Is comet C/2025 R2 (SWAN) still visible from Earth? Here’s how to spot it this week

The recently confirmed celestial visitor, Comet C/2025 R2 (SWAN), remains a potential target for skywatchers, even as it begins its retreat from Earth. Discovered just last month by the SOHO spacecraft’s SWAN camera, the comet has now passed its closest approach, or perigee, to our planet, according to EarthSky.
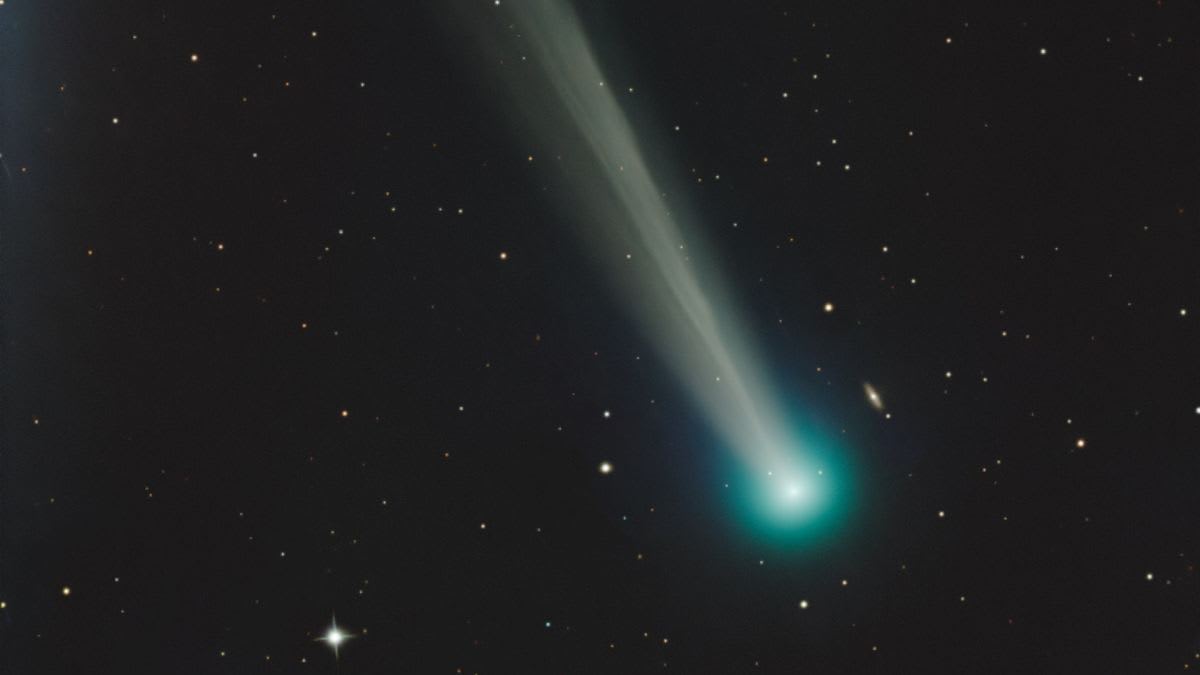

Despite its increasing distance from both the Sun and Earth, the comet is currently shining at an approximate magnitude of 6, making it technically visible to the unaided eye. However, observers are strongly advised to use binoculars for a more distinct view, especially when observing from areas with minimal light pollution. The comet’s current brightness marks its peak visibility for this pass. For those hoping to catch a glimpse, look towards the south roughly 90 minutes after sunset, once the sky has achieved full darkness.

