Astronomers uncover complex organic molecules in young star's disk, hinting at cosmic origins of life
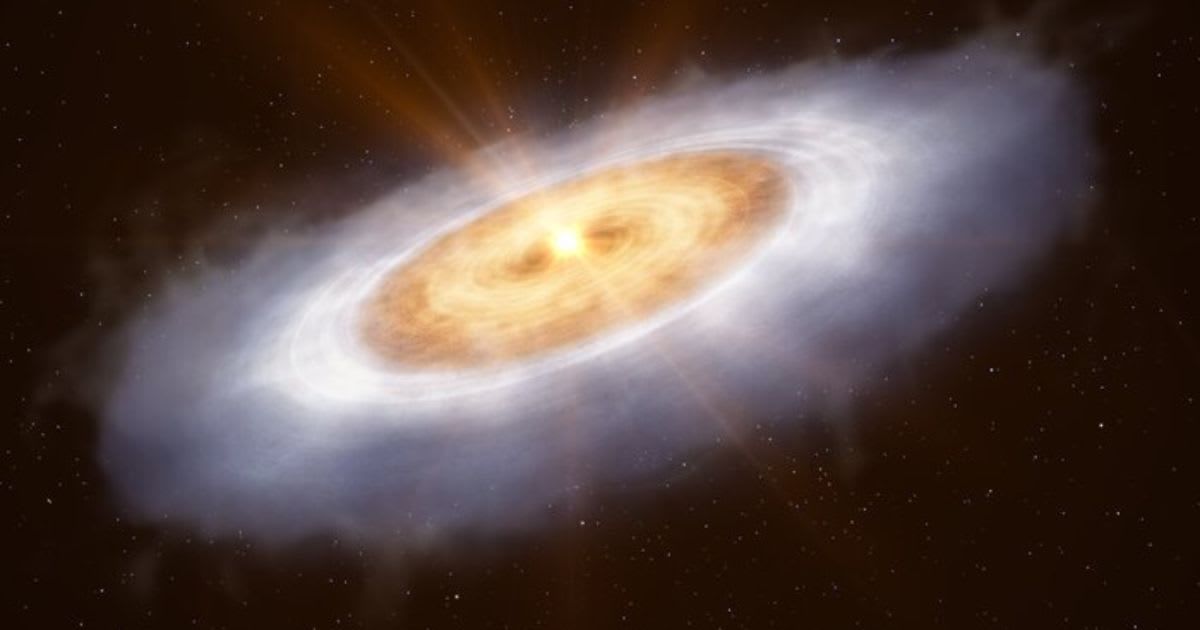

Astronomers have unearthed a trove of complex organic molecules, including potential precursors to the fundamental building blocks of life, within the swirling disc of a burgeoning star. This landmark finding challenges long-held theories about the origins may be more universally present across the cosmos than previously believed, according to the Max Planck Society.
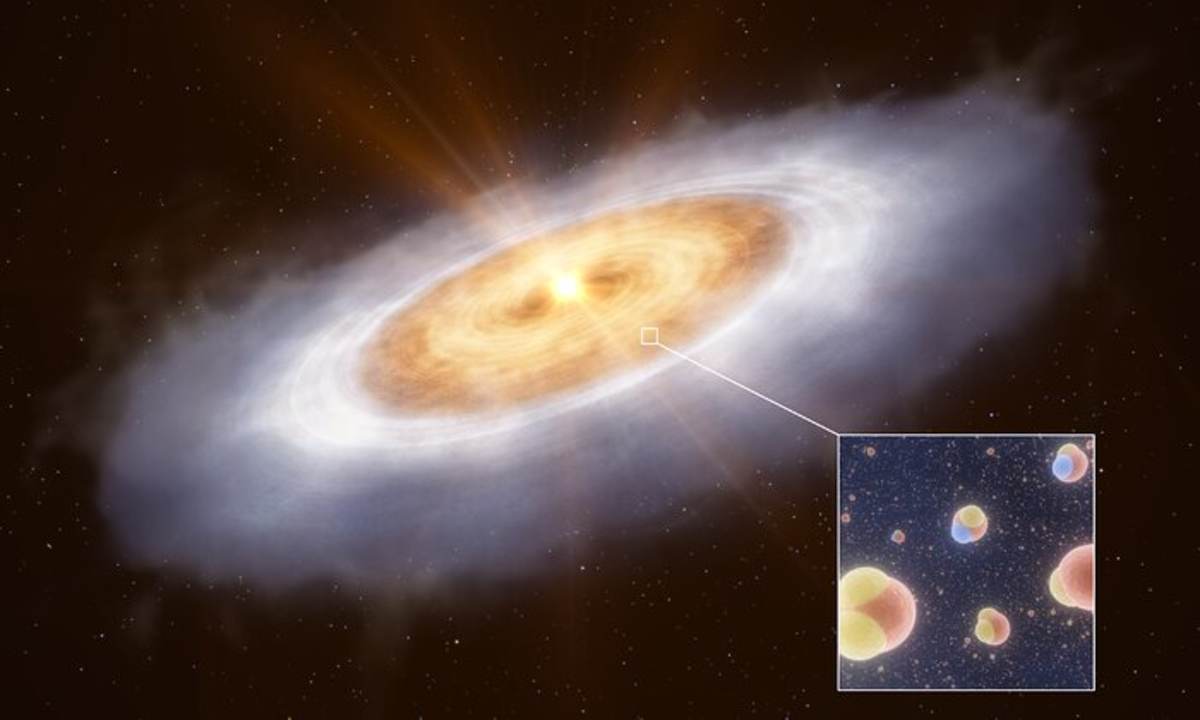

A team led by Abubakar Fadul of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA), utilising the powerful Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), identified 17 complex organic molecules (COMs) within the protoplanetary disk of V883 Orionis, an outbursting protostar. Among these, the first-ever tentative detections of ethylene glycol and glycolonitrile stand out. Glycolonitrile, in particular, is a known precursor to vital amino acids like glycine and alanine, as well as adenine, a key component of DNA and RNA.

