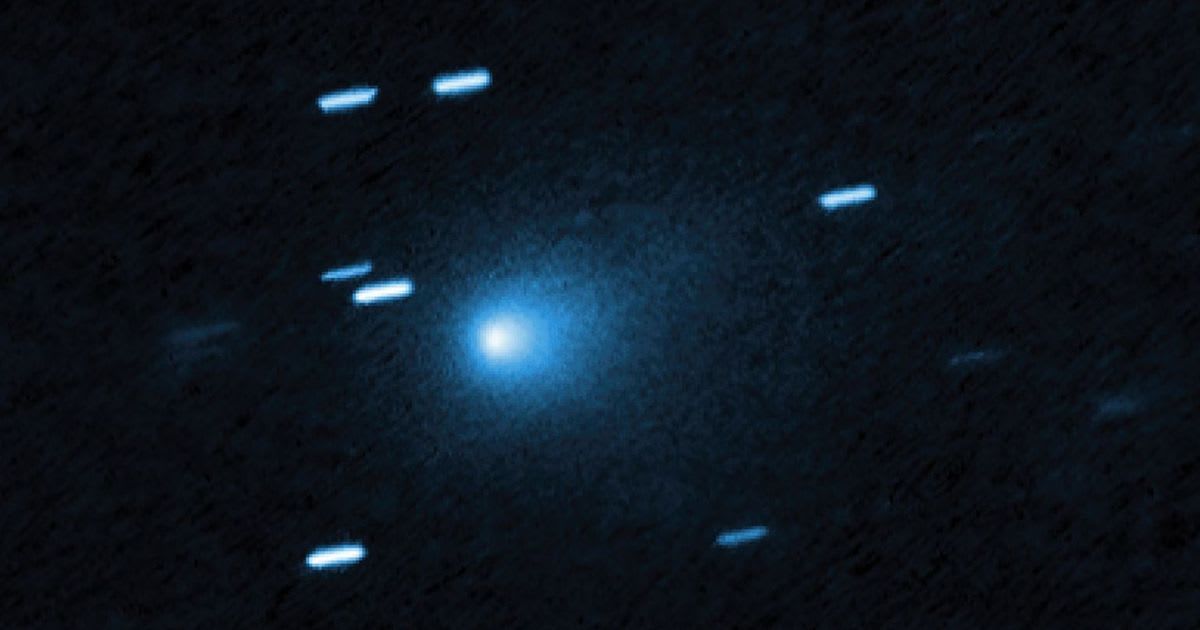

The X-Ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission (XRISM) satellite may have just achieved a monumental first in astronomical observation: the first-ever detection of X-rays emanating from an interstellar comet. This remarkable finding centers on the object known as C/2025 N1, also referred to as 3I/ATLAS, which was discovered this July and is confirmed to have arrived from beyond our solar system, thus earning it an exceptionally rare classification as a celestial interloper, according to XRISM.
XRISM has caught sight of interstellar #comet 3I/ATLAS !
— XRISM (@XRISM_jp) December 6, 2025
Our early data hint at a faint X-ray glow spreading hundreds of thousands of kilometers across its coma — a first glimpse of this rare visitor from beyond the Solar System.
Stay tuned for more.#JAXA #NASA pic.twitter.com/je3rT6UhyJ
This most recent observation delivers key information about these foreign visitors. Though there had been attempts in the study of interstellar comets with a host of wavelengths, including optical, infrared, and radio, scientists had yet to detect X-ray emission. That left a gap in our knowledge: Do interstellar comets act like ordinary comets in our solar system, or are they fundamentally different? The 17-hour observation between November 26 and November 28, 2025, carried out by the soft X-ray imaging telescope Xtend, showed a faint X-ray glow around the comet's nucleus. This diffuse halo was extended up to 400,000 kilometers from the core.
