How to watch comet C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) this week — while it’s still visible from Earth
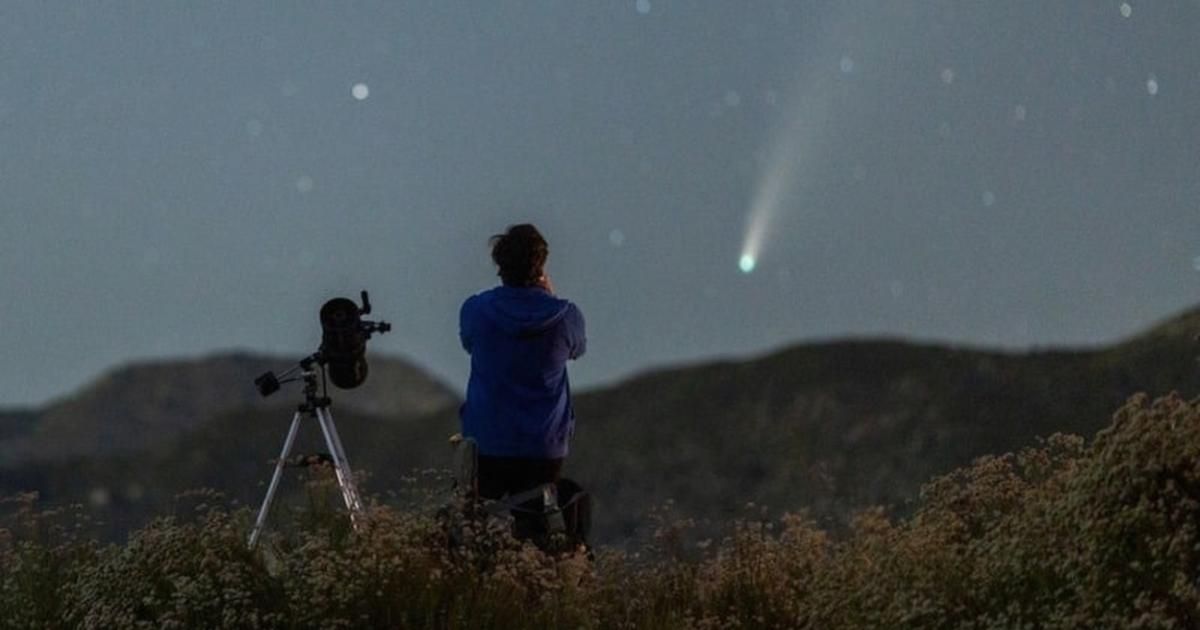

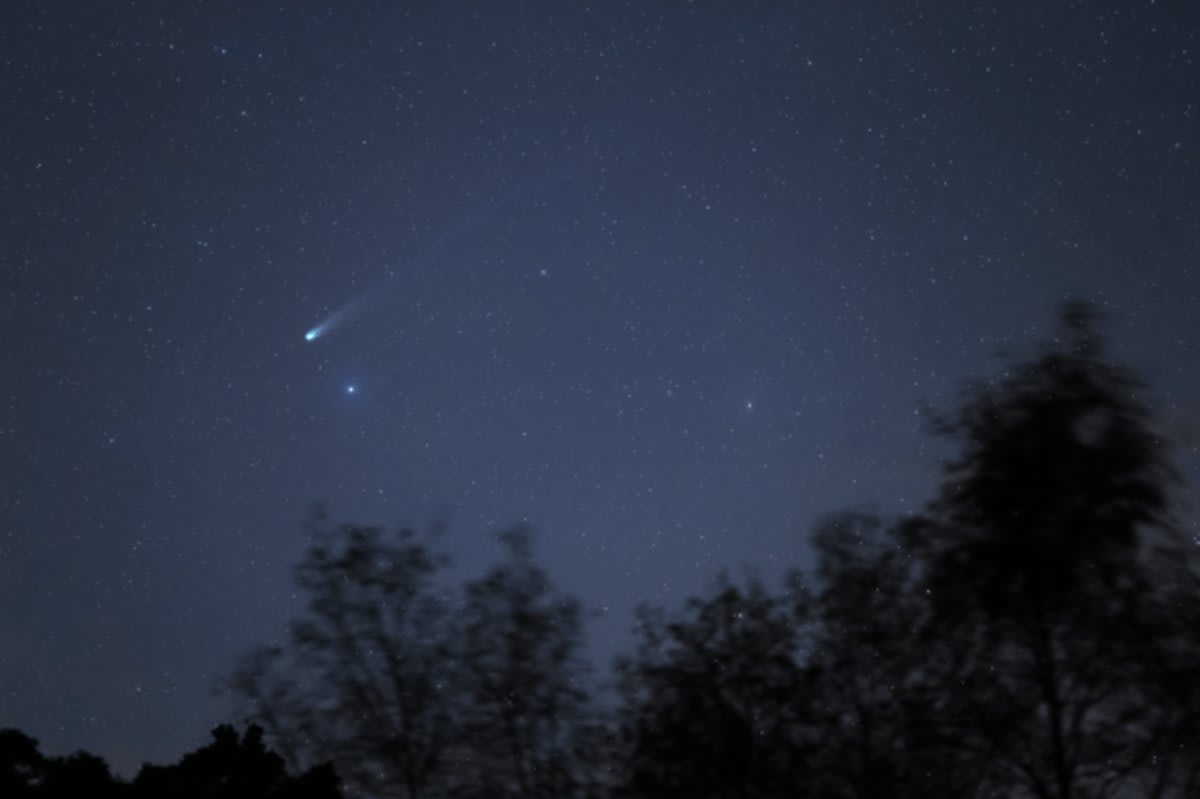
The brief, bright appearance of Comet C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) is rapidly drawing to a close, giving stargazers a final, narrow window to observe the icy object before it retreats. Having made its closest pass to Earth on Tuesday, October 21, at a distance of approximately 89.2 million kilometers, the comet is now fading and racing across the night sky, according to Sky Live.

As of today, October 24, Comet Lemmon is positioned within the constellation Boötes and stands at an apparent magnitude of 3.6. Over the weekend, the challenge for viewers increases. By the weekend, the comet will have