Take a tour through Milky Way's star-forming regions with Gaia's first 3D fly through map
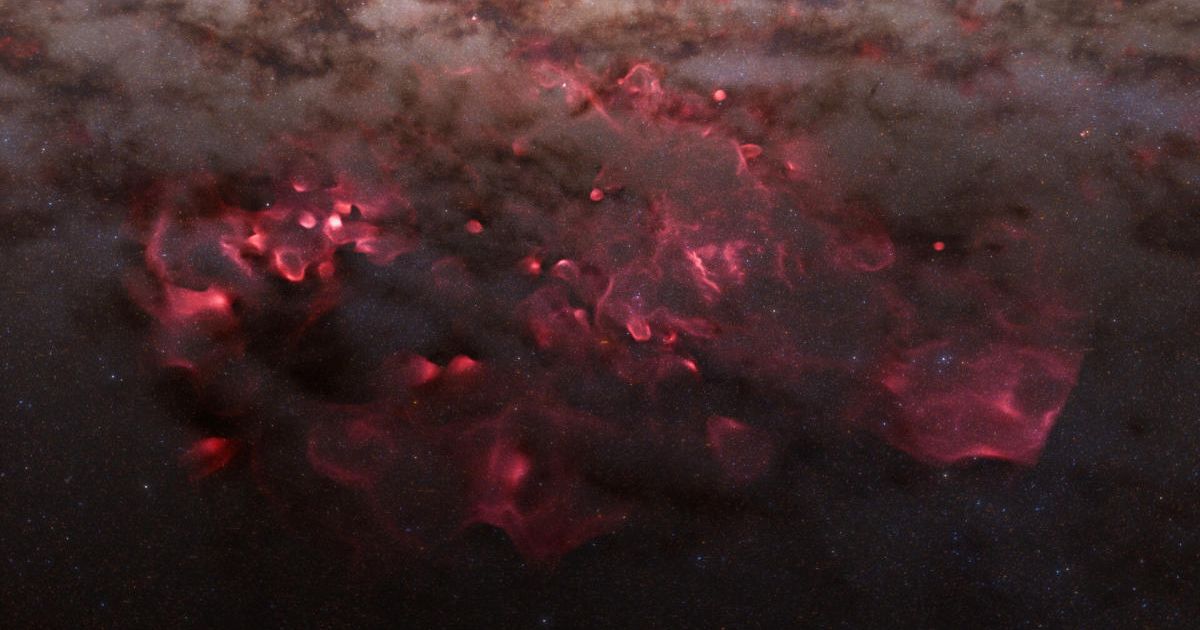

Astronomers have released a groundbreaking three-dimensional map of the Milky Way’s star-forming regions, offering an unprecedented "fly-through" view of the galaxy's stellar nurseries. The map, based on data from the European Space Agency's Gaia space telescope, provides the clearest look yet at these previously obscured cosmic clouds, according to the European Space Agency.
For decades, scientists have struggled to chart these areas due to the thick veils of gas and dust that hide them. While we’ve had two-dimensional views of these nebulous structures from Earth, their true three-dimensional shape has remained a mystery. The new map, however, changes that by using Gaia’s precise measurements of stellar positions and "extinction," the degree to which starlight is blocked by interstellar dust.
By charting the dust’s location, researchers were able to pinpoint clouds of ionized hydrogen gas, a telltale sign of ongoing star formation. The team also incorporated observations of 44 million ordinary stars and 87 rare, massive O-type stars, which are so bright and hot they energize the gas around them, making it glow.
