If we spent one second per galaxy, it would take 634 years to see all the galaxies Vera Rubin will capture in 10 years

The Vera C. Rubin Observatory is embarking on a monumental mission to chart the cosmos with unparalleled detail. Utilizing the largest camera ever constructed for astronomy, the observatory will undertake a decade-long, continuous scan of the night sky, culminating in the Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST). This ambitious project aims to create an ultrawide, ultra-high-definition time-lapse record, meticulously documenting every discernible celestial alteration.

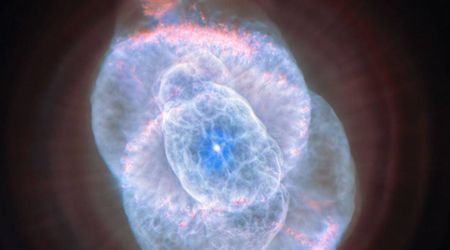
The observatory recently unveiled its inaugural set of three images on June 23, providing a stunning view of the universe. These initial observations included a spectacular nebula, a field of countless luminous stars, and an array of magnificent spiral galaxies. Equipped with the world's largest digital camera, this land-based telescope was poised to revolutionize astronomy through its powerful wide-angle and high-resolution imaging capabilities.
Whew, what a day!
— NSF-DOE Rubin Observatory (@VRubinObs) June 23, 2025
Today we revealed the preview of @NSF–@doescience Rubin Observatory's epic cosmic movie🎬 #RubinFirstLook
From wide-field and deep views of the Universe, to the dynamic and changing sky, Rubin is already bringing the night sky to life!https://t.co/j7zEeId8jY
At the heart of this endeavor is the LSST Camera, an instrument comparable in size to a small car and weighing approximately 6,200 pounds (2,800 kilograms). This colossal camera is engineered to capture extremely fine details of distant galaxies, stars, and other celestial bodies. Each image recorder by the LSST Camera is vast, covering an area equivalent to 45 full Moons, promising an extraordinary depth and breadth of observational data.

The observatory has already demonstrated its transformative potential. During its initial image release conference, the Vera C. Rubin Observatory unveiled a trove of newly identified asteroids. Within merely a few nights of initial data collection, the observatory impressively pinpointed 2,104 previously unseen asteroids within our solar system. This included seven near-Earth Objects (NEOs), eleven Jupiter Trojans, and nine Neptunian objects, highlighting the observatory's remarkable efficiency in discovery.
Among its initial captures, the Vera Rubin Telescope showcased an extragalactic view featuring an astonishing 10 million galaxies. This single image, so dense with celestial bodies that the background appears gray rather than black, offers a glimpse into the vastness of the universe. To put this into perspective, continuously viewing each galaxy in this image for one second would require nearly four months of uninterrupted observation, per IFL Science. Remarkably, this detailed image, comprising 10 million galaxies, was compiled from 1,185 exposures over just seven nights. This rapid creation of such a wide and deep cosmic view highlights the Rubin Observatory's unique capability as the sole astronomical instrument of this feat.

This initial cosmic panorama represents merely 0.5 percent of the total galaxies the Rubin Observatory is slated to capture for the LSST. Over its ten-year operational period, the observatory expects to observe a staggering 20 billion galaxies, an estimated one-tenth of all galaxies believed to exist in the visible universe. If one were to spend a single second examining each of these galaxies, it would take an astonishing 633.8 years to complete the task.

The observatory bears the name of Dr. Vera C. Rubin, the pioneering American astronomer whose foundational work provided compelling evidence for the existence of dark matter. Just as Dr. Rubin reshaped our understanding of the cosmos, the observatory named in her honor is set to be a game-changing instrument in the field of astronomy.