NASA's Artemis campaign taps Firefly for $176 million mission to advance lunar exploration

NASA has awarded a $176.7 million contract to Firefly Aerospace for a critical delivery mission to the Moon's South Pole. The Texas-based company, through the Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) initiative, will transport two advanced rovers and three scientific instruments to the lunar surface as part of the Artemis program, with a target landing date in 2029, as per NASA.
We’re over the Moon to share another #BlueGhost win. Firefly was awarded another @NASA CLPS contract for a 4th mission to the Moon! We’re taking our landing experience to the South Pole with 2 rovers and 3 instruments to evaluate the Moon’s resources. https://t.co/SziPc8WSVz
— Firefly Aerospace (@Firefly_Space) July 29, 2025
This mission marks a new approach to lunar exploration, leveraging multiple mobile and stationary scientific tools in a coordinated effort with the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the University of Bern. The goal is to conduct a detailed analysis of the South Pole's chemical composition and assess the viability of utilizing resources, particularly in perpetually shadowed regions. “Through CLPS, NASA is embracing a new era of lunar exploration, with commercial companies leading the way,” said Joel Kearns, deputy associate administrator for exploration at NASA's Science Mission Directorate. “These investigations will produce critical knowledge required for long-term sustainability and contribute to a deeper understanding of the lunar surface, allowing us to meet our scientific and exploration goals for the South Pole region of the Moon for the benefit of all.”
This robotic delivery is part of a larger strategy that includes human missions. Humanity's return to the lunar surface is slated for Artemis III, a mission currently planned for 2027 that will send astronauts to the South Pole for the first time in 50 years, according to NASA. The mission will launch four astronauts, selected from NASA's diverse corps, from Launch Pad 39B at Kennedy Space Center. Their journey will be powered by the Space Launch System (SLS), the only rocket capable of carrying the crew and supplies in a single launch. For their return, the crew will rely on the Orion spacecraft, whose uniquely designed heat shield was proven on the successful Artemis I mission to withstand the extreme temperatures of re-entry into Earth's atmosphere.

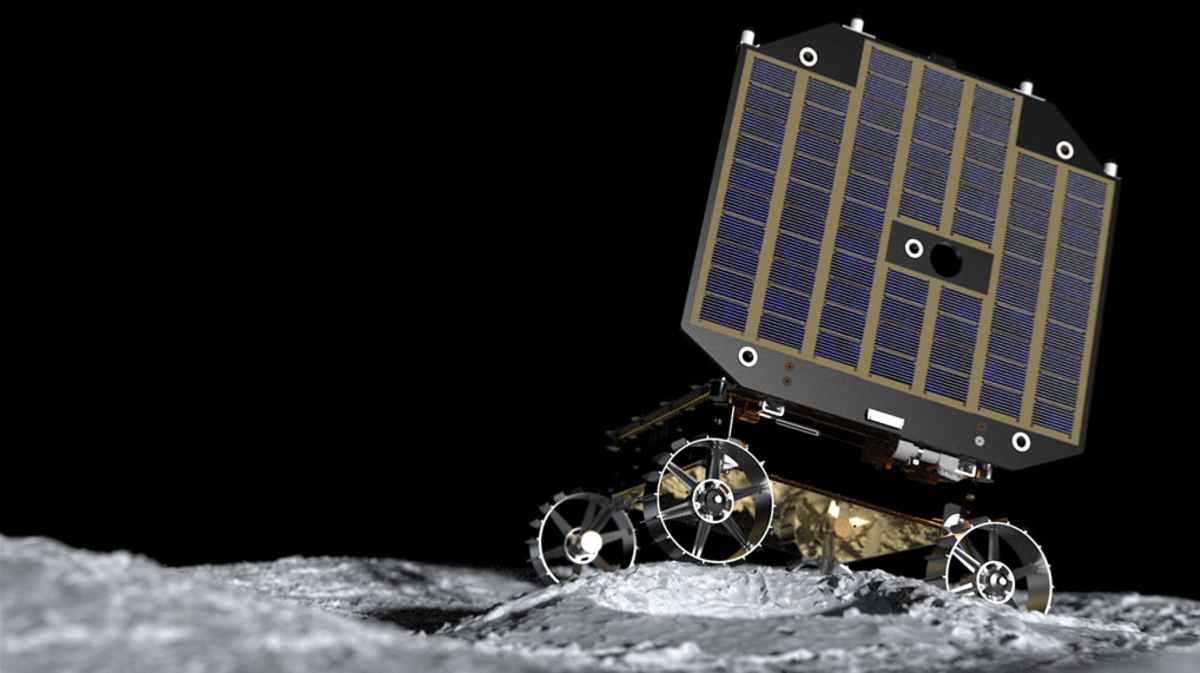
The mission will see Firefly's lunar lander deploy two rovers: MoonRanger, an autonomous microrover designed to navigate the lunar surface and map hydrogen-bearing compounds, and a CSA Rover, built to explore remote, permanently shadowed areas and withstand the extreme conditions of a lunar night. Both rovers are equipped with a suite of instruments to study the Moon's geological history, surface properties, and potential water ice resources, as mentioned on NASA.

In addition to the rovers, the lander will carry three stationary instruments to the South Pole. The Stereo Cameras for Lunar Plume Surface Studies will use enhanced imaging and sensors to capture the impact of the rocket's exhaust plume on lunar soil during descent. This data will be vital for predicting regolith erosion and ejecta characteristics for future, heavier spacecraft landings.
The Laser Retroreflector Array is a passive optical instrument that will serve as a permanent location marker on the Moon for decades, enabling precise distance measurements. Finally, a laser Ionization Mass Spectrometer will use a robotic arm and shovel to collect and analyze lunar regolith samples. This instrument will use a pulsed laser to identify differences in the soil's chemistry compared to past samples, such as those from the Apollo program, providing insights into the Moon's evolution.
This contract represents Firefly's fifth CLPS task order, building on its previous missions, including a successful delivery in March 2025. This latest award solidifies the partnership between NASA and commercial companies, driving forward a new era of lunar exploration and resource utilization.