This discovery, published in the Astrophysical Journal Letters, provides a crucial missing link in understanding the evolution of these life-enabling molecules. Before this, scientists had hypothesized a "reset" scenario, suggesting that the energetic processes accompanying star formation might destroy existing complex chemistry, necessitating a re-synthesis within the newly formed planetary disks.
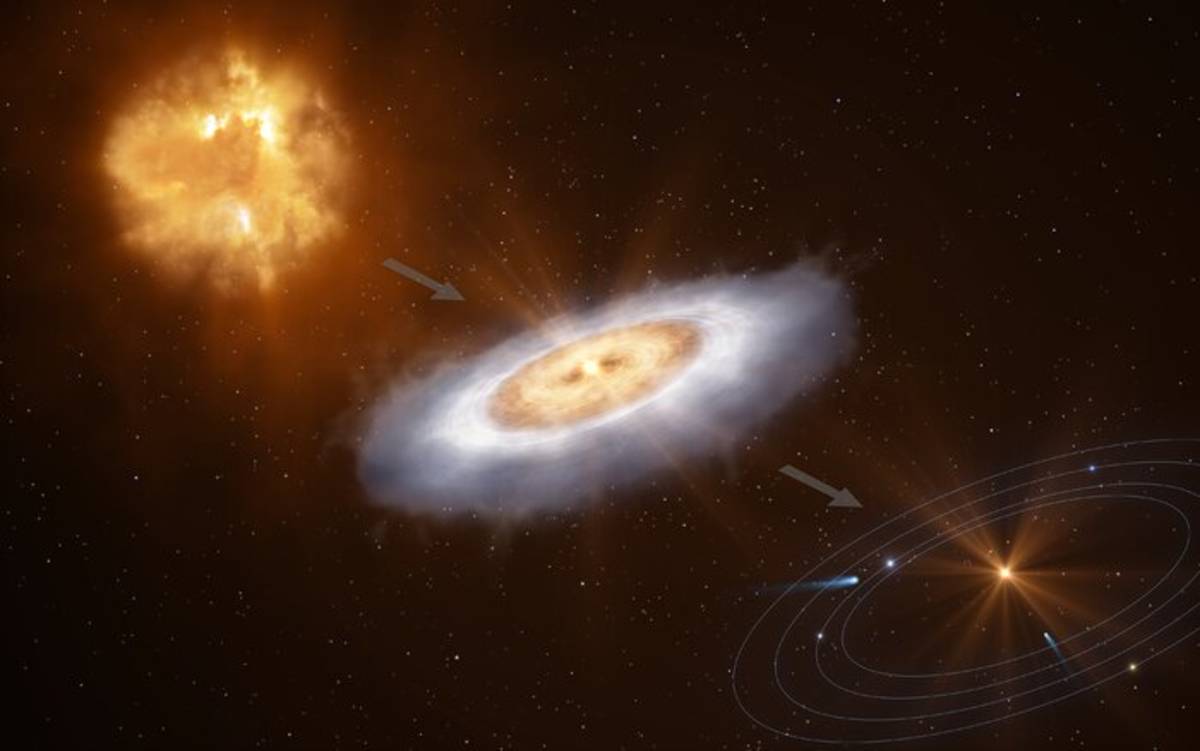

However, these new observations indicate a different story. “Our results suggest that protoplanetary discs inherit complex molecules from earlier stages, and the formation of complex molecules can continue during the protoplanetary disc stage,” stated MPIA co-author Kamber Schwarz. This implies a continuous chemical enrichment, with the seeds of life potentially being assembled much earlier in interstellar space. The presence of simpler organic molecules, such as methanol, in pre-stellar regions, and now the detection of more intricate compounds like ethylene glycol in a young star's disk, supports a direct evolutionary path for prebiotic chemistry. Tushar Suhasaria, head of MPIA's Origins of Life Lab and a co-author, noted that UV irradiation, common in these environments, could facilitate the formation of ethylene glycol.
