A look at NASA-ISRO’s billion-dollar 'first-of-its-kind satellite' NISAR in numbers

In a significant stride for international space collaboration, a joint satellite venture between the United States and India has successfully launched, promising an unprecedented three-dimensional view of Earth's dynamic surfaces. The NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) satellite, a culmination of years of collaborative development by NASA and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), commenced its mission on Wednesday, July 30.
GSLV-F16/NISAR
— ISRO (@isro) July 30, 2025
Liftoff Rewind
Catch the liftoff visuals from GSLV-F16/NISAR launch. #NISAR #GSLVF16 #ISRO #NASA pic.twitter.com/umEyrBCF8T
The launch took place from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh, with the satellite beginning its journey aboard an ISRO Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) rocket at 8:10 a.m. EDT (5:40 p.m. IST). Approximately 20 minutes after liftoff, ISRO ground control successfully established communication with NISAR, confirming its nominal operation and setting the stage for its vital role in monitoring our planet.

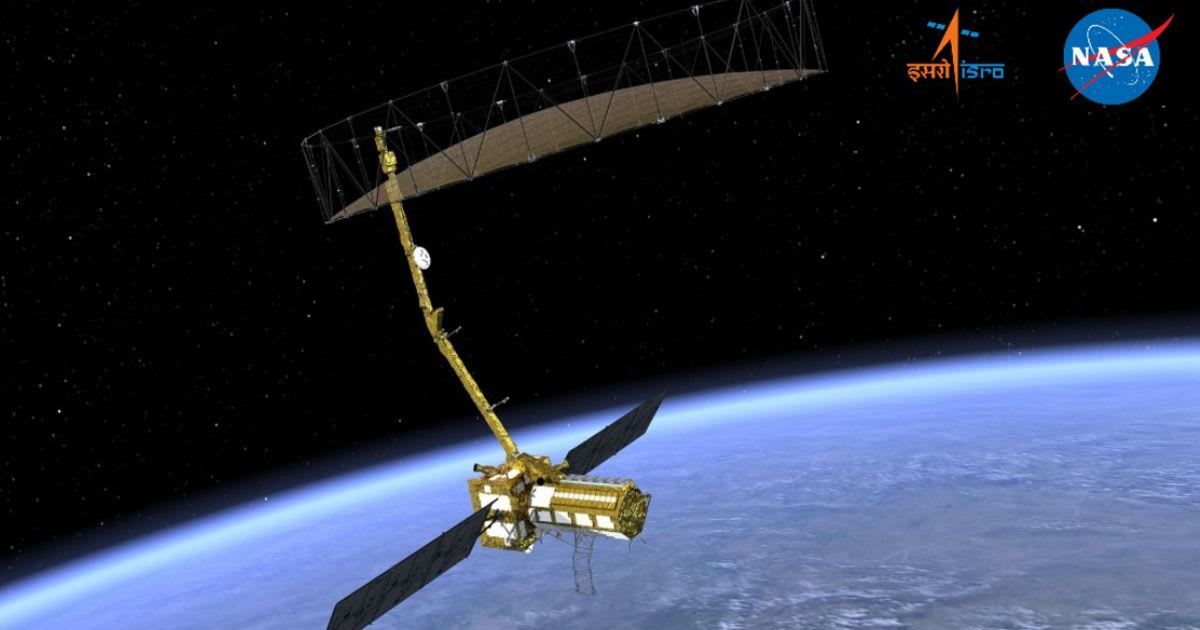
The NISAR observatory stands as a testament to cutting-edge aerospace engineering and scientific ambition, representing the maiden hardware partnership on an Earth-observing mission between NASA and ISRO, as per NASA. Beyond its unique inter-agency genesis, NISAR is distinguished as the inaugural satellite to integrate both L-band and S-band radar technologies onto a single platform. This striking fusion of radar capabilities promises an unparalleled synthetic aperture radar system, set to deliver high-resolution data crucial for exhaustive global surveillance of the planet's landmasses and ice surfaces, thereby establishing an intricate chronicle of environmental evolution.
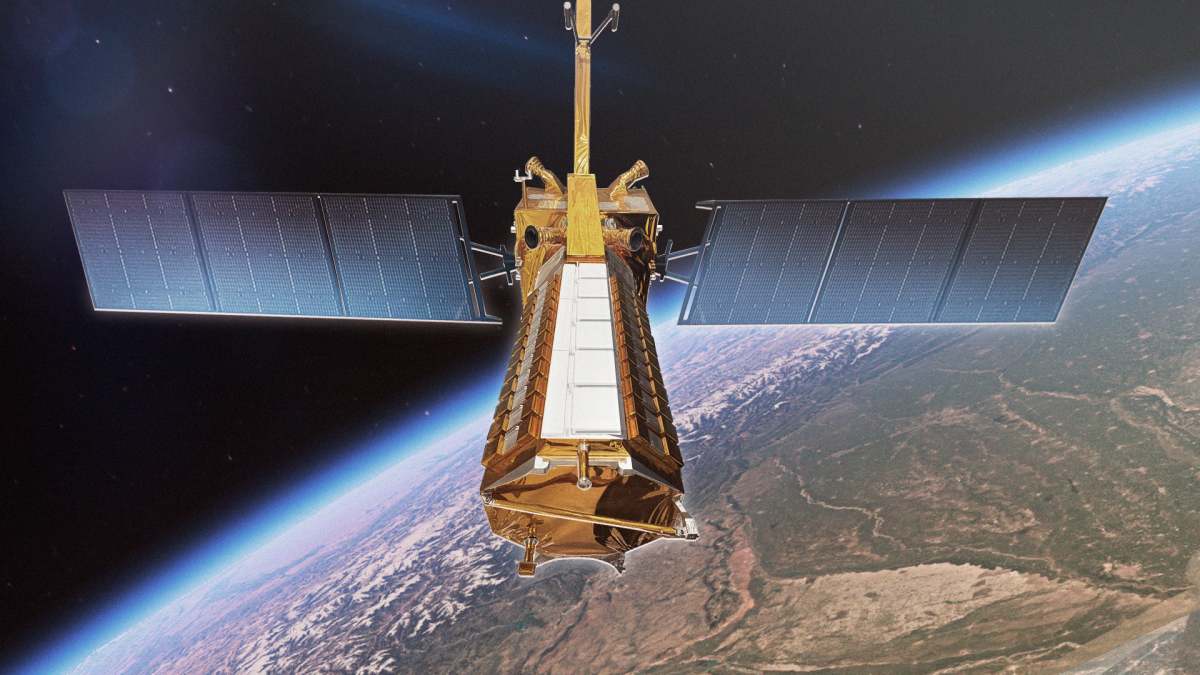

