Counting the comets: 2025’s discovery tally so far

Comets have had a busy year. As different sky surveys kept scanning the heavens, a surprising mix of new comets turned up, some bright, some barely there, and a few carrying unusual stories of their own. A couple brushed close to the Sun, one arrived from outside our Solar System, and others quietly revealed themselves only after patient follow-up work. Here are some notable comets that shaped 2025’s comet news, per the Institute of Astronomy at the University of Cambridge.
C/2025 R2 (SWAN)
C/2025 R2 (SWAN) first caught attention in early September when observer Vladimir Bezugly noticed it in SWAN (Solar Wind Anisotropies) images. Ground-based telescopes soon confirmed it, and it was initially designated as SWAN25B. It passed close to the Sun on September 12 and made its closest pass to Earth on October 20, 2025, at a distance of approximately 24.2 million miles.

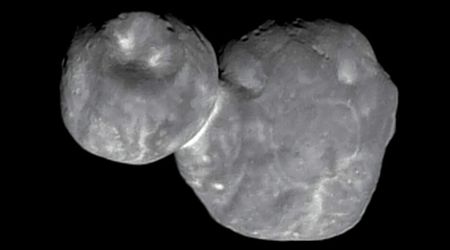
C/2025 3I/ATLAS
Discovered by the ATLAS team on July 1, it stands as the third known interstellar object to enter our solar system. It is being said that it has been wandering for around billions of years, and is older than our solar system. Comet 3I/ATLAS is currently in the constellation of Virgo, at a distance of about 188 million miles from Earth, and is set to make its closest approach to our planet on December 19, at a distance of around 167 million miles.
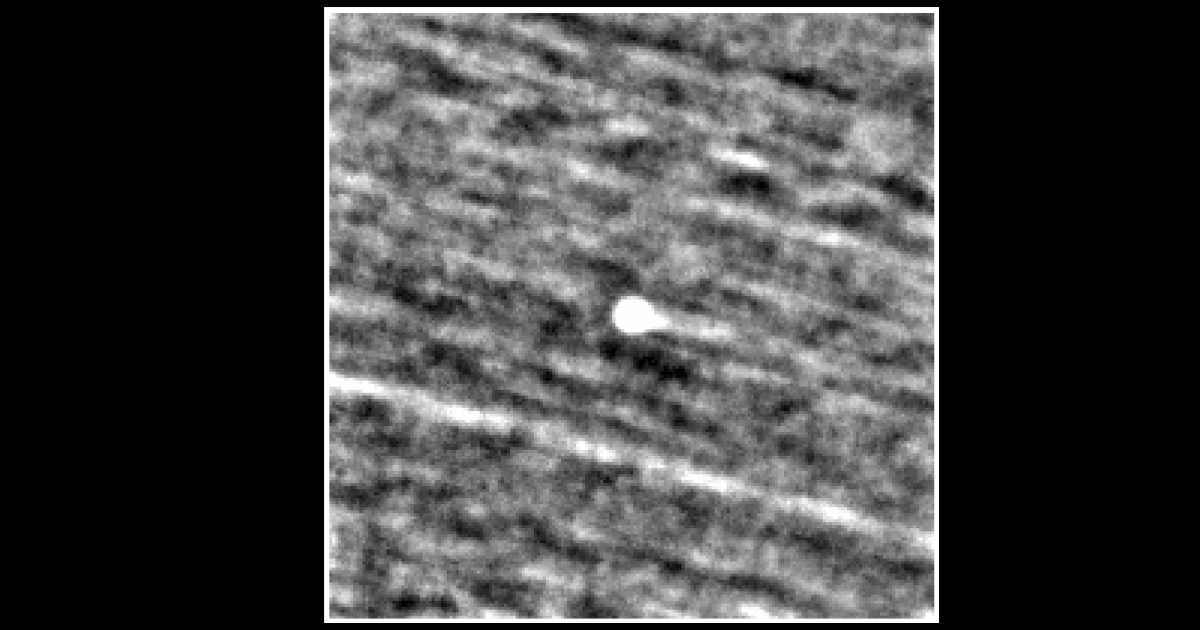
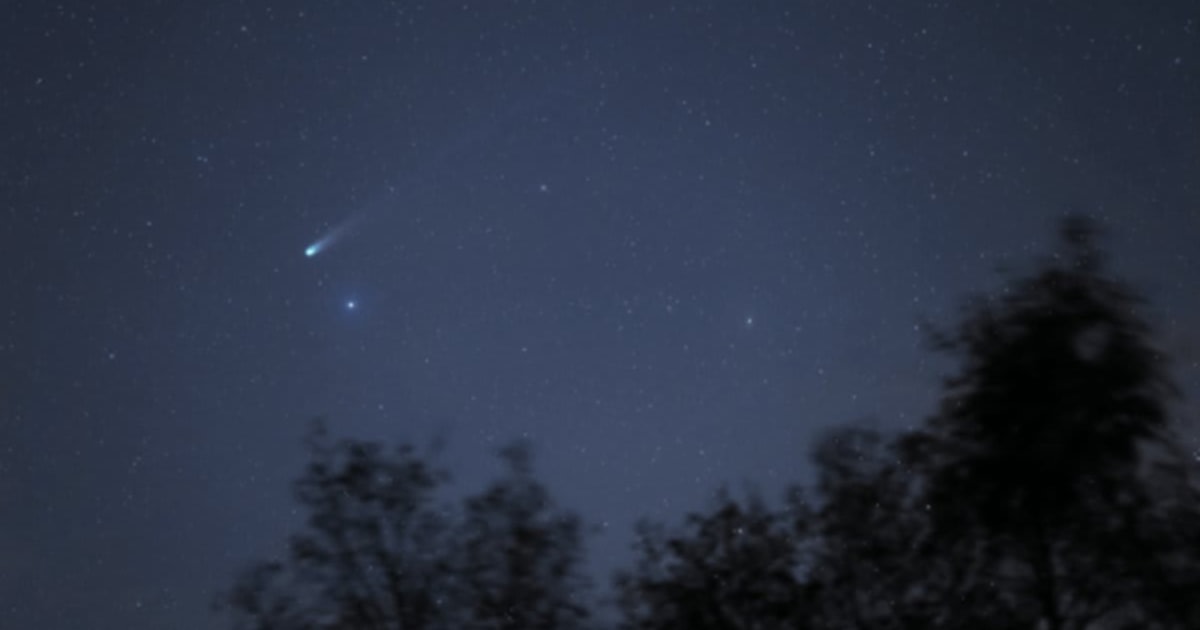
C/2025 A6 (Lemmon)
It was spotted by the Mount Lemmon Survey on January 3, 2025. However, precovery images of the comet in PanSTARRS data date back to early November 2024. It was the closest to Earth on October 21 at a distance of around 55.4 million miles, and is currently located in the constellation of Ophiuchus, at a distance of around 133 million miles from our planet.

