Saturn's icy moon harboring alien life? New discovery has scientists buzzing
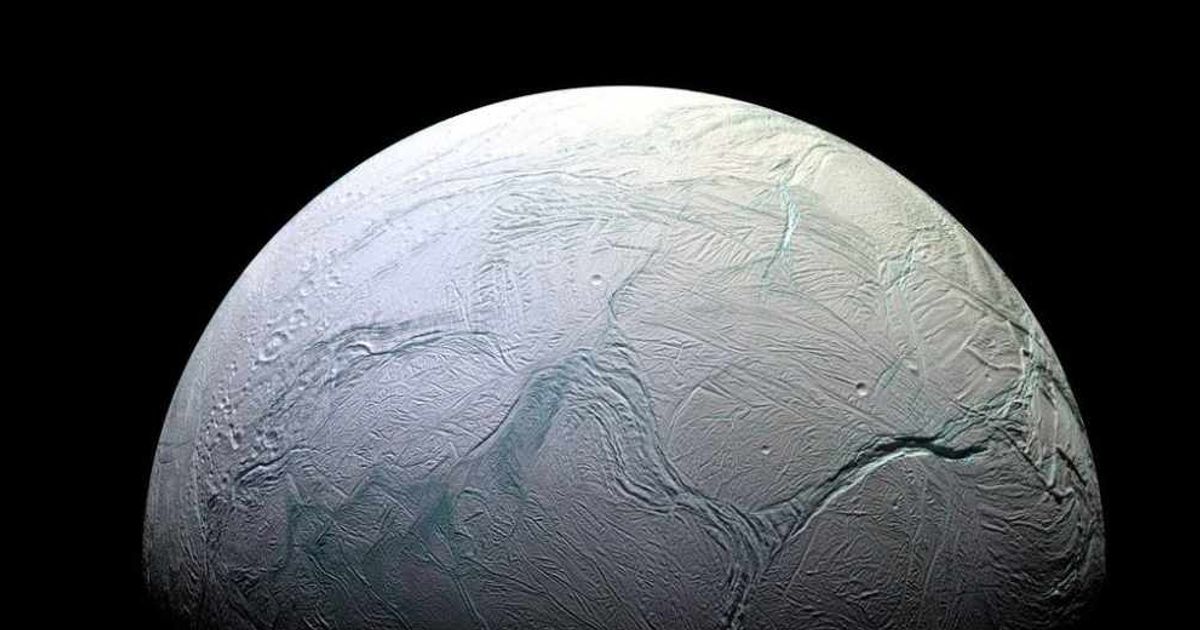

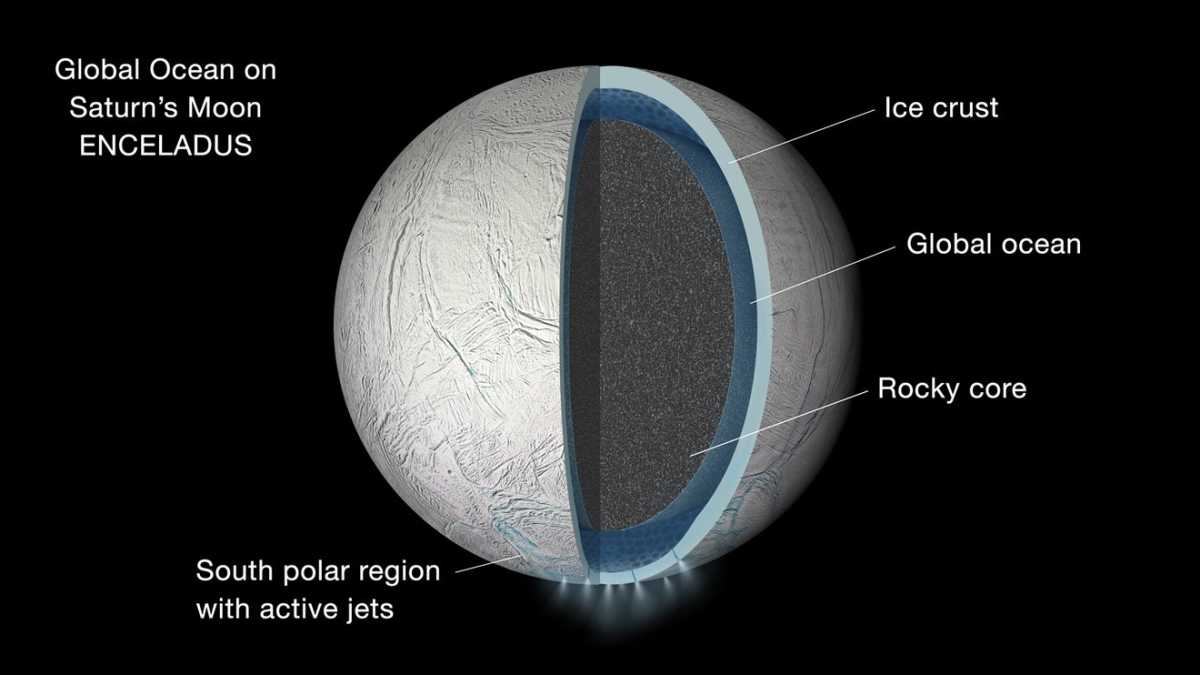
The frigid, ice-covered moon of Saturn, Enceladus, might not seem like a likely place to find life. However, it has been placed at the forefront of our quest for extraterrestrial life due to a remarkable discovery: a vast, hidden ocean of liquid water beneath its frozen surface, as reported by Phys.org.
