Alien artifact or freak of nature? 'Anomalously massive' interstellar object 3I/Atlas has scientists puzzled

A new study co-authored by leading astronomers - Harvard professors Richard Cloete, Avi Loeb, and Peter Vereš - suggests the interstellar object 3I/ATLAS is unlike any other comet ever seen before, presenting a major scientific puzzle. The object's sheer size and lack of a noticeable "rocket effect" from outgassing have led researchers to believe it is "anomalously massive and large," much bigger than the previously discovered interstellar objects, 1I/'Oumuamua and 2l/Borisov, as mentioned by Loeb in his blog on Medium. In their opinion, it could also be an "alien technology."
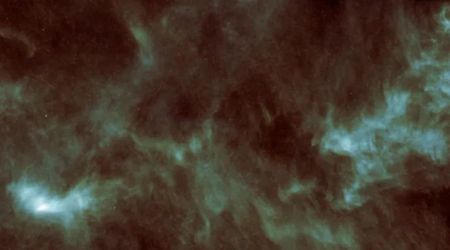
![Hubble captured this image of the interstellar comet 3I/ATLAS on July 21, 2025, when the comet was 277 million miles from Earth. [Image Source: NASA, ESA, David Jewitt (UCLA); Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)]](https://de40cj7fpezr7.cloudfront.net/c49eeb4e-e60a-46c0-b39f-68fbb2ee9297.jpeg)
New data reveals 3I/Atlas is at least 33 billion tons more massive than`Oumuamua. This is a significant anomaly, because it contradicts the astronomical models which predicts that a much larger number of smaller interstellar objects like 1I/`Oumuamua should have been detected before spotting something as big as 3I/Atlas.

The research team analyzed 4,022 observations from 227 observatories worldwide between May and September 2025. They tracked the object's movement to set a strict upper limit on any deviation from a path dictated solely by gravity. Despite data from the Webb Space Telescope showing material outflow at 330 pounds (150 kilograms) per second, the object's trajectory showed almost no acceleration. This absence of a "rocket effect," the pushback from escaping gases, implies that 3I/Atlas must be extraordinarily massive to remain stable. This minimum mass suggests a nucleus with a diameter of at least 3.1 miles (5 kilometers), which is a full order of magnitude larger than the interstellar comet 2I/Borisov.
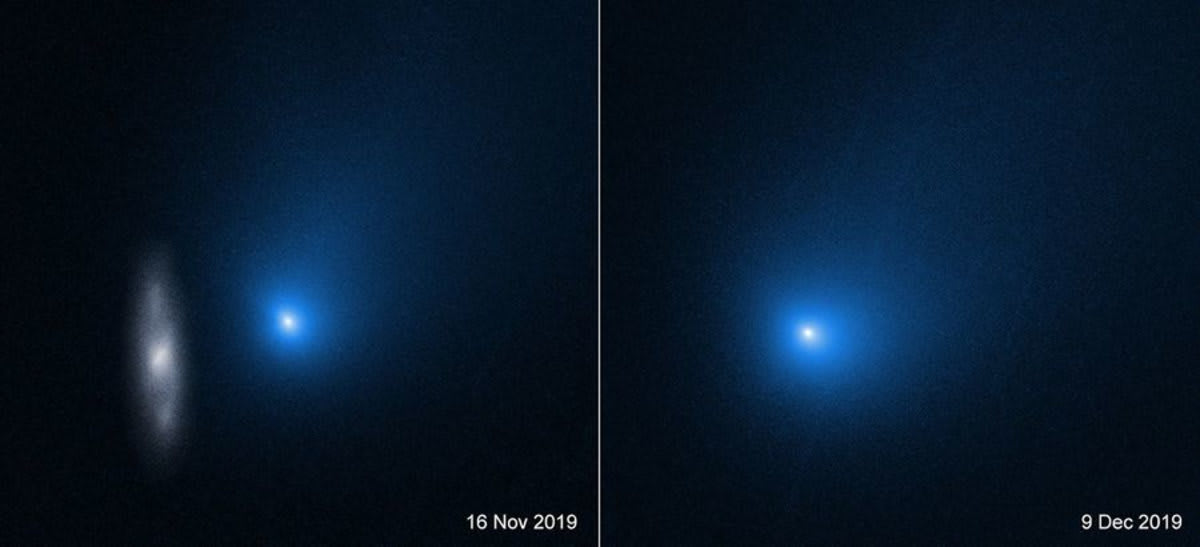

Adding to the mystery, the object's trajectory aligns with the ecliptic plane, a rarity with a one-in-500 chance of occurring randomly. The discovery of nickel without iron, a signature of industrially manufactured alloys, has also been reported, fueling speculation about its origins. Researchers are not ruling out a natural explanation. The object could simply be an unusually massive comet with an unusual chemical makeup.
Upcoming observations could provide more clarity. The HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter will get a close look at 3I/Atlas on October 3, 2025, when it passes by Mars. The Juno spacecraft is also scheduled for a close encounter near Jupiter on March 16, 2026. These upcoming flybys could either confirm the object's natural, cometary origins or provide more clues about its potentially technological nature.

Despite the intriguing findings, some experts advise a more cautious interpretation. NASA has urged restraint, with Tom Statler, the lead scientist for Solar System small bodies, stating that the object "looks like a comet" and "does comet things," as reported on IFL Science. He added that while it has some unique characteristics, "the evidence is overwhelmingly pointing to this object being a natural body." The study's lead author has also referred to the initial claims about the object's potential artificial origin as a "pedagogical exercise." However, the research does stand by the claim that 3I/Atlas may be significantly more massive than other interstellar visitors, a finding that adds a new dimension to our understanding of objects from beyond our solar system.
With the recent activation of the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, which has already demonstrated its incredible power by discovering over 2,100 new asteroids in a single 10-hour period, scientists are optimistic. The influx of new data from this and other observatories may soon provide more clues to help solve the mystery of 3I/Atlas and other similar objects.

For those hoping to catch a glimpse of the enigmatic object, Comet 3I/ATLAS is currently located in the constellation Libra, approximately 376 million kilometers from Earth, as per The Sky Live. With a latest observed magnitude of 13.3, the object continues its journey through our solar system, and its every movement is being scrutinized, with scientists eagerly awaiting the upcoming flybys that may finally reveal more of its secrets.