Some other prominent comets of the year were:
C/2025 K1 (ATLAS)
A faint long-period comet discovered by ATLAS on May 24, 2025. It is currently in the constellation of Ursa Major at a distance of around 38 million miles, and will make its closest approach to Earth on November 25, when it will be around 37 million miles from our planet.
2025 F2 (SWAN)
Detected in SWAN data in March 2025 by Michael Mattiazzo, this comet displayed noticeable activity early on and was later confirmed through ground-based follow-up observations by Qicheng Zhang.
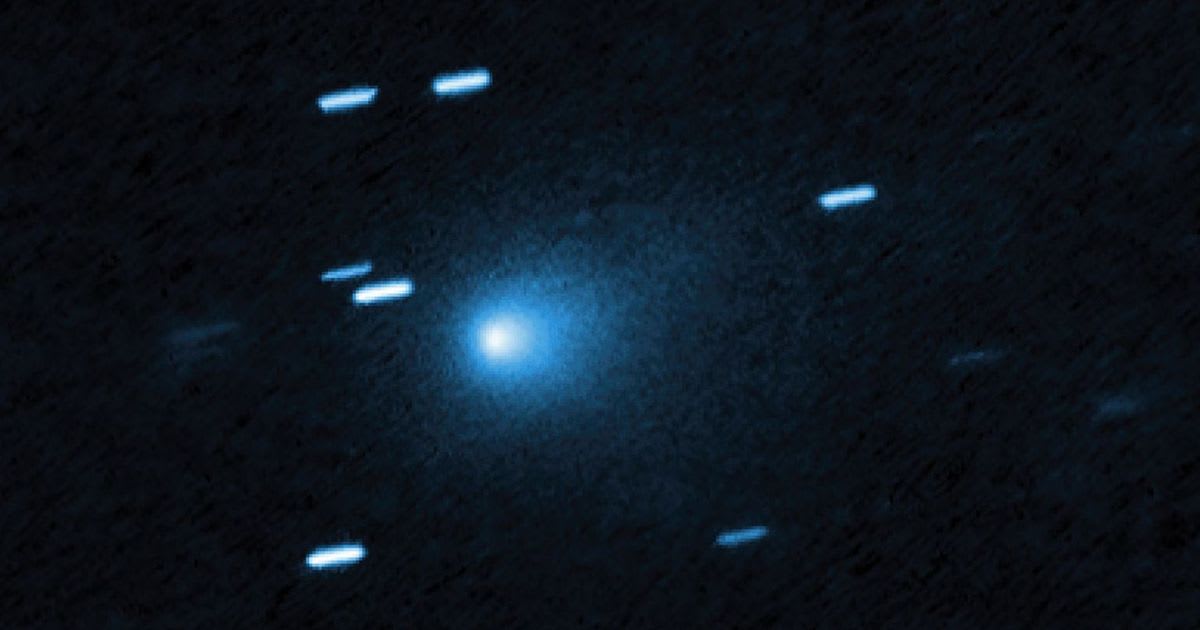