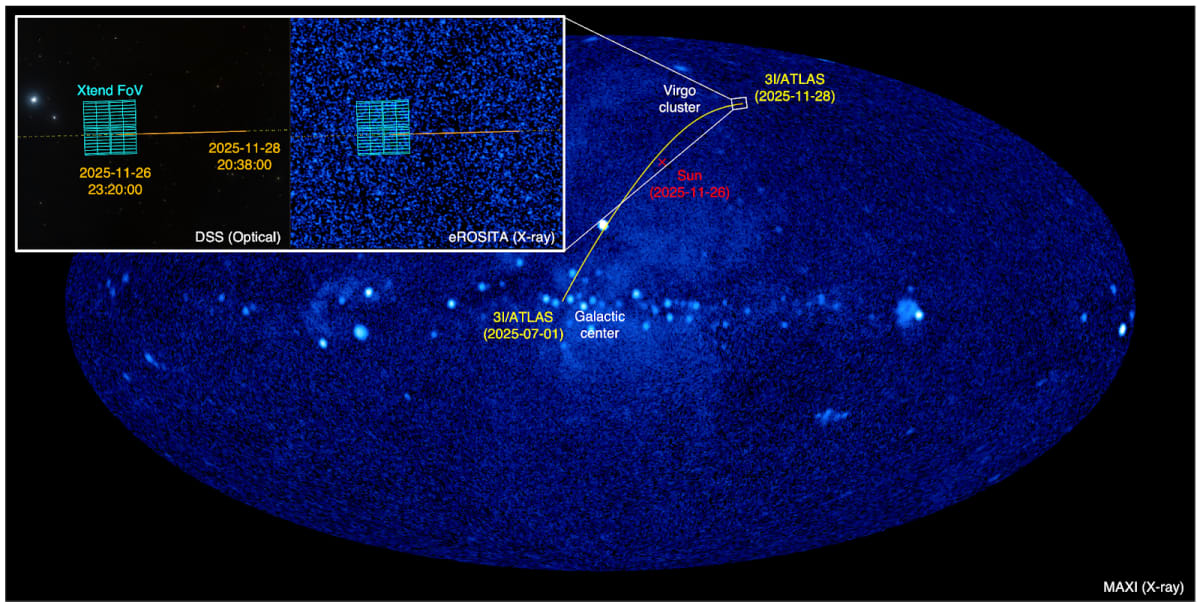
The crucially detected X-ray emission is believed to be the result of a charge-exchange reaction: a process that takes place when a highly energetic stream of charged particles flowing from the Sun, the solar wind, interacts with the vast cloud of gas and dust, or coma, that vaporizes off the comet's icy surface as it approaches the Sun. This interaction, in fact, is an established mechanism for X-ray generation in comets within our solar system, a phenomenon first observed in Comet Hyakutake in 1996.

The XRISM data reinforced this connection by showing tell-tale X-ray components likely associated with common elements such as carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen. These specific spectral signatures are difficult to explain by ordinary background sources, and they strongly point toward a scenario of their origin in this interaction between the cometary gas and the solar wind.
