Rubin Observatory unintentionally captured pre-discovery images of interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS

The Vera C. Rubin Observatory, currently undergoing its Science Validation phase, inadvertently captured crucial early images of the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS days before its official discovery. These unplanned observations provide the earliest high-resolution data on the comet to date, as reported on Universe Today.

The observatory, equipped with its 8.4-meter Simonyi Survey telescope and 3.2-gigapixel Legacy Survey of Space and Time (LSST) camera, was pointed at the specific celestial coordinates where 3I/ATLAS was located during its testing period. This resulted in the unintentional acquisition of images between June 21 and July 7, a period that notably predated the comet's formal identification and even the public release of the observatory's "First Look" images on June 23.
Introducing...your sneak peek at the cosmos captured by @NSF–@doescience Vera C. Rubin Observatory!
— NSF-DOE Rubin Observatory (@VRubinObs) June 23, 2025
Can you guess what regions of sky they are?
This is just a peek...join us at 11am US EDT for your full First Look at how Rubin will #CaptureTheCosmos!https://t.co/1a74X2edp8 pic.twitter.com/DE3tx2RQI4
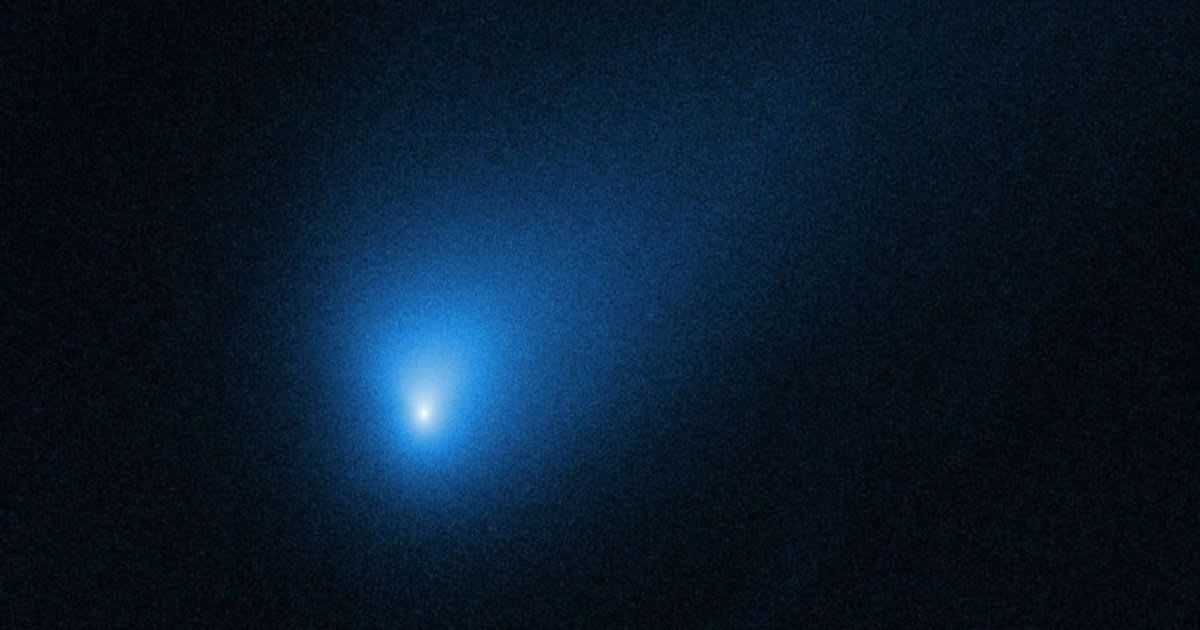
A new paper, published on arXiv, details 49 such images, with 19 deemed suitable for analysis after excluding those affected by alignment procedures, stellar blending, or focus issues. This dataset is particularly significant as it represents the highest-resolution observations of 3I/ATLAS to date, offering striking detail into its early behaviour. Given these images were taken before full commissioning, their data required processing through specialized customer pipelines rather than the observatory's standard automated systems.
The early images confirm 3I/ATLAS exhibits characteristics of cometary behaviour, including the presence of a distinct coma of gas and dust. Over the observational period, the coma's apparent size expanded by approximately 58% as the comet approached the Sun. Intriguingly, the comet displayed a sunward-pointing tail, a relatively rare phenomenon attributed in the paper to "anisotropic dust emission" or a rotational axis nearly aligned with its orbital plane.
Unlike interstellar object 1I/Oumuamua, 3I/ATLAS has not yet shown signs of non-gravitational acceleration. Astronomers will be closely monitoring for such effects as the comet approaches its perihelion in October. However, a challenging observational window awaits, as 3I/ATLAS will be obscured by the Sun from September through December, rendering it invisible to Earth-based telescopes. The Rubin Observatory itself is expected to lose sight of the comet around August 22 as it moves out of the survey's field of view. Researchers anticipate that at least 100 more images of 3I/ATLAS will be captured by Rubin before it becomes unobservable, potentially offering even higher quality data as the observatory's operations are now aware of the object's presence. A more detailed study is expected to follow, building upon these initial, unexpected discoveries.

Even as it provided early data on an interstellar comet, the Vera Rubin Observatory has also unveiled its astounding capabilities for wide-field astronomy. Among its initial captures, the telescope showcased an extragalactic view containing an astonishing 10 million galaxies. This single image is so densely packed with celestial bodies that the background appears gray, not black, offering an immediate sense of the universe's immense scale. To fully appreciate this, one would need nearly four months of uninterrupted observation just to view each galaxy in this image for a single second. Remarkably, this detailed panorama, encompassing 10 million galaxies, was compiled from 1,185 individual exposures taken over only seven nights. This rapid creation of such a vast and deep cosmic view underscores the Rubin Observatory's unique position as the sole astronomical instrument capable of such a feat.