NASA’s James Webb reveals strange anomalies in Saturn’s atmosphere, dark beads and star patterns
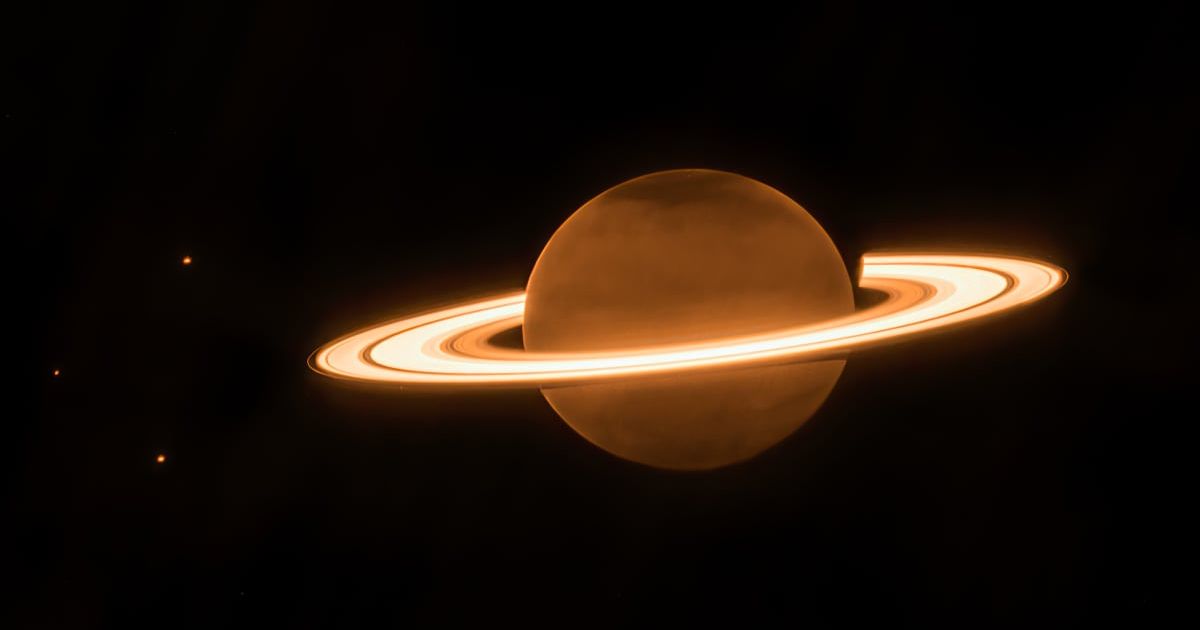

A new study into the atmospheric structure of Saturn using data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) revealed interesting insights. The atmosphere harbors complex features that were never seen before on any planet in our system. As published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters, scientists found a series of ionospheric dark beads. They also found extending dark arms, which formed the image of an asymmetric star pattern in the stratosphere, as per Sci Tech Daily. These might be connected to Saturn’s iconic hexagonal storm, though not confirmed.
Professor Tom Stallard of Northumbria University presented the results at the EPSC-DPS2025 Joint Meeting in Helsinki. JWST was used to procure detailed near-infrared observations of Saturn's aurora and upper atmosphere. According to Northumbria University, the international team of researchers had 23 scientists from institutions across the UK, the US, and France. They spotted the anomalies during a continuous 10-hour observation period on November 29, 2024. The focus was to detect infrared emissions by a positively charged molecular form of hydrogen.
