Which Is the Hottest Planet in Our Solar System?


Although Earth is the only planet we have been able to physically explore so far (besides robotic exploration), scientists have developed various methods to survey, assess and analyze neighboring planets. As a result, researchers have been able to discover which planet is the hottest in our solar system.
Although Mercury is the closest planet to the Sun, it is actually Venus that is the hottest planet in our solar system. Indeed, its surface regularly reaches temperatures above 869 degrees Fahrenheit (465 degrees Celsius). Both the composition of its atmosphere and the dense cloud layers that cover this planet contribute to the intense heat retention.
In this article, we will discuss in detail why Venus has such a fiery surface.
How do scientists measure the temperature of a planet?
Before we look at the temperatures of other planets, it is worth pondering about scientists are able to measure them. The answer is simple: it is the result of decades of assessment and data collection.
As mentioned earlier, scientists working for organizations such as NASA have been exploring the solar system with robotic space probes since the 1950s, when the first satellites were deployed in space.
The former Soviet Union had developed a space program called "Venera" which objective was to collect more data about Venus. Between 1961 and 1984, 10 space probes landed on the surface of Venus. However, as Venus is extremely hot, none of these robots survived more than two hours.
Since then, more advanced and more accurate instruments have been developed. These are capable of measuring light and heat energy from great distances. Most of the temperature readings on other planets are made by probes equipped with infrared sensors flown as close as possible to the planet's surface.
These measurements are then analyzed and verified based on the planet's distance from the sun, the composition of its atmosphere and how we know these elements interact with heat, as well as the size of the planet itself.
The average temperature on each planet
- Venus: 880°F (471°C)
- Mercury: 800°F (430°C)
- Earth: 61°F (16°C)
- Mars: -20°F (-28°C)
- Jupiter: -162°F (-108°C)
- Saturn: -218°F (-138°C)
- Uranus: -320°F (-195°C)
- Neptune: -331°F (-201°C)
- Pluto: -388°F (-233°C)

NASA's various space probes are equipped with state-of-the-art technology. They can perform various scans from orbit, including the measurement of surface temperatures.
How does Venus retain heat?
Venus, the second planet in orbit around the sun, was the first planet to be explored by a spacecraft. Venus displays phases like those of the Moon that can be observed from Earth with an ordinary telescope, which explains why Venus has been examined since antiquity.
Its atmosphere is dense and composed of elements that allow massive retention of heat: more than 96% carbon dioxide and 3.5% molecular nitrogen. Thus, the high temperatures on the surface of Venus are due to an intense runaway greenhouse effect covering the whole planet.

