Biggest Martian rock on Earth sells for $5.3 million at auction, marking a record-breaking moment in space memorabilia

A substantial fragment of Mars, the largest ever discovered on Earth, commanded a record-breaking $5.3 million at a recent New York auction, as per Phys.org.
The largest piece of Mars on Earth is now the most valuable meteorite ever sold at auction after it achieved $5.3 million in the Natural History sale during Sotheby's Geek Week. #AuctionUpdate
— Sotheby's (@Sothebys) July 16, 2025
The auction continues LIVE from #SothebysNewYork: https://t.co/VFFgQ4UVDB pic.twitter.com/qVVgJDpcau
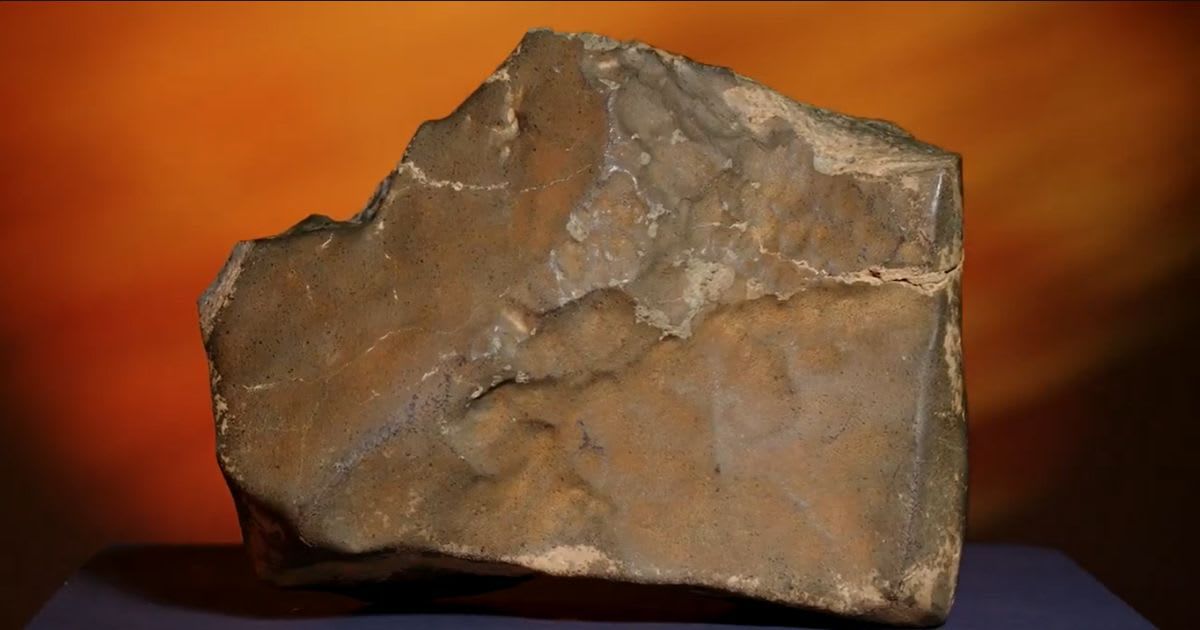
The 54-pound (25-kilogram) Martian Rock, designated NWA 16788, was unearthed in Niger's Sahara Desert in November 2023. Scientists believe it was ejected from Mars following a massive asteroid impact, subsequently traversing an estimated 140 million miles (225 kilometers) to reach Earth. Sotheby's, the auction house, had initially projected a sale price between $2 million and $4 million. The buyer's identity remains undisclosed. The final bid for the meteorite was $4.3 million, with additional fees bringing the total to approximately $5.3 million, making it the most valuable meteorite ever sold at auction. Bidding for the extraterrestrial artifact was notably subdued as it was overshadowed by the bidding for a rare juvenile dinosaur skeleton.

