Ceres, the only dwarf planet in the inner solar system, reaches opposition on October 2—how to watch
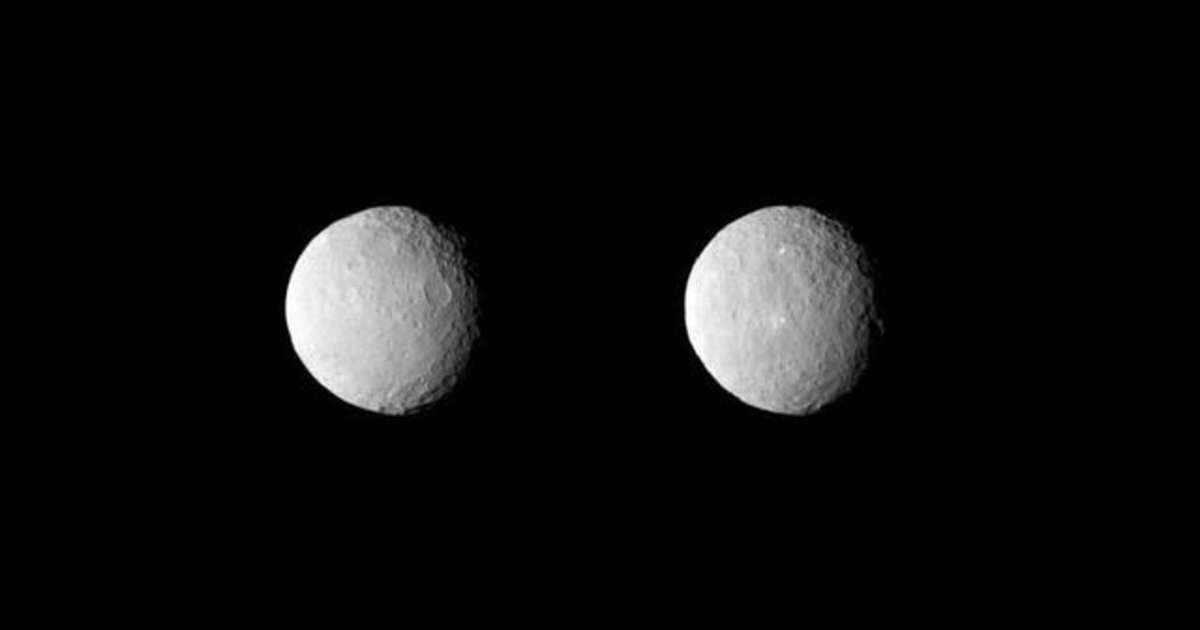

Dwarf planet Ceres, the only one located within the inner solar system, will reach opposition on October 2 at 9 a.m. EDT. This celestial event means Ceres is directly opposite the Sun in Earth's sky, making it optimally situated for observation. As the most massive object in the main asteroid belt, Ceres will be visible throughout the entire night, rising in the east as the Sun sets and remaining high in the sky until sunrise, as per Astronomy.com.

Viewers can locate this prime target in the constellation Cetus, the Sea Monster. According to NASA, the dwarf planet visible in the night sky is named Ceres after the Roman goddess of agriculture and harvests, the very root of the English word "cereal." While its name is historic, its scientific importance is modern, particularly in the search for extraterrestrial life.
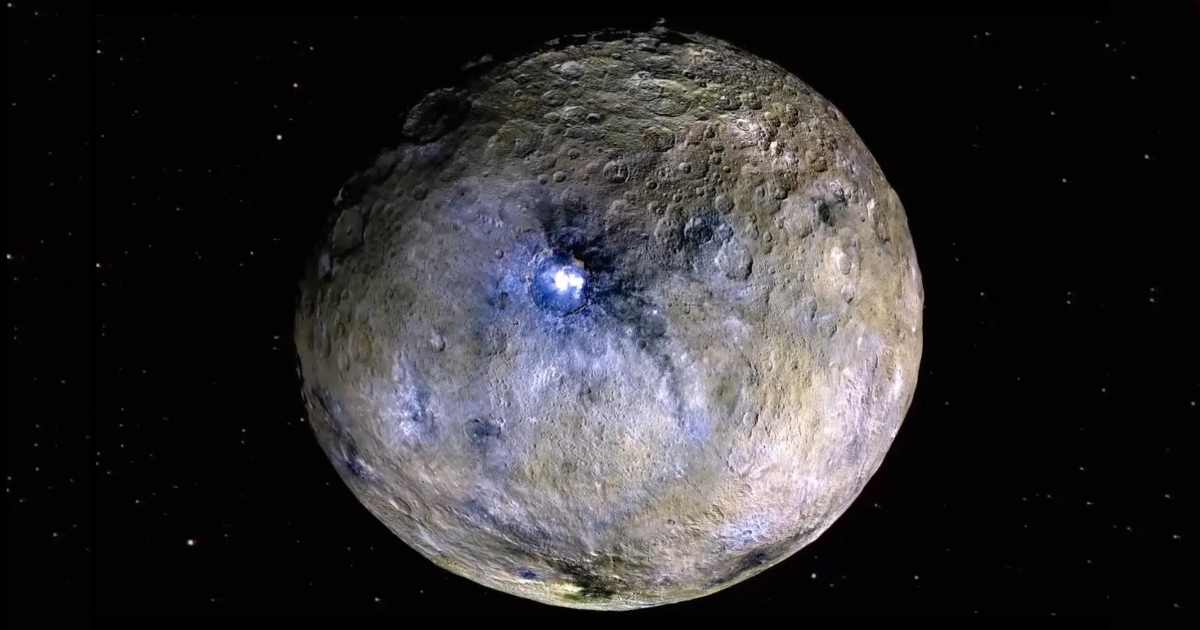