moved into the constellation Serpens, with its expected magnitude dropping to roughly 5.0, making it significantly fainter. On Saturday, October 25, observers should look for the comet in the constellation Serpens at coordinates 15h 18m 56s, +19° 48’ 42” (magnitude 5.04), with the position shifting rapidly to 15h 31m 18s, +17° 06’ 28” (magnitude 4.97) by Sunday, October 26.
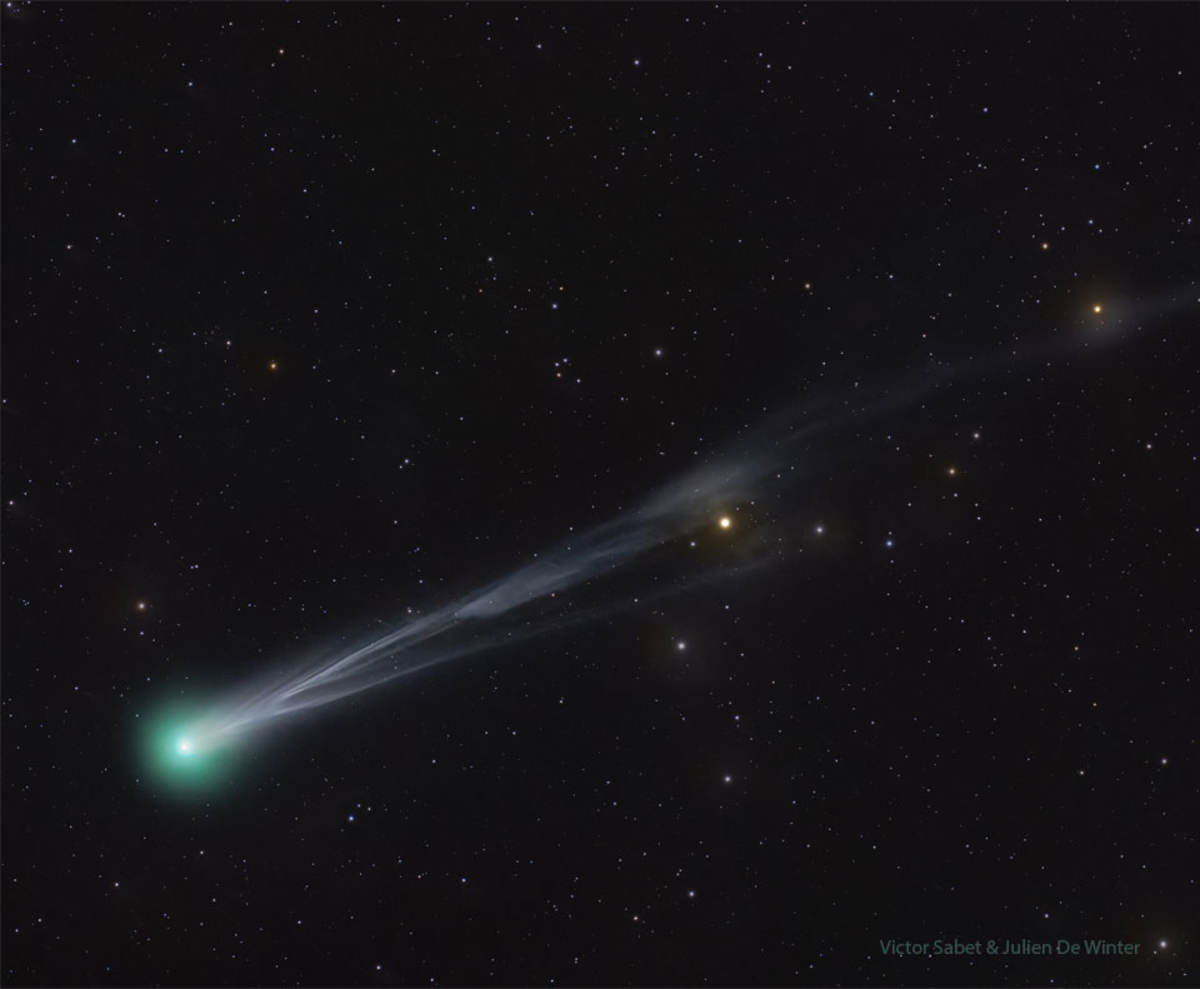
Given the comet's decreasing luminosity, viewing it will require more than just the naked eye. An object with a magnitude of 5.0 is typically at the limit of human vision, meaning light-polluted urban and suburban skies will make detection almost impossible. For the best chance of viewing, using binoculars (such as a 7x50 or 10x50 model) is recommended. These will gather enough light to reveal the comet as a faint, diffuse