Solar wind is causing 'major disturbance' to comet SWAN (C/2025 R2) gliding through space
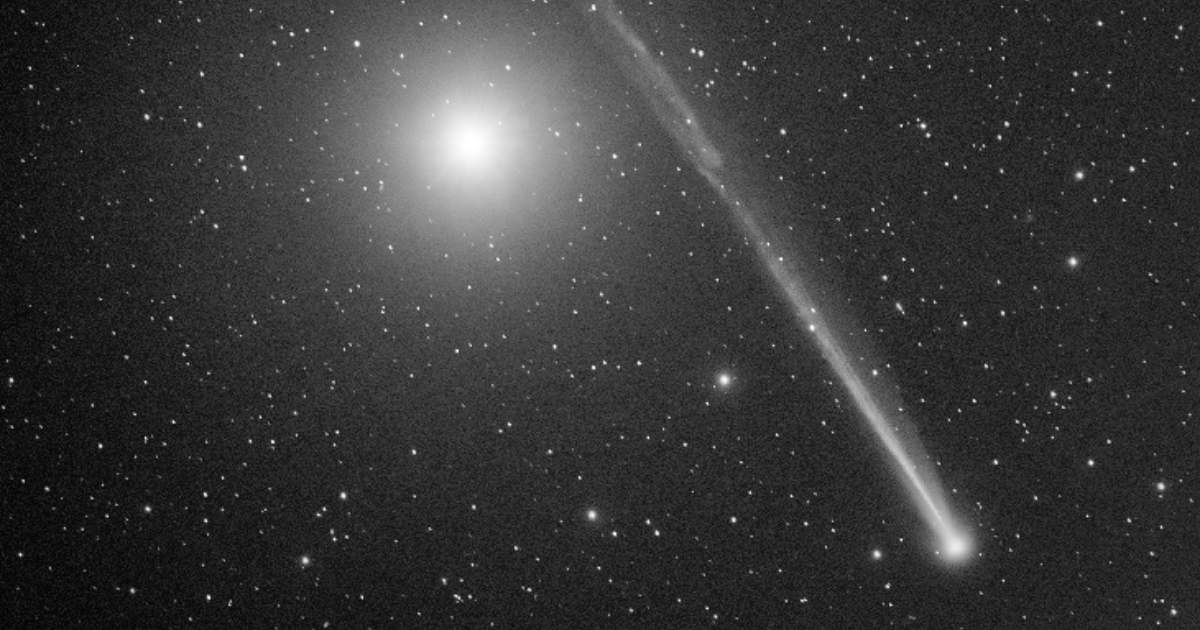

Comet SWAN (C/2025 R2), formerly known as Comet SWAN25B, is navigating a tumultuous environment, with its tail showing significant disruption from intense solar winds and a likely coronal mass ejection (CME). The comet's trajectory, positioned near Mercury’s orbit, places it directly in the path of powerful solar activity, as per SpaceWeather.

Astronomer Gerald Rhemann's observations from September 16 highlight the comet's highly reactive tail, noting remarkable changes in just ten minutes. "These changes are powered by the solar wind," Rhemann stated, observing the sun's influence shaping every aspect of the comet's tail.

The disturbance is visible on a broader scale. A new image from Australian astronomer Michael Mattiazzo shows a dramatic "wild corkscrew" extending more than five degrees from the comet. Mattiazzo speculates that the disfigurement is the result of a direct hit from a CME, a massive burst of plasma and magnetic field from the Sun's corona. This type of powerful solar interaction has precedent. A similar event in 2007 completely detached the tail of Comet Encke. Scientists are now watching to see if Comet SWAN will face a similar fate.
