Comet C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) is approaching the Sun—when and how you can spot it this week
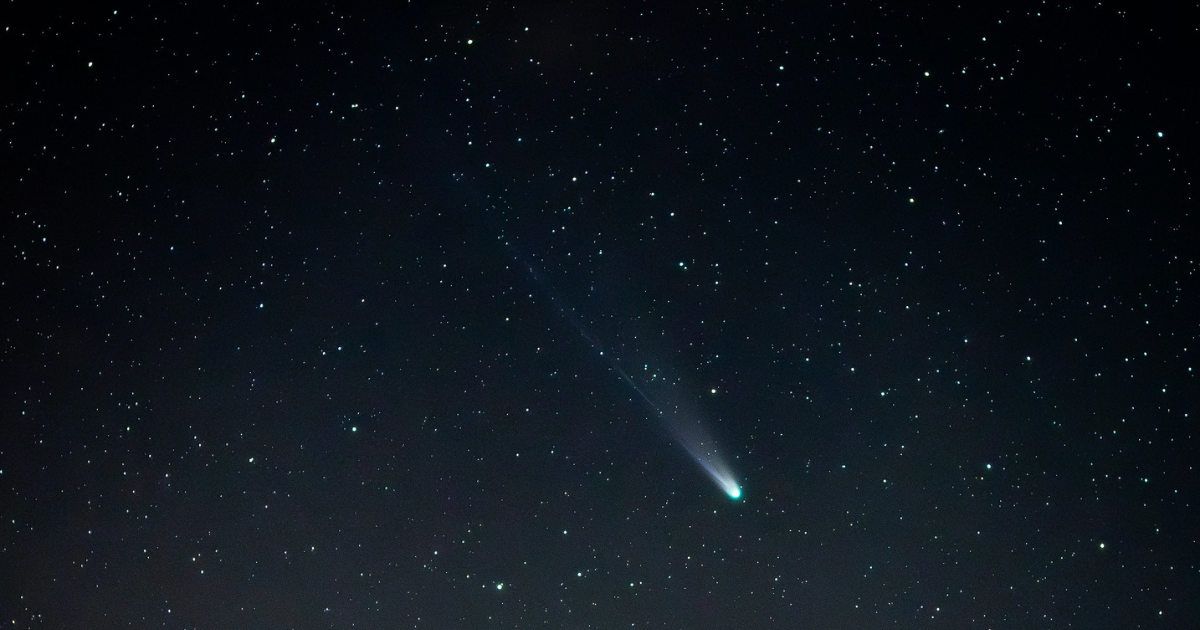

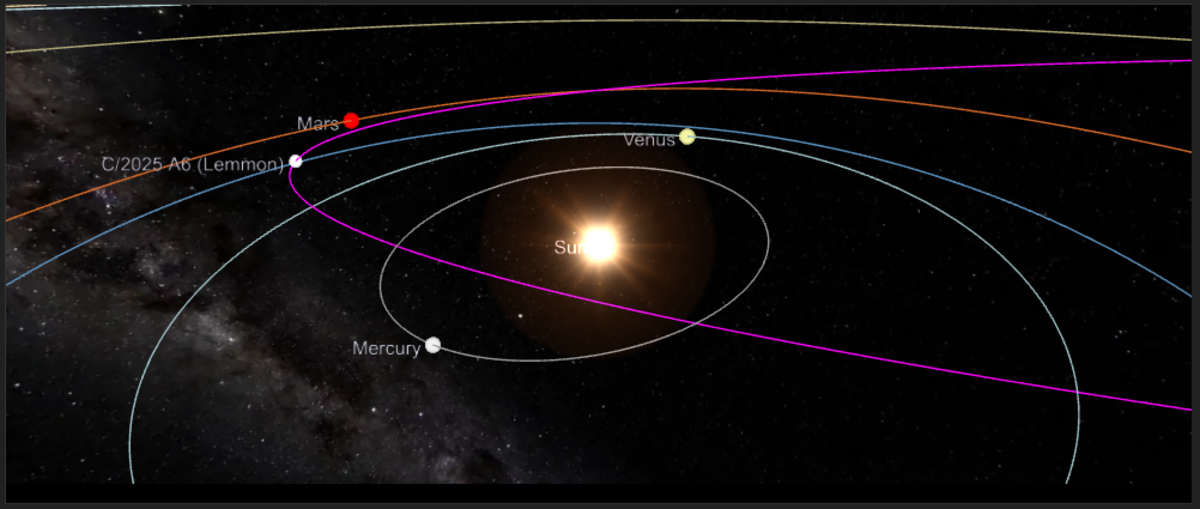
Comet C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) is set for its perihelion, the closest point to the Sun in its orbit, on November 8, when it will reach a distance of 0.53 AU from our star, according to Space Weather.
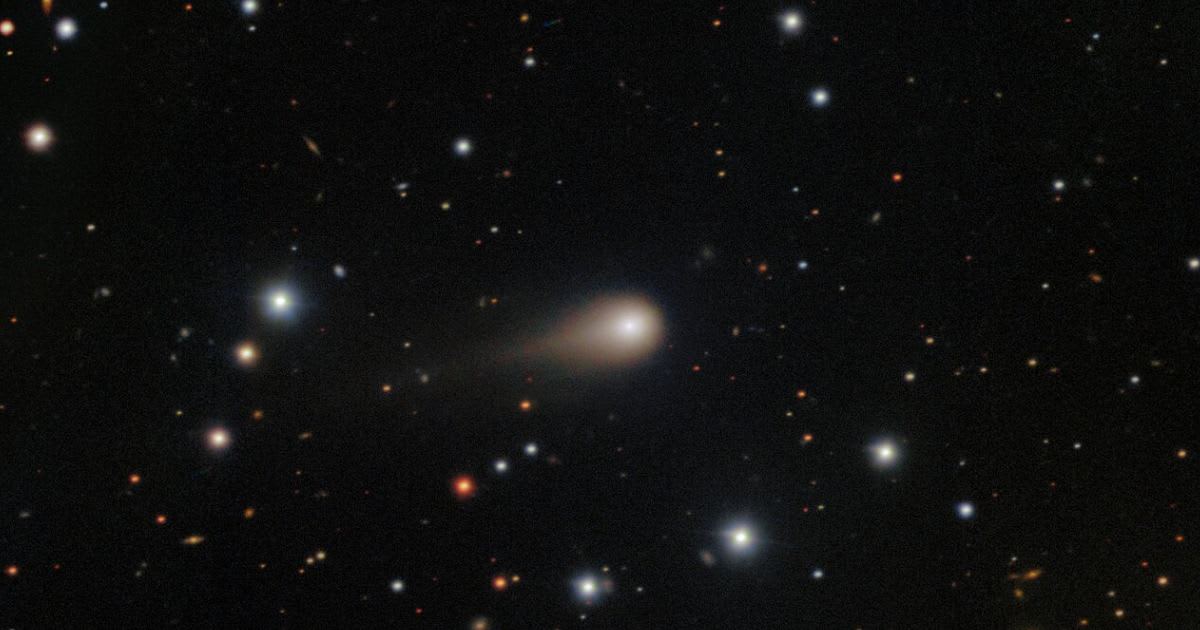