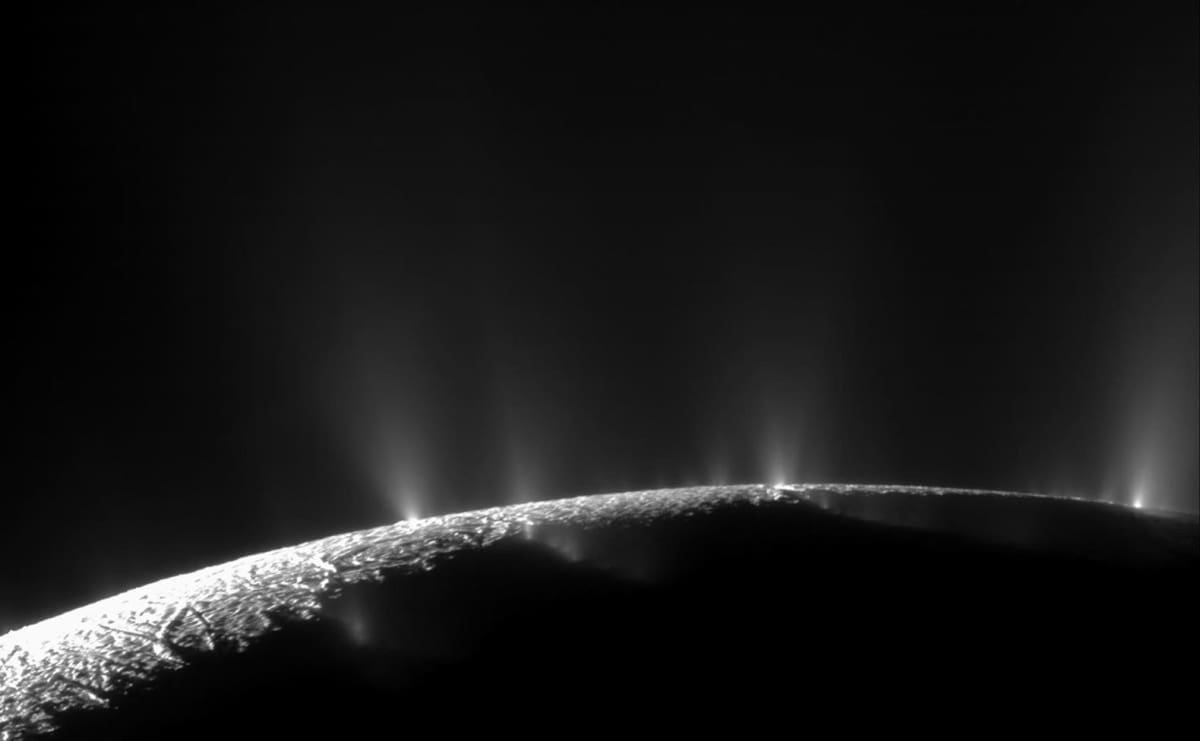

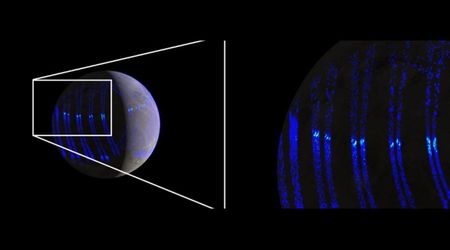
This subterranean sea has made Enceladus a primary target for astrobiologists. "Where there is water, life is possible," said astrobiologist Nozair Khawaja, who is leading a research team at the Free University of Berlin. His team is now preparing to conduct experiments to replicate the unique conditions on Enceladus to understand what kind of substances might form there. Scientists once dismissed the outer regions of our solar system as too cold and dark to support life. This view was challenged in 2005 when instruments aboard the Cassini spacecraft detected geysers of water vapor and ice particles erupting from fissures at Enceladus' south pole. This provided the first evidence of a subsurface ocean — a finding that was hailed as a breakthrough.