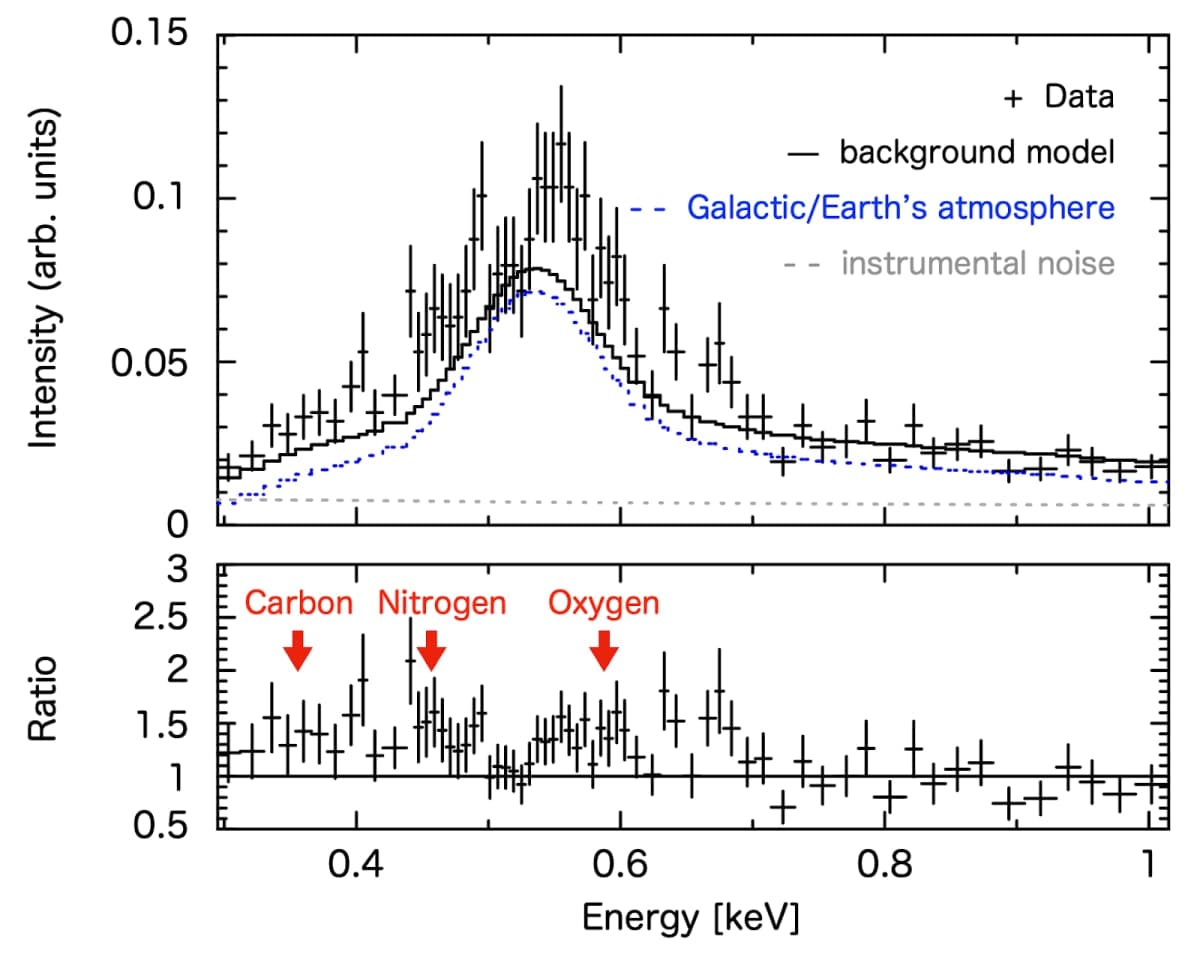
As the XRISM team explained, "This provides an important clue that the observed emission may indeed arise from charge-exchange interactions between the cometary gas and the solar wind." What this suggests is that the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS is behaving very similarly to a "normal" solar system comet when it passes close to the Sun. Its highly active nature made it an ideal candidate for this pivotal observation.

This finding is in agreement with the view of the prominent Harvard astronomer Avi Loeb, who has been studying the interstellar visitor since its discovery. Loeb said the detection, emanating from the gas plume enveloping the comet, was remarkably enlightening. "This pioneering detection of X-ray from an interstellar object will no doubt be followed on by other research teams," Loeb wrote, underlining the importance of the result of XRISM for future research into these enigmatic travelers, per the Avi Loeb Medium blog.
All that said and done, the XRISM team did note that more careful analysis is necessary to confirm that the emission originated from the comet. The XRISM team is continuing with the refinement of its data processing to further reveal the activity of this interstellar comet and the precise nature of its interaction with the solar wind, which can finally help understand the composition and activity of matter originating outside our cosmic neighborhood.
More on Starlust
Interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS appears to be covered in erupting 'icy volcanoes,' scientists say