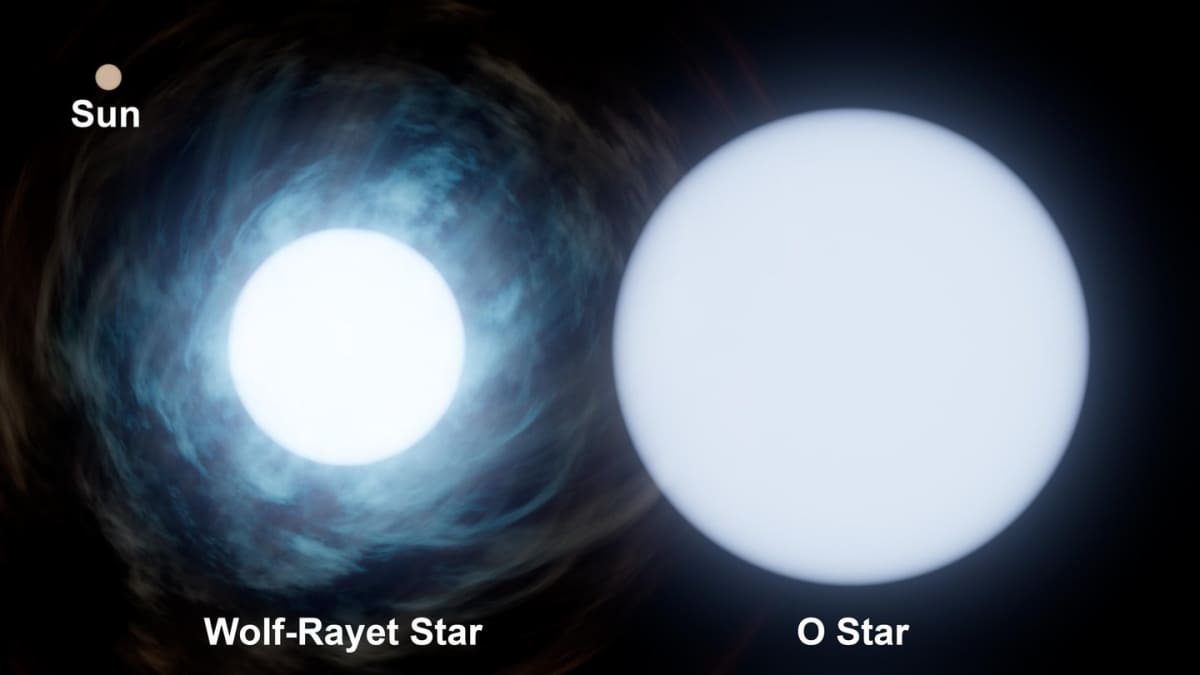

“Gaia provides the first accurate view of what our section of the Milky Way would look like from above,” explains Lewis McCallum, an astronomer at the University of St Andrews and lead author of the two scientific papers detailing the new model. “There has never been a model of the distribution of the ionised gas in the local Milky Way that matches other telescopes’ observations of the sky so well. That’s why we are confident that our top-down view and fly-through movies are a good approximation of what these clouds would look like in 3D.”
The map, which extends 4,000 light-years from the Sun, includes well-known stellar nurseries such as the Gum Nebula, North American Nebula, and the Orion-Eridanus superbubble. The new model has already yielded fresh insights. Scientists have observed that some star-forming regions appear to be venting streams of gas and dust into a giant interstellar cavity, a process believed to be driven by the immense energy of the O-type stars within them.