2025 V1 (Borisov)
I was discovered by Gennady Borisov in November 2025, through images taken with the MARGO reflector at Nauchnij, Crimea.
2025 A3 (Tsuchinshan)
First identified as an asteroid, this comet was discovered by Zhijian Xu in January using the Schmidt telescope at the Xuyi Observatory of Purple Mountain (Tsuchinshan).

List of all comets discovered in 2025:
1743 X1, 2007 SA24 (507P/Lemmon), 2009 KF37 (505P/Palomar), 2010 KG43 (506P/WISE-LINEAR), 2010 LH155 (504P/WISE-PANSTARRS), 2012 KA51 (Palomar), 2017 FL36 (P/PANSTARRS), 2025 A1 [A/Lemmon], 2025 A2 (P/PANSTARRS), 2025 A3 (Tsuchinshan), 2025 A4 (PANSTARRS), 2025 A5 (P/Catalina), 2025 A6 (Lemmon), 2025 A7 [A/Lemmon], 2025 B1 (PANSTARRS), 2025 B2 (Borisov), 2025 B3 (P/PANSTARRS), 2025 C1 (P/ATLAS), 2025 D1 (Groeller), 2025 D2 (P/PANSTARRS), 2025 D3 (P/PANSTARRS), 2025 D4 (P/ATLAS),
2025 D5 (PANSTARRS), 2025 D6 (ATLAS), 2025 E1 (PANSTARRS), 2025 F1 (ATLAS), 2025 F2 (SWAN), 2025 F3 (503P/PANSTARRS), 2025 H1 (P/NEAT), 2025 J1 (Borisov), 2025 K1 (ATLAS), 2025 K2 (PANSTARRS), 2025 K3 (PANSTARRS), 2025 K4 (Siverd), 2025 L1 (ATLAS), 2025 L2 (MAPS), 2025 M1 (PANSTARRS), 2025 M2 (PANSTARRS), 2025 M3 (PANSTARRS), 2025 N1 (3I/ATLAS), 2025 N2 (ATLAS), 2025 O1 (P/McNaught), 2025 O2 (MAPS), 2025 O3 (512P/PANSTARRS), 2025 P1 [PANSTARRS], 2025 Q1 (ATLAS),
2025 Q2 (511P/PANSTARRS), 2025 Q3 (ATLAS), 2025 R1 (ATLAS), 2025 R2 (SWAN), 2025 R3 (PANSTARRS), 2025 S1 (513P/Broughton), 2025 S2 (A/PANSTARRS), 2025 S3 (A/PANSTARRS), 2025 S4 (P/Lemmon-PANSTARRS), 2025 SB57 [A/Lemmon], 2025 T1 (ATLAS), 2025 TT13 [A/Kitt Peak], 2025 U1 (P/Hogan), 2025 UX109 [A/ZTF], 2025 V1 (Borisov).
It has been a promising year for astronomers and skywatchers, as there have been many discoveries that have made us excited about the intriguing world out there.
More or Starlust
ESA tracks interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS with 10x accuracy, thanks to Mars orbiter