NASA’s Juno Mission finally detects 'missing' auroral signature of Jupiter's second-biggest moon
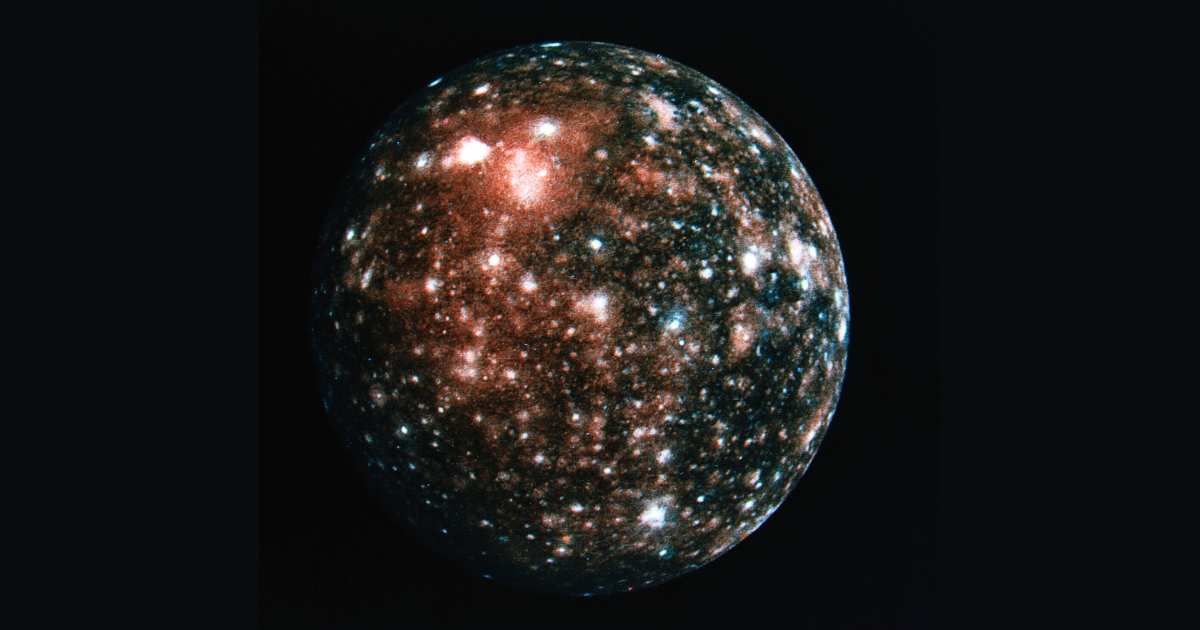

Some of the brightest and eye-catching auroral spectacles in the solar system are hosted by Jupiter. The largest moons of Jupiter develop their individual auroral signatures in the planet’s atmosphere, unlike the northern lights on Earth, which do not involve our moon. However, the most distant among Jupiter's 95 moons, Callisto, remained a mystery. According to NASA, the Juno mission revealed the first detections of Callisto’s auroral footprint, and the close-up images showed the process in great detail. These signatures, known as “satellite footprints,” show how the moon interacts with the atmosphere of the planet it orbits.

NASA’s Juno mission has been orbiting Jupiter since 2016, and it has provided some of the clearest images of Jupiter. The instruments on the craft were capable of providing extremely close-up views of these "polar light displays." Earlier, Callisto's footprint was found to be faint, evading detection while being trapped under the luminous "main auroral oval." So, to reach Callisto and capture its footprint, the main auroral region needed to be moved aside while imaging the polar region. This meant that the trajectory of the spacecraft had to pass along the magnetic field line that links Callisto with Jupiter.
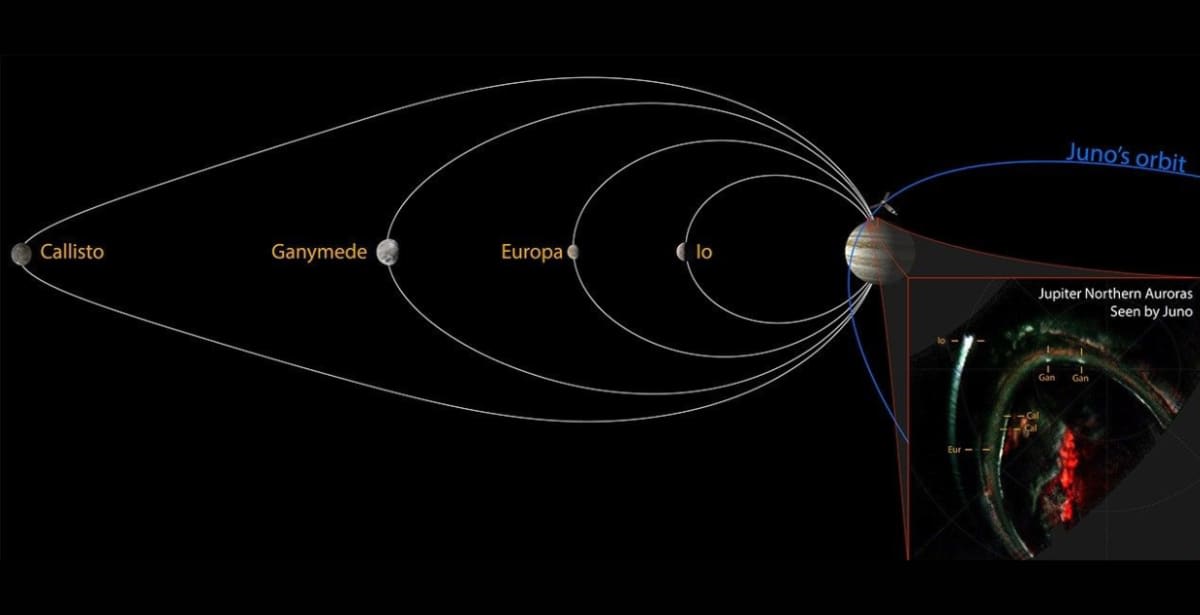
During Juno's 22nd flyby in September 2019, it was able to ascertain Callisto's different particle samples (and their population), electromagnetic waves, and magnetic force as it produced these auroras. They found that the magnetic field of the giant planet extends much beyond its significant moons. This marks a massive region in space — the magnetosphere — covered by the solar wind spreading from the Sun. These solar storms affect the auroras' position, as discovered in 2019 when a high-density solar storm pushed into the magnetosphere, shifting the auroras towards Jupiter's equatorial region.

The discovery was evaluated by an international team of scientists led by Jonas Rabia of the Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (IRAP), CNRS, CNES, in Toulouse, France. The findings and their analysis were published in the journal Nature Communications. They pored over the UV maps, rotation rate, electron density, electron energy flux, magnetic mapping, and Cyclotron Maser Instability, in order to determine the specific characteristics of Callisto's functioning. "Magnetic mapping of the Juno position onto Jupiter’s upper atmosphere shows that Juno crossed magnetic field lines connected to one spot of the Callisto footprint," researchers wrote. This once-in-a-lifetime opportunity allowed them to ascertain specific physical parameters of the moon's "electrodynamic interaction" with its host planet.

Before NASA’s Juno mission, the Galilean moons Io, Europa, and Ganymede were witnessed producing these unique signatures. The initial attempts to capture the footprints were made by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. This discovery completes a long-standing gap in understanding the auroral projections on Jupiter. Studying the auroras provides deep insight into how they interact with the solar wind and moons influenced by Jupiter’s magnetic field.
More on Starlust
James Webb Telescope uncovers Jupiter moon Europa's surprisingly dynamic and shifting ice shell