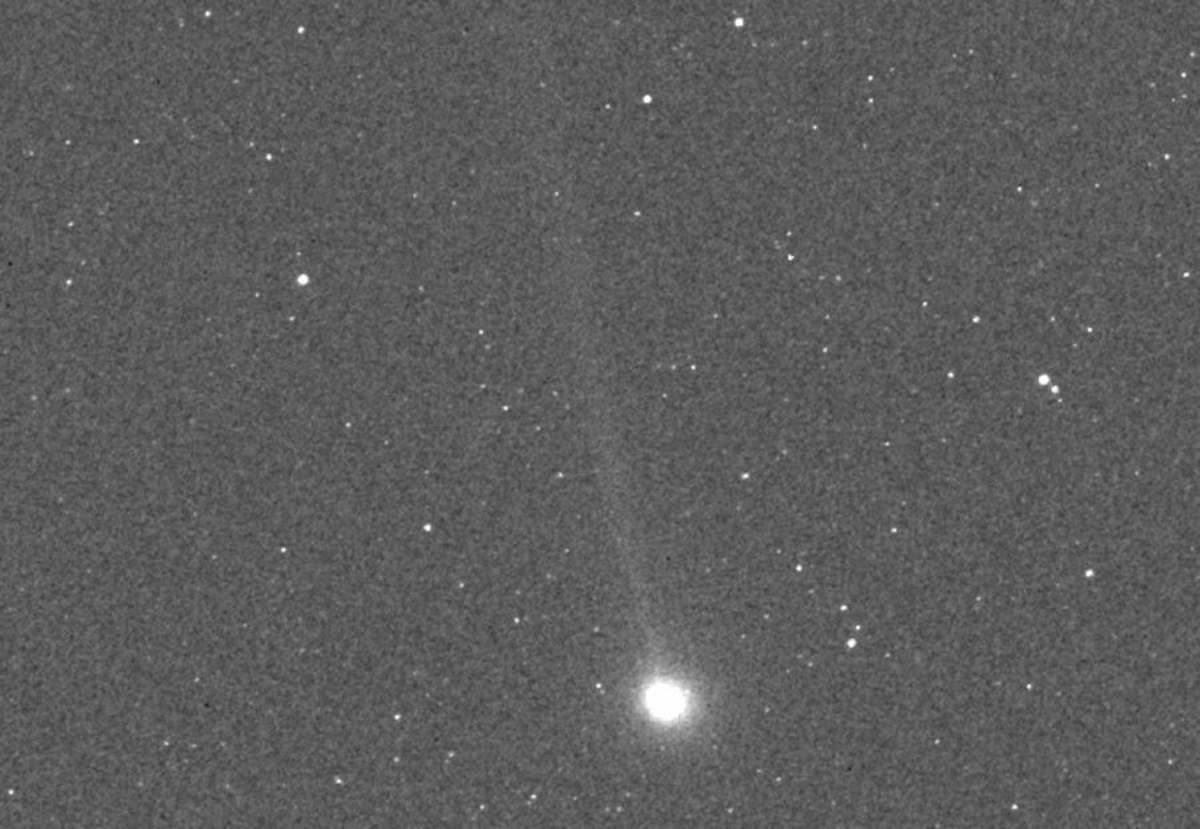

Comet SWAN25B, a new celestial body, is now an object of significant interest for astronomers and space enthusiasts. Discovered on September 12, 2025, by the Solar Wind Anisotropies (SWAN) instrument aboard the SOHO spacecraft, the comet has an estimated brightness of magnitude 7. While this makes it too faint for the naked eye, it can be seen with binoculars or a camera with a telephoto lens.