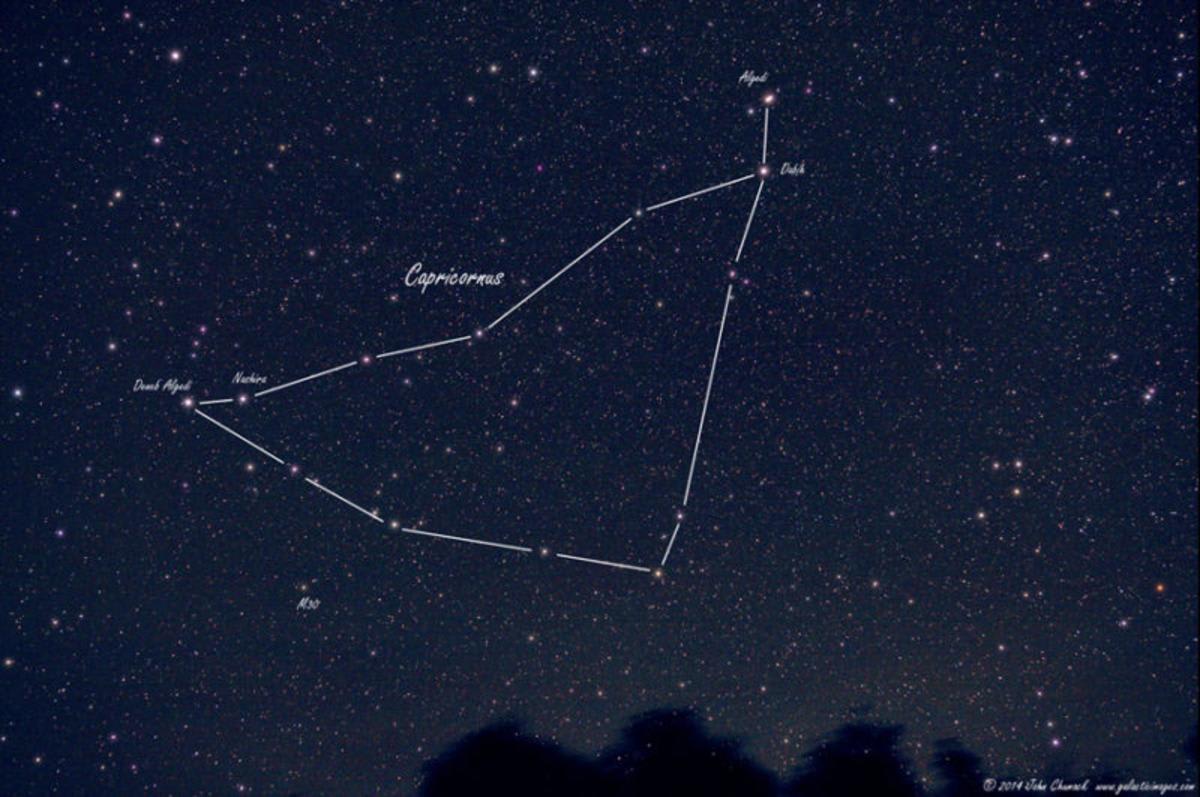
As of today, October 24, the comet is positioned within the constellation of Capricornus. Current astronomical data places Comet SWAN approximately 25.48 million miles (41 million kilometers) from Earth, according to the data shared on Sky Live. For precise tracking, its apparent coordinates are Right Ascension 20h 13m 11s and Declination -08° 36’ 36”. At its current distance, the light we are seeing tonight left the comet just 2 minutes and 18 seconds ago.
Tracking data from NASA/JPL has unveiled the extraordinary nature of Comet C/2025 R2 (SWAN)'s path: it completes a single orbit around the Sun approximately every 22,554 years, per EarthSky. This makes its current visibility a truly once-in-a-lifetime event. Should the comet remain intact after this close passage, its projected return will not be until the year 24,579.

The celestial object was recently identified by comet hunter Vladimir Bezugly in SWAN images, rapidly attracting the attention of the astronomical community. Comet astrophotographers have since captured striking images of the new visitor. Experts have been quick to confirm its impressive appearance. Comet specialist Michael Mattiazzo, observing from Australia, reported a visual sighting on September 12 using 15 x 70 binoculars. Martin Mašek of the Institute of Physics of the Czech Academy of Sciences also shared his successful observation, noting his surprise at its unexpected brightness and distinct tail. "I was very pleasantly surprised by such a bright comet with a long tail," Mašek stated, adding that he had initially anticipated searching for only a faint patch.
The brightness of the comet raises an important question: why couldn't we spot it sooner? Scientists hypothesize that its trajectory kept it obscured, perhaps positioned behind the Sun or too close to the solar glare during its approach. It may have only recently emerged into a visible area shortly after passing its perihelion (closest point to the Sun). However, researchers are still actively comparing observational data to precisely determine its trajectory and explain its late discovery. According to Sky Live, the comet's closest approach to Earth took place on Monday, October 20, 2025. At that time, it soared past our planet at a distance of approximately 24.29 million miles (39.1 million kilometers or 0.26 Astronomical Units).
More on Starlust
Comets C/2025 K1 ATLAS and C/2025 R2 SWAN appear to 'race' each other in extraordinary sky moment
Solar wind is causing 'major disturbance' to comet SWAN (C/2025 R2) gliding through space