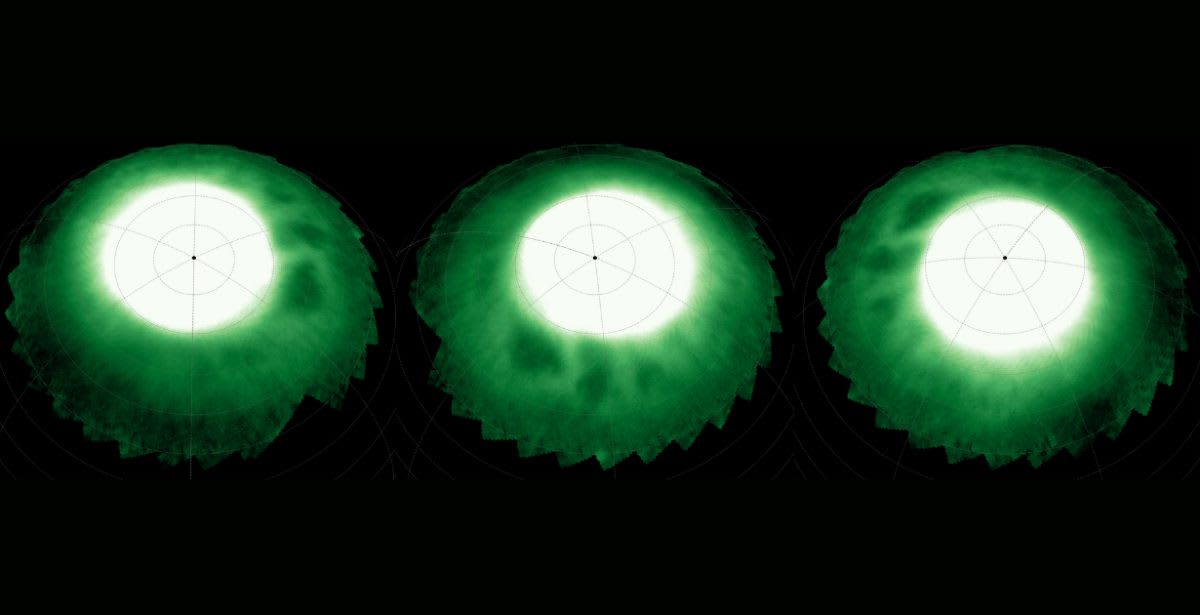
“We anticipated seeing emissions in broad bands at the various levels. Instead, we’ve seen fine-scaled patterns of beads and stars that, despite being separated by huge distances in altitude, may somehow be interconnected – and may also be linked to the famous hexagon deeper in Saturn’s clouds. These features were completely unexpected and, at present, are completely unexplained,” stated Professor Stallard. The ionosphere’s electrically charged plasma revealed a collection of dark, bead-like elements in bright auroral halos.
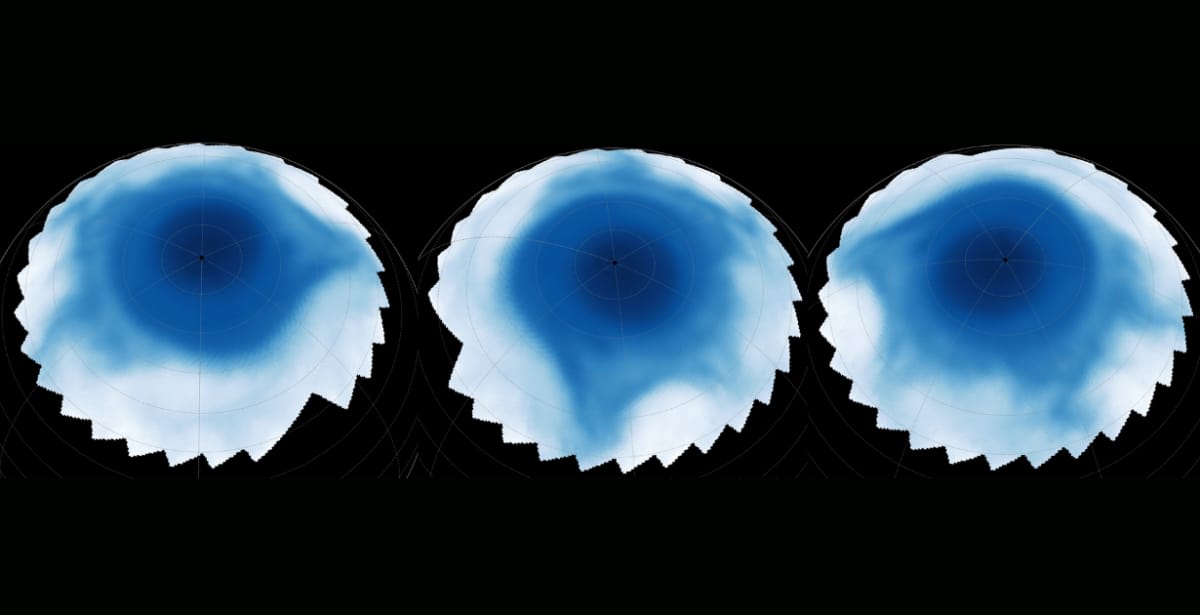
They found that these structures were stable and remained so for hours, but were slowly drifting over longer periods of time. This was at an altitude of 600 kilometres in the stratosphere, while at 500 kilometres lower, they found an asymmetric star-shaped feature. This structure expanded from Saturn's north pole towards the equator and had six arms. However, only four of them were visible, and the structures presented a lopsided pattern. Mapping the exact location of the anomalies revealed that they overlaid the same region of Saturn at different levels.