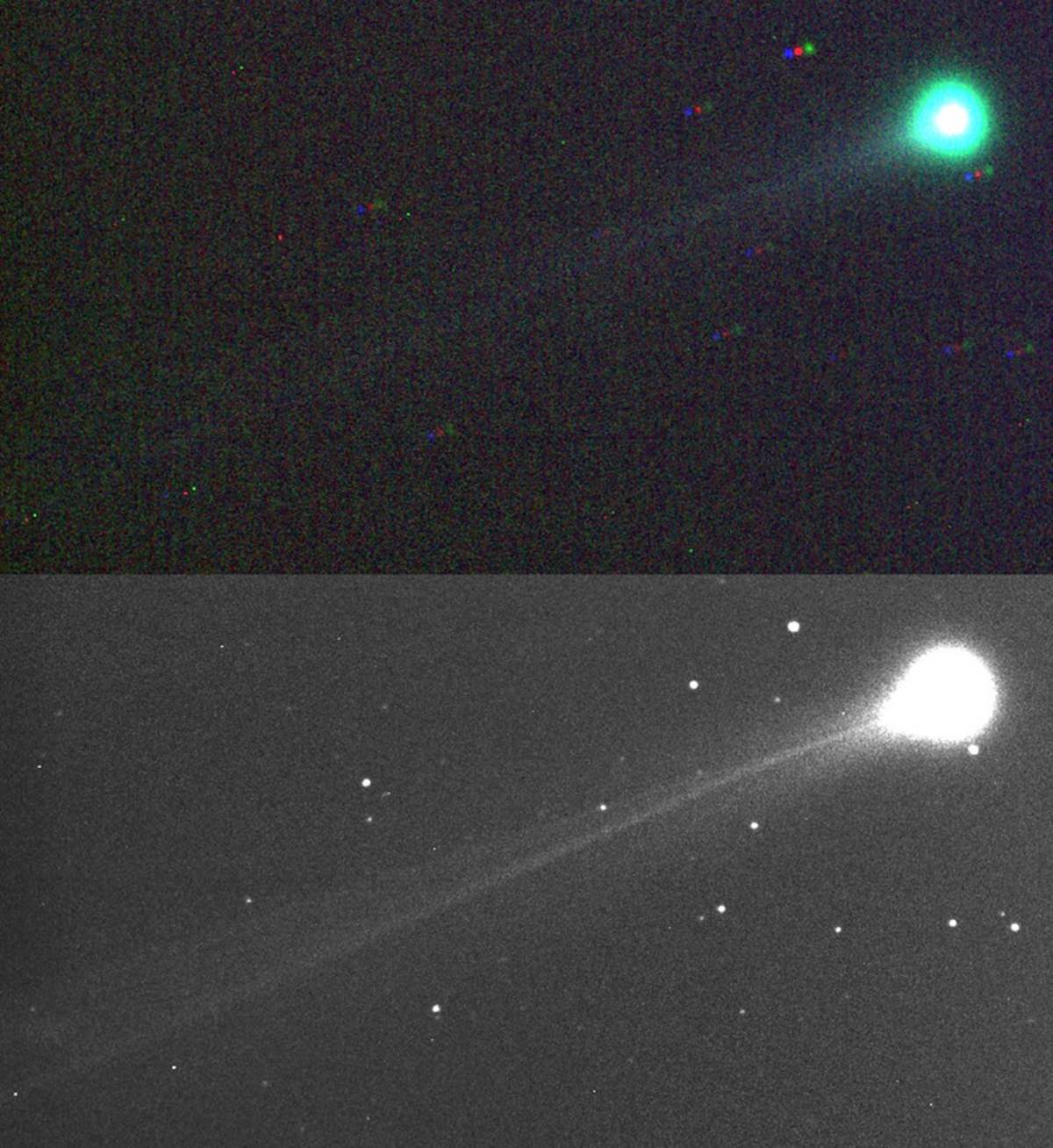

The comet is currently located in the Virgo constellation. While its trajectory is still being analyzed, initial projections suggest it will become more visible to observers in the Northern Hemisphere as it moves away from the sun. The comet is currently best seen from the Southern Hemisphere, but its nightly upward movement offers a promising view for northern observers as well. The name "SWAN25B" was a temporary designation, with its official name now being Comet SWAN (C/2025 R2). Its most recent coordinates are Right Ascension (RA) 13h 08.5m and Declination (Dec) -09° 10'.