Currently situated in the constellation Ophiuchus (The Serpent-bearer), the comet is approximately 147 million kilometers away from Earth, per Sky Live. Recent observations place its brightness near magnitude 4.9 to 5.0, a range that potentially allows for naked-eye visibility under extremely dark, pristine skies. The comet's closest approach to Earth occurred earlier, on October 21, at a distance of about 89.2 million kilometers (0.596 AU). Its apparent coordinates are shifting daily as it tracks across the sky.

Observers in the Northern Hemisphere should target the evening sky shortly after sunset, specifically 45 to 90 minutes following local twilight. The comet is sinking lower toward the western/northwestern horizon, meaning the window for observation is closing quickly as it heads south. Observers in the Southern Hemisphere may still find better viewing opportunities before the comet fades further.

While technically near peak brightness, the comet will likely appear as a faint, fuzzy patch. Binoculars are essential for transforming the view from a potential naked-eye smudge into a more defined target with a visible coma. A low-power telescope is also effective. To maximize chances, escape urban light pollution. Dark skies are non-negotiable for spotting objects near magnitude 5.0. Allow your eyes 15 to 20 minutes to fully adjust to the darkness; avoid exposure to bright screens during this crucial period. Use a planisphere or astronomy application to navigate to the coordinates within Ophiuchus, as the constellation is not rich in bright guiding stars.

Today, Comet Lemmon is expected to be found at a Right Ascension of 16h 52m 52s and a Declination of -07° 32’ 14” within the constellation Ophiuchus, holding an estimated magnitude of 4.92. Following this, on November 8, 2025, the date of perihelion, the comet will have shifted its position to Right Ascension 16h 55m 52s and Declination -08° 54’ 48”, remaining in Ophiuchus, with its brightness potentially increasing slightly to an estimated magnitude of 4.98. Finally, by November 9, 2025, observers will find it further south and east at Right Ascension 16h 58m 31s and Declination -10° 12’ 41”, still tracked through Ophiuchus, with its estimated magnitude dimming to 5.05.
Astrophotographers are presented with a potential rare photo opportunity over the coming nights: capturing Comet Lemmon juxtaposed against the aurora borealis, per Space Weather. The comet's current position in the sunset sky makes it favorably placed to potentially share the view with expected geomagnetic storms linked to the Sun's coronal mass ejection (CME) impact near the November 8 perihelion.
This convergence is so unusual that it has already caused imaging frustration for some experts, as evidenced by photographer Peter Rosen in Abisko, Sweden, who noted trying to photograph the comet only to have a brilliant Northern Lights display "ruin the shot." Observers hoping to capture this unique alignment should look for the comet, which may reach a brighter 4th magnitude around its closest solar pass, setting near the familiar star patterns of Ophiuchus just after sunset.
More on Starlust
Solar storm temporarily rips apart comet Lemmon's tail in rare celestial spectacle
Is comet C/2025 A6 (Lemmon) still visible to the naked eye this week? Here's how to spot it









