NASA Chandra discovers 'baby' exoplanet shrinking under attack from its host star
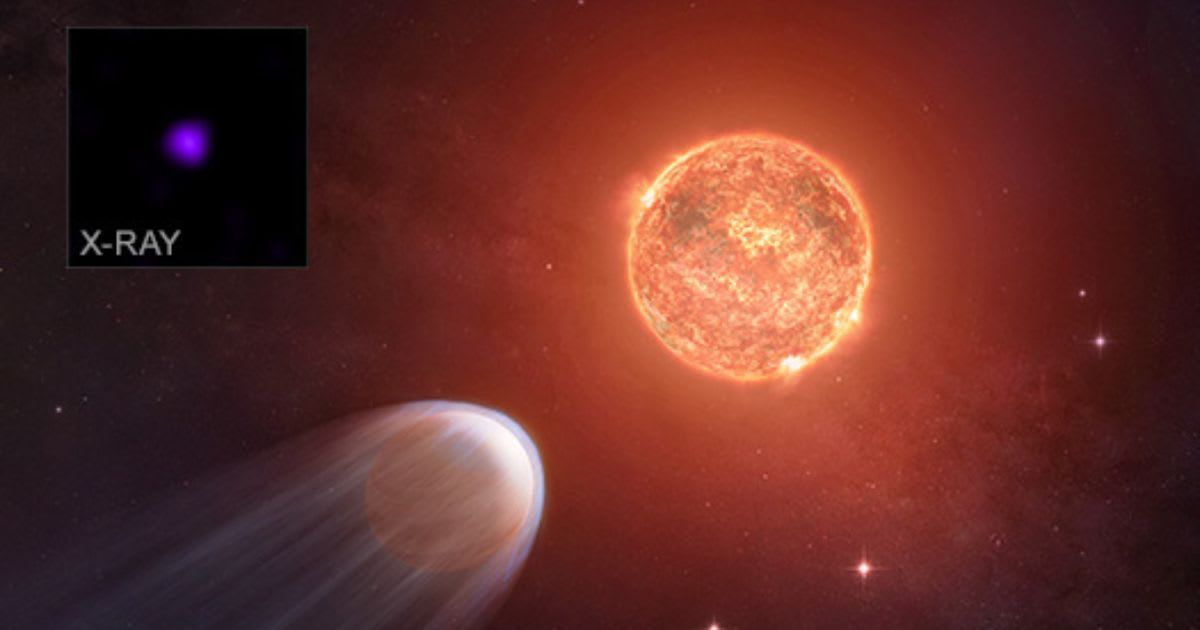

A newly formed exoplanet is rapidly diminishing in size due to intense X-ray bombardment from its host star, according to groundbreaking observations from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory. This revelation, detailed in a recent study, paints a grim future for the "baby" planet, currently comparable in size to Jupiter, which is projected to shrink into a desolate, barren world, per NASA.
A star is bombarding a baby planet with X-rays, shrinking it from the size of Jupiter to a small, barren world, according to a new Chandra study. Scientists estimate the planet is losing a mass equivalent to a full Earth's atmosphere about every 200 years. https://t.co/Qs3xtxlvwi pic.twitter.com/ndWsEF0DsQ
— Chandra Observatory (@chandraxray) July 16, 2025
The young exoplanet, designated TOI 1227 b, is a mere 8 million years old, which is a staggering thousand times younger than our Sun. It orbits its faint red star, TOI 1227, at a fraction of the distance separating Mercury from the Sun. An artist's rendering depicts the Jupiter-sized world losing its atmosphere, described as a trailing blue tail, under the relentless assault of stellar X-rays. These powerful emissions are systematically stripping away the planet's gaseous envelope, a process that could eventually leave it completely devoid of an atmosphere.
Researchers leveraged new Chandra data to precisely quantify the X-ray flux from TOI 1227 impacting the planet. Their sophisticated computer models demonstrate the transformative effect of these X-rays, concluding that the planet is shedding an equivalent of Earth's entire atmosphere approximately every 200 years. The age of TOI 1227 b was independently confirmed through two distinct methods: analyzing its host star's brightness and surface temperature in comparison to theoretical stellar evolution models. This makes TOI 1227 b the second-youngest planet ever observed transiting its star. Despite previous estimates placing its age at around 11 million years, the new findings solidify its status as an exceptionally young celestial body.

Among all exoplanets discovered under 50 million years old, TOI 1227 b uniquely possesses the longest orbital period and a host star with the lowest mass. These characteristics, combined with the severe X-ray exposure, position it as a critical subject for ongoing and future astronomical investigations. The findings have been accepted for publication in The Astrophysical Journal. The research team includes Attila Varga, Joel Kastner, Alexander Binks, Hans Moritz Guenther, and Simon J. Murphy. The Chandra program is managed by NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, with science operations controlled by the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
In other cosmic news, NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, working in concert with other prominent observatories, has recently unveiled a groundbreaking composite image of the Andromeda galaxy (M31). This striking visual offers fresh insights into our nearest spiral galactic neighbor and stands as a fitting tribute to pioneering astronomer Vera Rubin, whose seminal research on Andromeda provided the first compelling evidence for the existence of dark matter.
This new image shows the Andromeda Galaxy in 5 different types of light — X-ray, UV, optical, infrared, and radio. Andromeda, also known as Messier 31 (M31), is the closest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way at a distance of about 2.5 million light-years. https://t.co/EdOhaXhGHb pic.twitter.com/j6MjeEo78w
— Chandra Observatory (@chandraxray) June 25, 2025
This newly released image integrates data from across the entire electromagnetic spectrum, providing astronomers with a comprehensive understanding of M31's intricate structure and evolutionary processes. Specifically, X-ray data from both NASA's Chandra and the European Space Agency's XMM-Newton missions illuminate high-energy phenomena within the galaxy, including powerful emissions originating from Andromeda's central supermassive black hole and a multitude of compact objects dispersed throughout its vast expanse.

The Chandra X-ray Observatory isn't just an individual mission; it's a vital component of NASA's esteemed "Great Observatories" program. This elite fleet also includes the Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Compton Gamma Ray Observatory, which has since concluded its mission. Chandra empowers scientists globally to capture X-ray images of extreme cosmic environments, providing crucial data that deepens our understanding of the universe's fundamental structure and evolution, as mentioned on NASA.