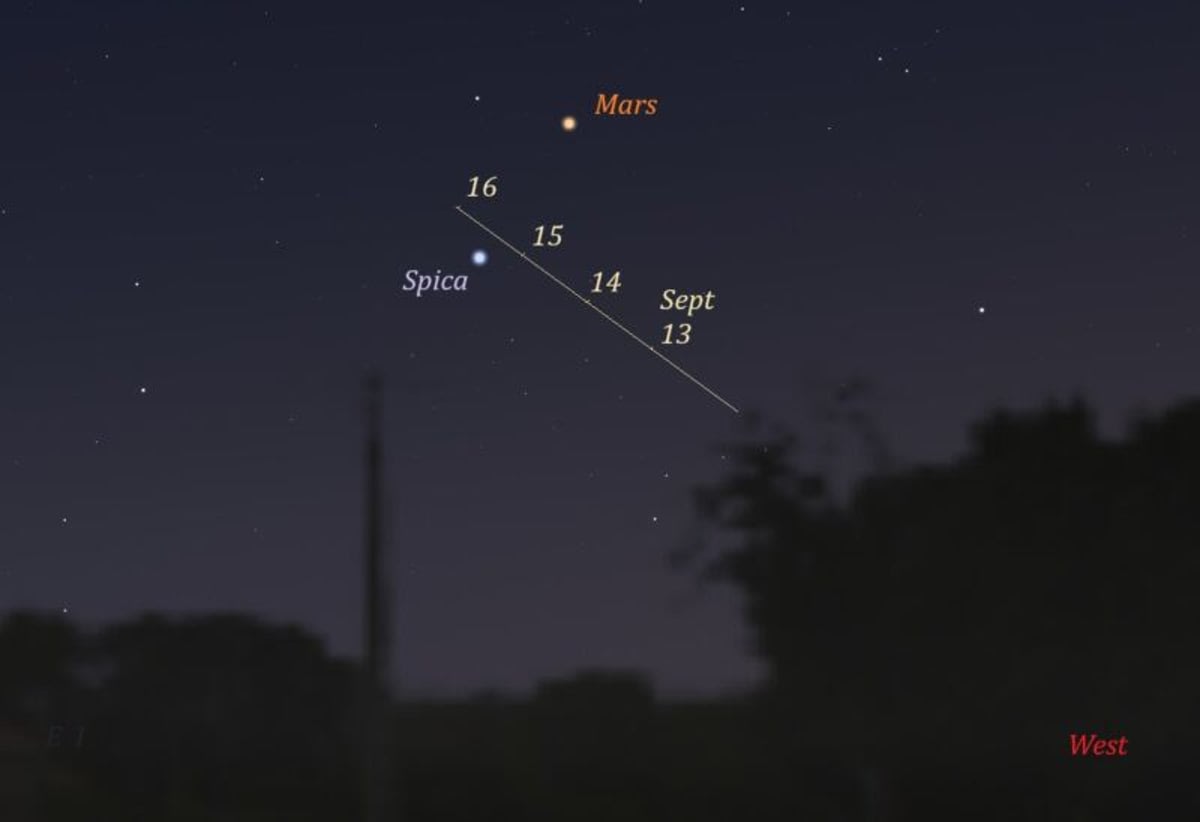
For those hoping to spot the new comet, experts offer a key tip: point your telescope toward the bright star Spica. A gaseous plume just below the star can serve as a guide, leading directly to the comet. This technique was recently used by observer Ujvárosi Beáta, who captured an image on September 14 using a remote-controlled telescope in Namibia. Beáta noted the comet's impressive size, saying, "The FSQ106 telescope has a huge field of view, but still, it looks like the tail is too long to fit into the image."
Images captured by experts, including one from Australian comet expert Michael Mattiazzo on September 14, reveal a prominent tail measuring approximately 2.5 degrees in length, roughly five times the apparent width of a full moon, according to EarthSky.org. While this impressive tail is visible in photographs, it may not appear as prominent to the human eye due to the camera's enhanced sensitivity. The comet's brightness has already increased to about magnitude 6.9, making it a challenging but viable target for observers. Faint images have already been captured by sky-watchers in Mexico and Arizona, suggesting the comet could soon become a more accessible viewing target for stargazers across the U.S.