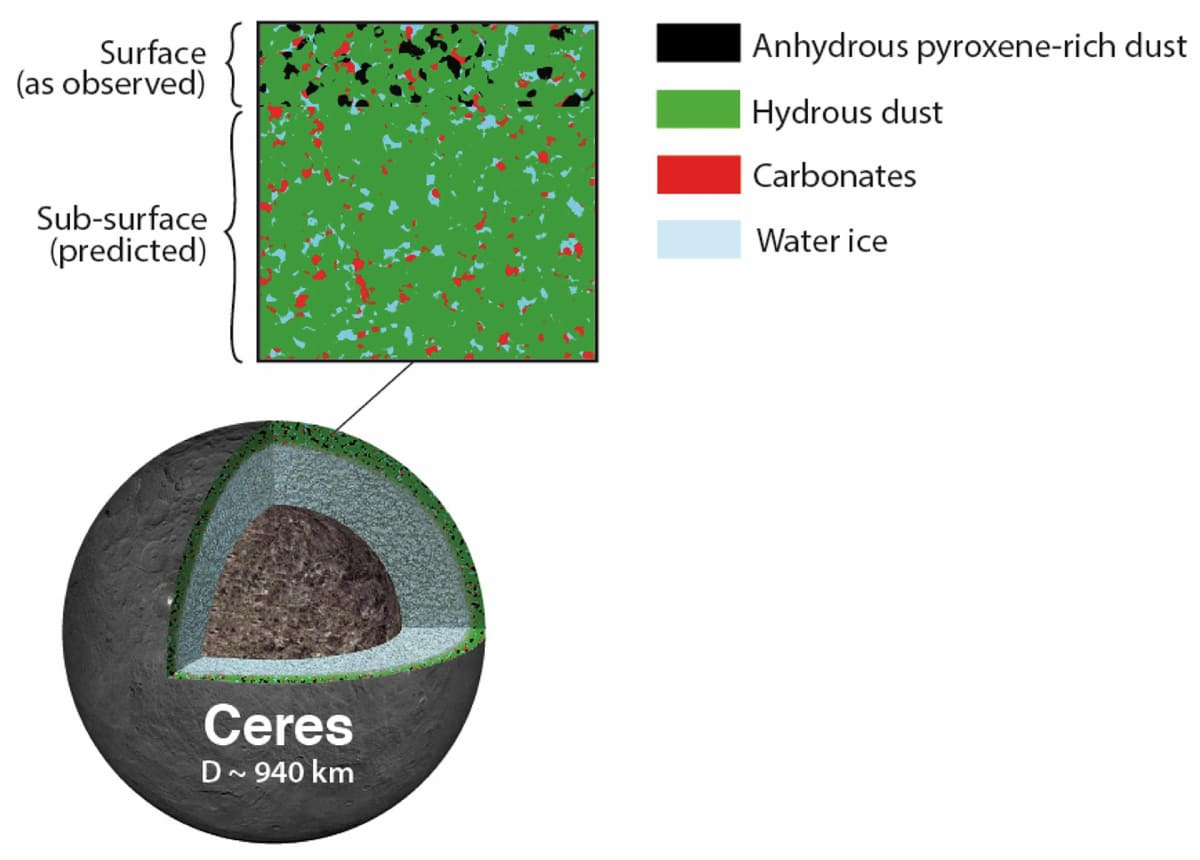
Ceres is considered a prime target in the solar system for seeking possible signs of life. Unlike many other celestial bodies, Ceres is known to possess water. Given that water is fundamental to all known life on Earth, its presence on Ceres, combined with other potential conditions, raises the possibility that it could support biological activity. Scientists suggest any life on Ceres would likely be very small microbes, similar to bacteria. Furthermore, even if life does not currently thrive there, the dwarf planet may hold evidence that it once harbored living organisms in the past.
The scale of this opposition target is modest. With a radius of 296 miles (476 kilometers), Ceres is tiny; it’s approximately one-thirteenth the size of Earth's radius. To put its size into perspective, if Earth were the size of a nickel coin, Ceres would be no bigger than a poppy seed. Orbiting at an average distance of 257 million miles (413 million kilometers) from the Sun, Ceres is approximately 2.8 Astronomical Units (AU) away. An AU is defined as the distance between the Earth and the Sun. At this great distance, sunlight takes about 22 minutes to traverse the gap and reach the surface of Ceres.
The viewing opportunity for Ceres continues on Friday, October 3, just one day after its opposition. The dwarf planet remains an easy target, glowing brightly at magnitude 7.6, a luminosity that puts it well within the range of binoculars or any small telescope, per Astronomy.com. To spot Ceres, observers should look toward the constellation Cetus, the Whale. The dwarf planet is currently tracing a slow path slightly north of Cetus's second-brightest star, Diphda (Beta Ceti), which shines at magnitude 2.0. Around 10 P.M. local time, when Diphda sits approximately 20 degrees above the southeastern horizon, Ceres will be found just over 8 degrees directly north of this star.

To pinpoint its exact location, observers can use a distinctive chain of four fainter stars, ranging from fifth to sixth magnitude, that runs roughly horizontally from east to west in the region. This chain is composed of the stars Phi1, Phi2, Phi3, and Phi4 Ceti. Ceres is positioned approximately 1 degree due north of the magnitude 5.4 star Phi3 Ceti on October 3. This same string of stars will serve as an excellent guide for tracking Ceres’ movement throughout October, as it will pass close to Phi2 Ceti on the 10th and will hang due south of Phi1 Ceti by the 18th.
More on Starlust
Will Comet C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) be bright enough to see with the naked eye on October 21?
Here's when Comet C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) will make closest approach to Earth next month