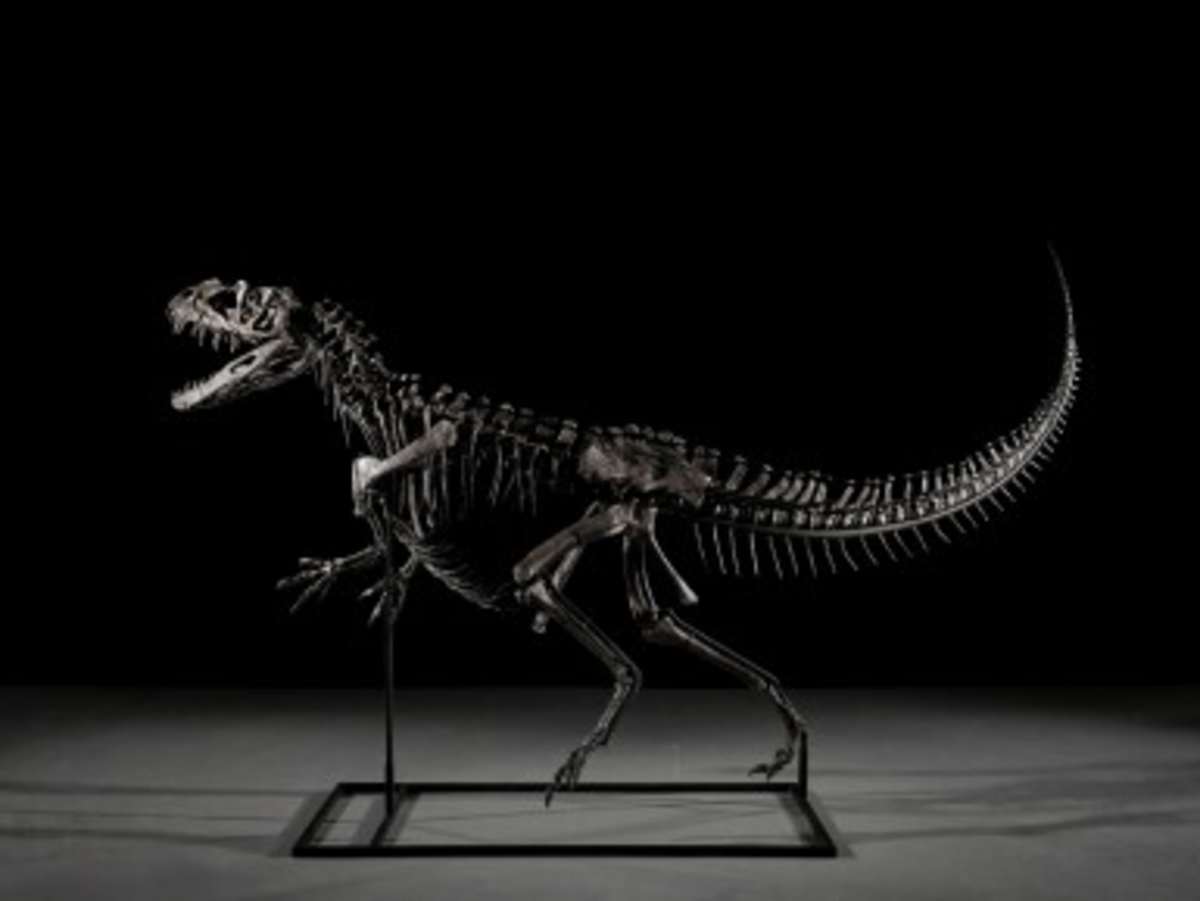
A rare juvenile Ceratosaurus nasicornis skeleton sold for $30.5 million, including fees. The pre-auction estimate for the dinosaur, a smaller relative of the Tyrannosaurus Rex, was a mere $4 million to $6 million. This specimen is one of four known Ceratosaurus nasicornis skeletons and the sole juvenile of its species. The intense six-minute bidding frenzy saw offers escalate rapidly, concluding with widespread applause. Sotheby's confirmed the buyer intends to loan the skeleton to an institution. This sale marks the third-highest price ever paid for a dinosaur at auction, with a Stegosaurus named "Apex" holding the record at $44.6 million, sold last year by Sotheby's.
The only known juvenile Ceratosaurus fossil just sold in the #SothebysNewYork sale room for a staggering $30.5 million, making it the third most valuable dinosaur fossil ever sold at auction. #AuctionUpdate
— Sotheby's (@Sothebys) July 16, 2025
The Natural History sale continues LIVE: https://t.co/VFFgQ4UVDB pic.twitter.com/f0BlXrWwkZ
Portions of the Ceratosaurus skeletons were first discovered in 1996 near Laramie, Wyoming. Specialists meticulously reconstructed the creature from nearly 140 fossilized bones, supplementing with sculpted materials, to create an exhibit-ready display. Acquired last year by Fossilogic, a Utah-based fossil preparation company, the skeleton stands over 6 feet (2 meters) tall and extends nearly 11 feet (3 meters) long. It is believed to date back approximately 150 million years, to the late Jurassic period.

The Martian meteorite, a distinct specimen characterized by its red, brown, and gray colors, is approximately 70% larger than the next largest Martian fragment found on Earth. It accounts for nearly 7% of all known Martian material on our planet, measuring close to 15 inches by 11 inches by 6 inches (375 millimeters by 279 millimeters by 152 millimeters). Its rarity is significant, as only 400 Martian meteorites have been identified among the more than 77,000 officially recognized meteorites on Earth.
"This Martian meteorite is the largest piece of Mars we have ever found by a long shot," stated Cassandra Hatton, Sotheby's vice chairman for science and natural history, before the auction, noting it more than doubles the size of the previously considered largest fragment. While the exact timing of its expulsion from Mars remains unclear, testing suggests it occurred in recent geological history. A specialized laboratory confirmed the meteorite's Martian origin by comparing its chemical composition to samples obtained by the Viking space probe in 1976. The analysis identified it as an "olivine-microgabbroic shergottite," a type of Martian rock formed from slowly cooled magma, characterized by a coarse-grained texture and the presence of pyroxene and olivine minerals. The meteorite also exhibits a glassy surface, likely a result of the intense heat generated during its fiery descent through Earth's atmosphere.