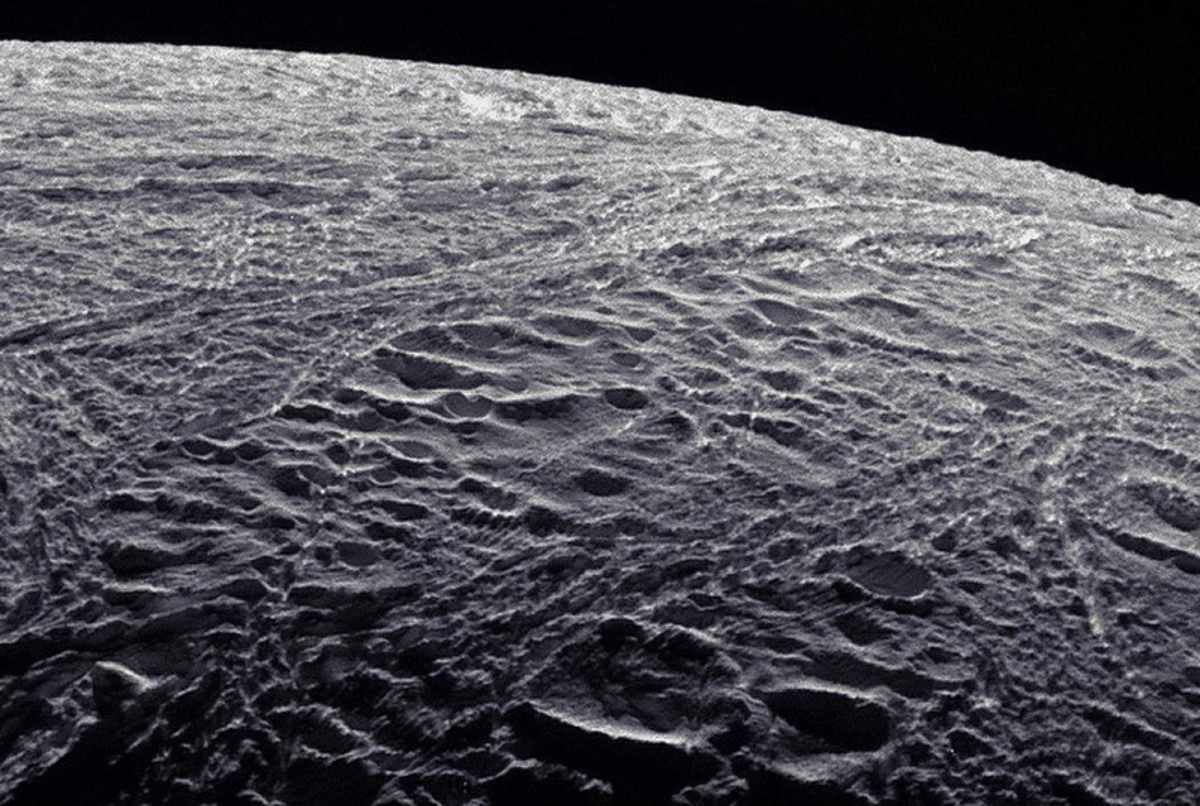

Khawaja's team has since analyzed some of the ice particles, discovering small, simple organic molecules as well as larger, more complex ones. "For the first time, we found very large organic molecules in an extraterrestrial ocean," he stated. While these molecules could hint at biological activity, they might also be the result of hydrothermal reactions. The upcoming lab experiments aim to distinguish between these two possibilities.
The potential discovery of microbial life on Enceladus would be a monumental event, bolstering hopes that life could exist elsewhere in the universe. "The discovery of extraterrestrial microbial life would raise hopes that traces of life might also exist in other places in the universe, and that conditions could exist where human-like life is possible or could be established in the future," Khawaja noted. While the find wouldn't be the stuff of science fiction, it would be a major step toward understanding our place in the cosmos. "We are not looking for something that resembles us, with two eyes, a nose, and arms," he clarified.
Recent analysis of data from NASA’s Cassini mission has provided new and compelling evidence that Enceladus contains not only the building blocks for life but also a powerful energy source to sustain it, per NASA. A study published in December 2023 zeroed in on the massive plume of ice grains and water vapor erupting from the moon’s surface, revealing the presence of hydrogen cyanide. This molecule is considered a vital precursor for the origin of life as we know it.
