Millions of light years old 'warm' interstellar dust found in Makani galaxy's hot halo

The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) has made a landmark discovery, directly observing warm cosmic dust in the vast, hot gas halo surrounding a distant galaxy. This finding challenges existing theories about how these particles survive the perilous journey from their galactic homes, according to the University of Maryland. The pathbreaking study was published in The Astrophysical Journal on August 25, 2025
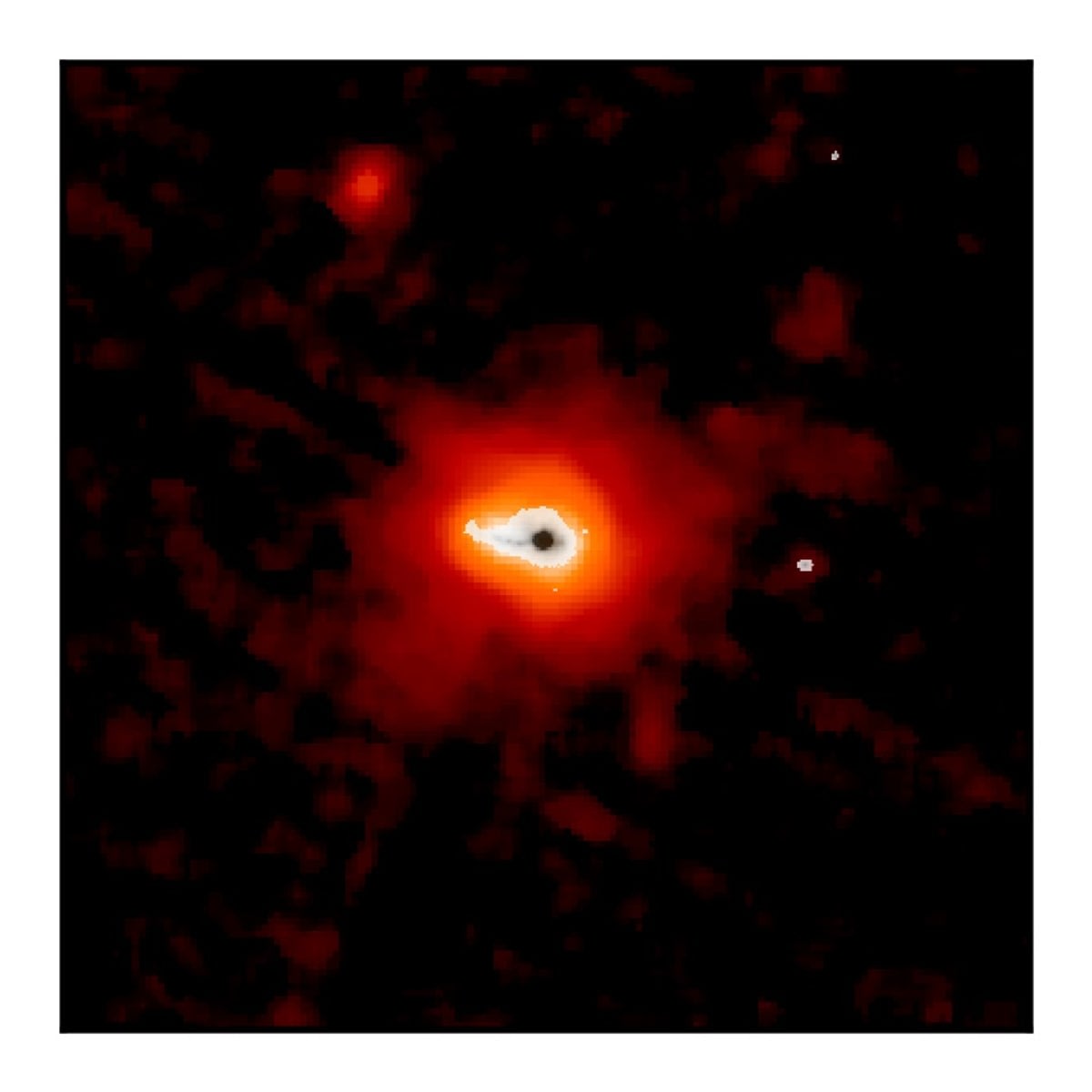

A team of astronomers, led by University of Maryland Professor Sylvain Veilleux, used the JWST to study the Makani galaxy, a celestial object with a Hawaiian name meaning "wind." Makani is known for its powerful galactic winds, which are created by intense star formation and propel gas and dust away from the galaxy's core.