An artistic illustration of what the surface of Venus might look like.
Venus' toxic atmosphere
The atmospheric layers enveloping Venus are incredibly dense, more than 90 times denser than the Earth's atmosphere, and consist mainly of clouds of carbon dioxide and sulfuric acid. As a result, Venus is extremely toxic.
This pressure and the composition of the atmosphere create an intense "runaway greenhouse effect" at the surface. The thick atmosphere traps the Sun's heat quicker and easier than any other planet in the solar system. As a result, the planet can reach temperatures of over 869 degrees Fahrenheit (465 degrees Celsius), high enough to melt lead.
The days on Venus are incredibly long, the equivalent of 243 days on Earth, so one part of the surface is exposed to more intense solar radiation. This, combined with the incredible heat retention of the atmosphere, means that the nights on Venus are as hot as the days.
Why Mercury isn’t the hottest planet in our solar system
You may be thinking, "Wait a minute! Isn't Mercury very close to the Sun? Why would Venus be hotter than Mercury?"
Although Mercury is indeed the closest planet to the sun and while it has not been studied as extensively as Venus, the data collected over the years allow us to know a lot about this planet.
Mercury is subject to the most intense solar radiation because of its proximity. The side of the planet facing the sun regularly reaches temperatures of about 800 degrees Fahrenheit (426 degrees Celsius). Therefore, on its sun-exposed surface, Mercury is almost as hot as Venus.
The main reason why Mercury is not the hottest planet in our solar system is its atmosphere, or rather its lack of atmosphere... Like Venus and Earth, Mercury is surrounded by a gaseous layer. But unlike the two twin planets, this layer is incredibly thin.
Scientists refer to it as an exosphere, given that it only covers the outermost layer of the planet, far from the surface. It’s composed primarily of oxygen, sodium, hydrogen, helium, and potassium. It’s incredibly thin and therefore makes a poor conductor of heat.
Scientists call this thin atmosphere an "exosphere" because it covers only the outermost layer of the planet, far from the surface. It is composed mainly of oxygen, sodium, hydrogen, helium and potassium. It is extremely thin and therefore a poor conductor of heat. Thus, the side of the planet that does not face the sun becomes incredibly cold... -292°F (-180°C).
That is why Venus is warmer than Mercury!
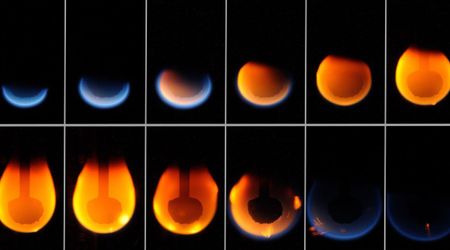
The scorching truth: Venus's heat versus everyday objects
To demonstrate the hellish temperatures of the surface of Venus, I thought it would be fun to compare how long different objects would last.
- An egg: the eggshell would quickly become brittle and crack, and the contents of the egg would begin to cook. I would estimate that an egg would last less than 15 seconds.
- A piece of paper: Paper is made from cellulose, which is a type of organic compound that is highly flammable. A piece of paper would ignite and burn quickly, within 5 seconds.
- A metal spoon: Metal is a much more heat-resistant material than paper or an egg. However, even most metals have melting points that are lower than 900 degrees Fahrenheit. The metal spoon would begin to soften and lose its shape within a few minutes on Venus.
- A block of ice: I would expect a block of ice to start the sublimation process instantly and be gone in less than 10 seconds.
- A car: The heat would cause the car's tires to melt, the metal components of the car to warp or deform, and the plastic parts of the car to melt or burn. It probably would not last an hour.
Conclusion
Using the most reliable information available, scientists have confirmed that Venus, although more similar to Earth than any other planet in our solar system, is not nearly as habitable.
Venus is the hottest planet in our solar system for many reasons, including the composition of its atmosphere and its very slow rotation speed. It has a solid, rocky surface with multiple (potentially active) volcanoes and asteroid impact craters along massive plateaus and mountain ranges obscured by cloud cover. Scientists have even given it the nickname: Earth's "toxic twin".
Millions of years ago, Venus could have been a habitable world, but unfortunately, it is located too far from the circumstellar habitable zone, which unfortunately turned this planet into a burning and toxic world.
Frequently Asked Question
Can Venus support life despite the heat?
These conditions make it inhospitable for most known forms of life. Additionally, the atmosphere of Venus is primarily composed of carbon dioxide, with clouds of sulfuric acid, which would be toxic to many forms of life. However, astronomers are not against the idea that life might have been possible in the distant past when Venus was cooler and more hospitable to life.
Could Venus be cooled down?
Any attempts at colonization would face significant challenges indeed. More importantly, there's just no incentive to do so. Venus does not hold a lot of scientific interest or value in its current state. Especially when more promising options such as Mars and the Moon exist. With the exception of robotic exploration, it's unlikely that any human will ever set foot on Venus in the near future.
Is Venus too hot to colonize?
It is unlikely that Venus could be cooled down to make it habitable for human life. This would be an incredibly challenging and expensive undertaking spanning thousands of years. More importantly, the planet would need to spin faster in order to generate a strong magnetic field to protect its surface against the harsh radiation particles coming from the Sun. We just do not have the technology to achieve such a feat.