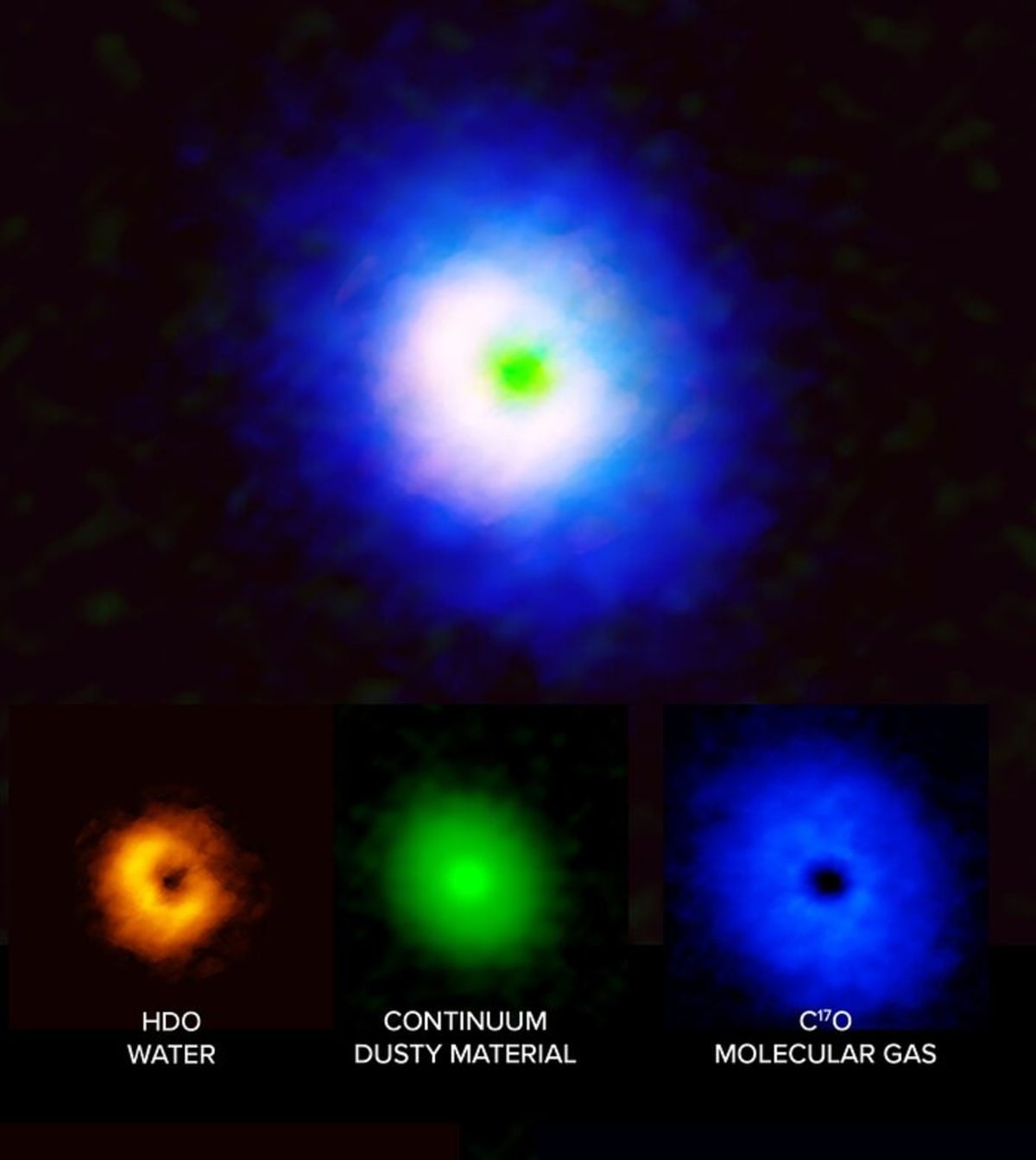
The complex organic molecules are typically locked away in icy dust grains within these nascent systems. Their detection in V883 Orionis was made possible by intense outbursts from the central star. As the protostar accretes gas, these growth spurts generate powerful radiation, heating the surrounding disc and sublimating the ice, thereby releasing the trapped molecules into a gaseous state detectable by ALMA. “Complex molecules, including ethylene glycol and glycolonitrile, radiate at radio frequencies. ALMA is perfectly suited to detect those signals,” explained Schwarz. The high-altitude observatory in Chile allowed astronomers to pinpoint the V883 Orionis system and identify these faint spectral signatures, as mentioned by the Max Planck Society.
While highly promising, the research team acknowledges that further analysis is needed. “Higher resolution data will confirm the detections of ethylene glycol and glycolonitrile and maybe even reveal more complex chemicals we simply haven't identified yet,” Schwarz added. Fadul also suggested exploring other regions of the electromagnetic spectrum to potentially uncover even more evolved molecules. This groundbreaking finding significantly strengthens the hypothesis that the conditions for life's emergence are fore unique, instead hinting at a widespread cosmic predisposition for biological processes. The ongoing quest to unravel the full spectrum of molecules in these stellar nurseries promises to reshape our understanding of life's cosmic origins.