patch of light. A small telescope will offer superior views, potentially allowing observers to discern details within the comet’s head, or coma, and possibly a hint of its tail.

For Northern Hemisphere observers, the window for viewing Comet Lemmon is now centered squarely on the early evening hours, according to BBC Sky. Viewing is optimal between 7:00 PM and 8:00 PM local time this week before the comet descends toward the horizon. Observers should be aware that comets shift position noticeably each night. Comet Lemmon will appear to move consistently eastward across the sky, passing through the constellation Serpens by the end of the month. Given that this icy visitor will not return for another 1,300 years, this current viewing period represents the best, and last, opportunity for a generation to spot C/2025 A6 (Lemmon).
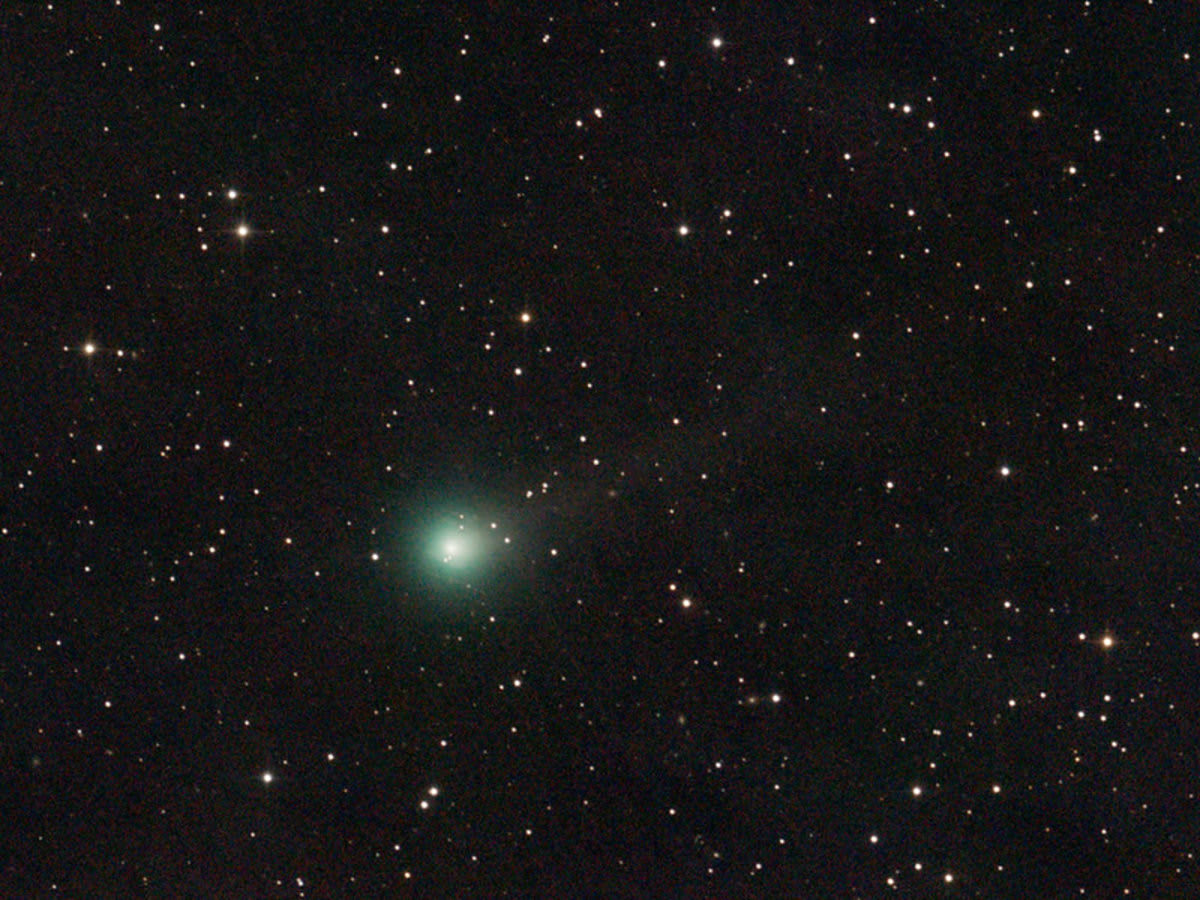

The comet, officially designated C/2025 A6 (Lemmon), is an extremely distant traveler, having spent the majority of its existence in the remote reaches of the outer Solar System, far beyond the orbit of the ice giant Neptune. As per the UK Space Agency, it was first identified in January of this year by astronomers operating the Mount Lemmon Survey in Arizona.
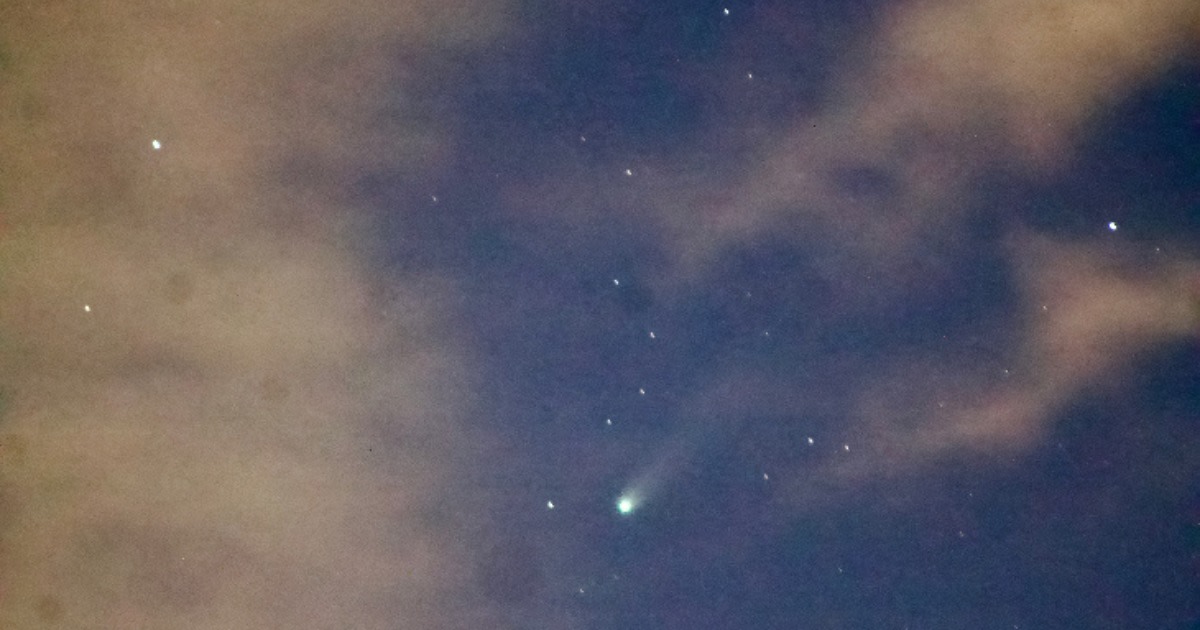

The celestial body's recent surge in visibility is a direct result of its approach to the Sun. As the comet, a structure primarily composed of ice and dust, gets nearer to our star, solar heat causes the frozen materials on its surface to vaporize. Catching a view of Comet Lemmon this weekend offers a chance to observe this ancient physical transformation in real time.