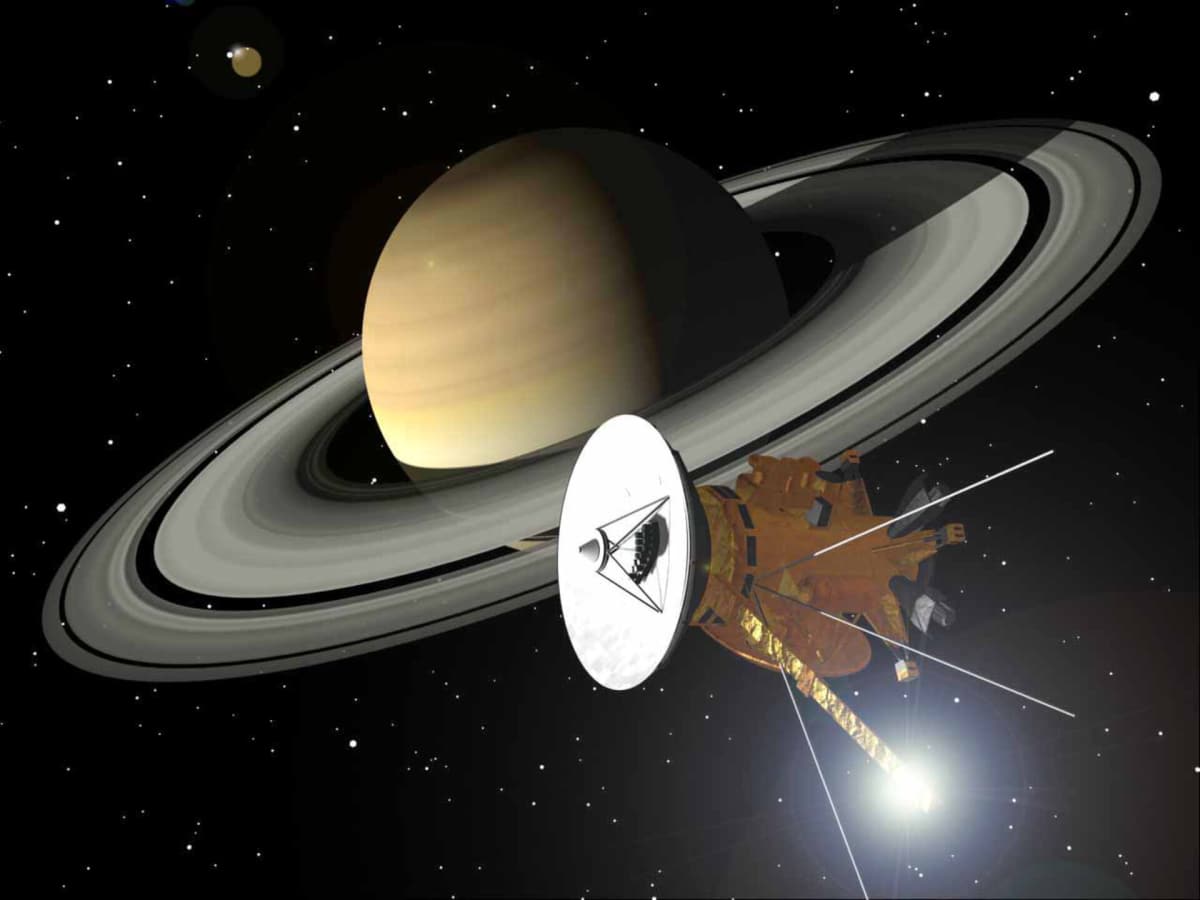

Beyond the presence of these crucial organic compounds, researchers also found indications that the moon's hidden ocean is rich in chemical energy. This previously unidentified energy source comes from several organic compounds that, on Earth, serve as fuel for various organisms. These findings suggest that the tiny moon may have far more available energy than previously believed. The greater the energy supply, the higher the chance that life could flourish and be sustained.
These discoveries add significant weight to the argument that Enceladus is one of the most promising places in our solar system to search for extraterrestrial life, transforming it from a mere curiosity to a prime target for future missions.
More on Starlust
Alien life on planet K2-18b? Scientists say otherwise after reassessing new James Webb data
Earth-like exoplanet 41 light-years away has no atmosphere to support life, new JWST data reveal
Earth’s radio signals highlight regions where extraterrestrial life could find us