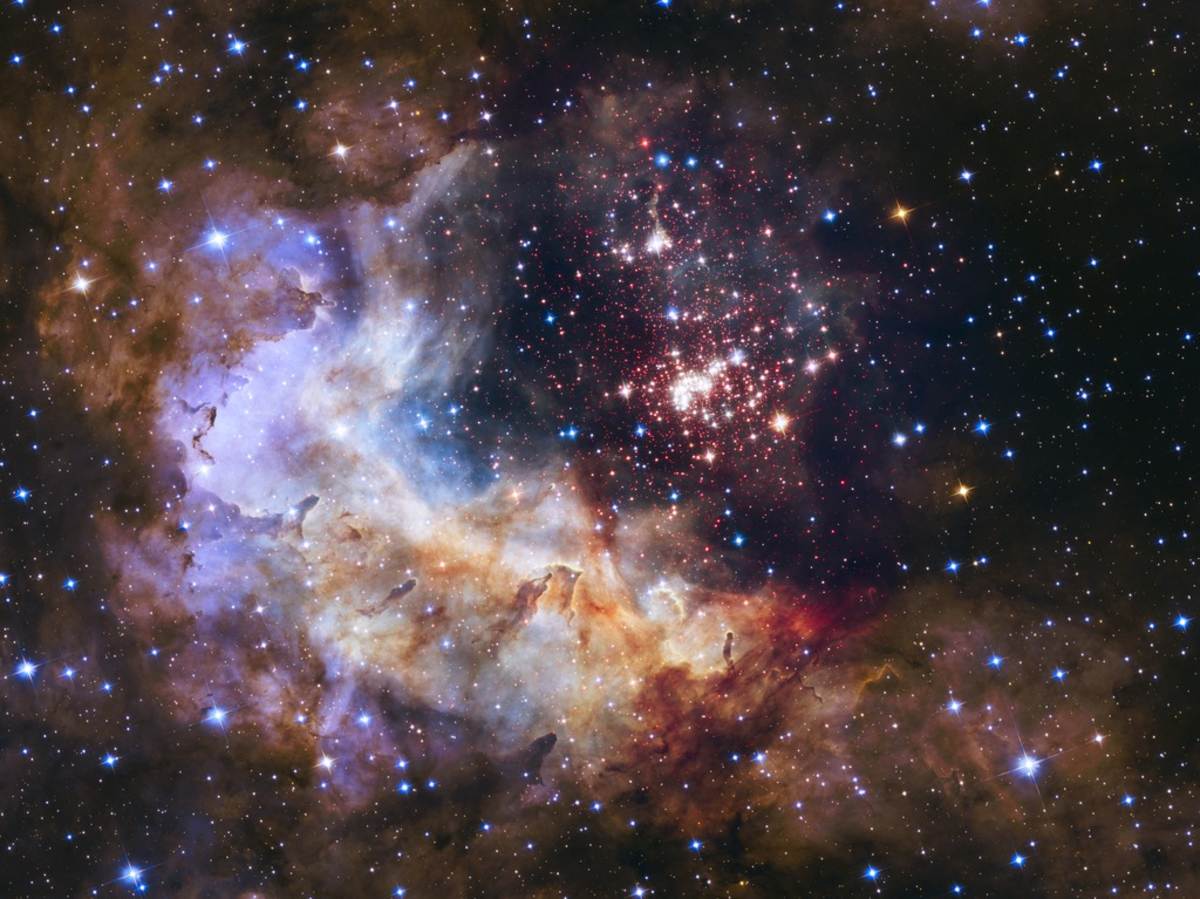

“This map nicely shows how radiation of massive stars ionises the surrounding interstellar medium and how dust and gas interact with this radiation. The 3D model provides a detailed look at the processes that shape our local galactic environment and helps astronomers understand interactions between the warm and cold components of the local Universe," noted Sasha Zeegers, ESA Research Fellow and an expert on interstellar dust. As Gaia continues to gather data, the map is expected to expand, providing an even more comprehensive picture of our galaxy's ongoing cosmic evolution.
In a related development, astronomers have also captured the first detailed images of protostellar jets and outflows in the Milky Way's outer reaches. This significant breakthrough confirms that the fundamental principles of star formation are consistent throughout the galaxy, regardless of differences in chemical composition. Using the powerful Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA), researchers focused on a specific protostar, Sh 2-283-1a SMM1, located roughly 51,000 light-years from the galactic center. This remote environment, with only one-third of the heavy elements found near the Sun, serves as a natural laboratory, providing a window into the conditions of the early Milky Way.
More on Starlust
Researchers accidentally discover a giant stellar 'blowtorch' at the Milky Way's border