The arms of the star could be seen illuminating from locations directly above the points of the storm-cloud-level hexagon. This indicates that the processes that create the patterns might also cause a column to stretch through Saturn’s atmosphere. The dark beads may be the result of complex interactions between Saturn's magnetosphere and its rotating atmosphere. The star, on the other hand, is caused by previously unknown atmospheric processes in Saturn's stratosphere. Though these might be intricate revelations, more work is needed to confirm their implications.
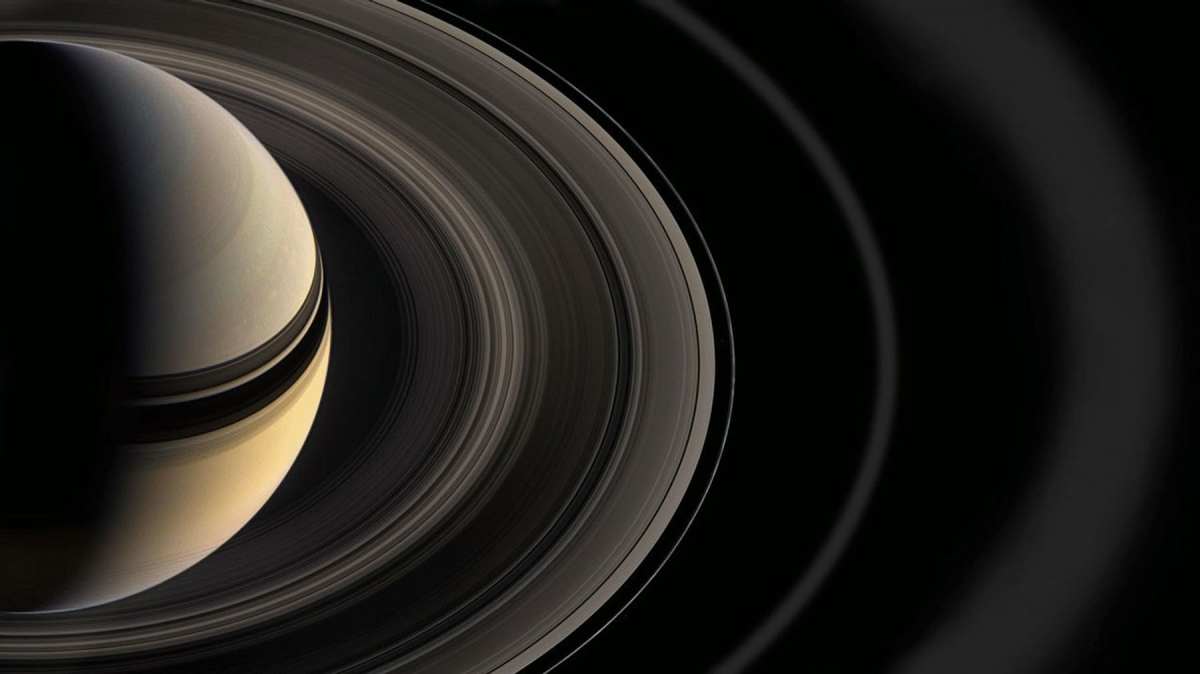

It has been quite a challenge for the astronomical community to study Saturn as its emissions are too weak to detect. However, JWST has made these studies easier with its sensitive instruments capable of spotting such anomalies. For us on Earth, identifying these new factors opened a window into the intricacies of our universe and helped us compare planetary processes. To learn whether one process on a planet could be observed on another means that we learn about a universal influence. This discovery adds to a long list of such anomalies that define planets.
More on Starlust
Saturn's icy moon harboring alien life? New discovery has scientists buzzing
James Webb Telescope directly images a Saturn-mass planet orbiting a distant young star
NASA observes peculiar red glowing formation floating on Saturn's biggest moon