For millions of years, the dust traveled away from Makani, carried by these powerful winds. It eventually settled in the circumgalactic medium (CGM), a massive halo of hot gas that surrounds galaxies. The team's study marks the first time dust has been directly detected at such a great distance from a galaxy's center. “Before this study, there had not been a direct detection of dust on such a large scale, and Webb was the key that made it happen,” Veilleux said. The discovery raises significant questions because the dust was expected to be vaporized by the high temperatures of the CGM, which can exceed 10,000 Kelvin. The team theorizes that the dust particles are being shielded from the hotter gas, possibly by cooler pockets of gas acting as protective cocoons.
This finding could provide critical insight into how galaxies evolve. Galactic dust, though microscopic, is a crucial ingredient for forming new stars and planets. Understanding how these materials cycle into and out of a galaxy gives astronomers a more complete picture of how they change and grow over time. Looking ahead, the research team plans to conduct a follow-up study using the JWST to obtain a spectral "fingerprint" of the dust. This data will help them determine the dust particles' properties, including their size, which could shed more light on their surprising durability. In the future, Veilleux hopes to find dust on a larger scale, especially in the gaps between galaxies, referred to as the "intergalactic medium." If dust can be found there, then “that would be very exciting because it would mean that the full cycle is closed — that dust is not only in the halo of the galaxy, but even beyond that,” concludes Veilleux.

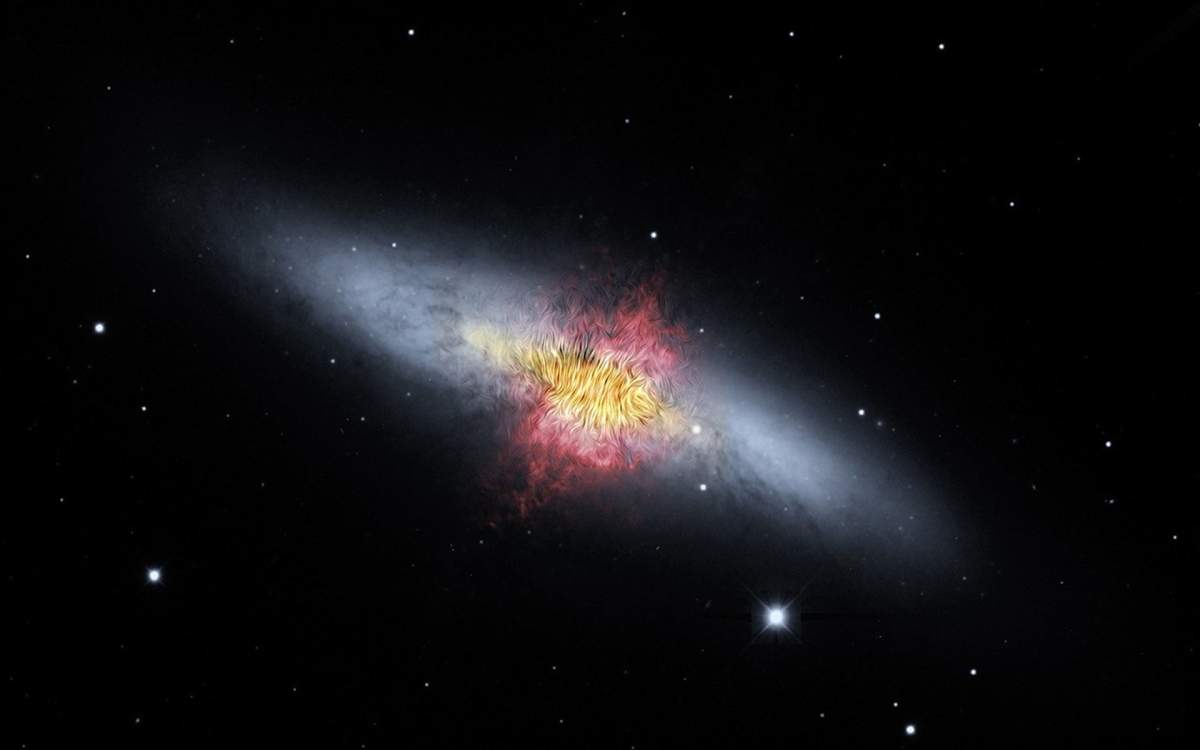
The JWST's unique infrared capabilities continue to offer unprecedented views into galactic processes. In a separate observation, the telescope captured a spectacular image of the Cigar Galaxy (Messier 82), revealing an extraordinary star formation previously hidden from view. Located just 12 million light-years away in the constellation Ursa Major, M82 is designated as the NASA/ESA/CSA "Picture of the Month."
We aren’t blowing smoke, M82 is working overtime forming new stars!
— NASA Webb Telescope (@NASAWebb) June 30, 2025
This galaxy, also called the Cigar Galaxy, is smaller than our Milky Way, but 5x as luminous and forms stars 10x faster! Webb’s NIRCam allows us to see billions of stars through all the dust!… pic.twitter.com/dWD2uhlS9I
Though a fraction of the size of our own Milky Way, the Cigar Galaxy generates stars at an astonishing rate, ten times faster than our home galaxy, and shines five times brighter. M82 is classified as a starburst galaxy, a term for galaxies experiencing an exceptionally high rate of star production. This rapid stellar birth has long been shrouded by thick dust clouds, but Webb's Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam) successfully penetrated this cosmic veil, exposing the luminous heart of the galaxy for the first time.
More on Starlust
NASA's Perseverance rover captures the visual of Martian 'dust devils' devouring each other
Dust collected by Apollo 17 astronauts in 1970s reveals the moon’s true age