NISAR's design incorporates two main science instruments (L-band and S-band radar systems), an 18-foot (5.5-meter) spacecraft body and radar payload, and two 18-foot (5.5-meter) deployable solar arrays providing 5 kilowatts of power. A massive 39-foot (12-meter) radar antenna reflector, deployed from a 30-foot (9-meter) boom, is central to its observational capabilities. The satellite, weighing approximately 5,250 pounds (2,380 kilograms) at launch, is equipped with 15 thrusters.
Built across continents in phases, NISAR is a result of global teamwork and tech. NISAR came together through years of integration and testing.
— ISRO (@isro) July 25, 2025
2 Nations, 1 Mission.
NISAR’s build journey is a story of teamwork.
Milestone of Firsts
✅ First dual-band radar satellite
✅ First… pic.twitter.com/ykQwPjN7lP
After a rigorous 90-day commissioning phase to check systems and deploy instruments, NISAR will begin scientific operations. It's programmed to orbit Earth 14 times daily at an altitude of 464 miles (747 kilometers), scanning nearly all land and ice surfaces twice every 12 days. The satellite is expected to send 80 terrabytes of data daily, with the remarkable ability to detect vertical movements as small as 0.4 inches (1 centimeter) over areas about the size of half a tennis court. NISAR's prime mission is set for three years, promising a wealth of invaluable data for the global scientific community.
NISAR's main body houses the crucial dual radar payload: a 10-inch L-band and a 4-inch S-band system. These distinct radar wavelengths are specifically engineered to detect varying land and ice features, providing comprehensive data on attributes such as moisture content, surface roughness, and motion. ISRO's Space Application Centre in Ahmedabad was responsible for deploying the S-band radar, while NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Southern California led the development of the L-band radar. The satellite's instruments were meticulously integrated with a modified ISRO 13k bus and underwent rigorous testing before their transfer to the launch site in May 2025.
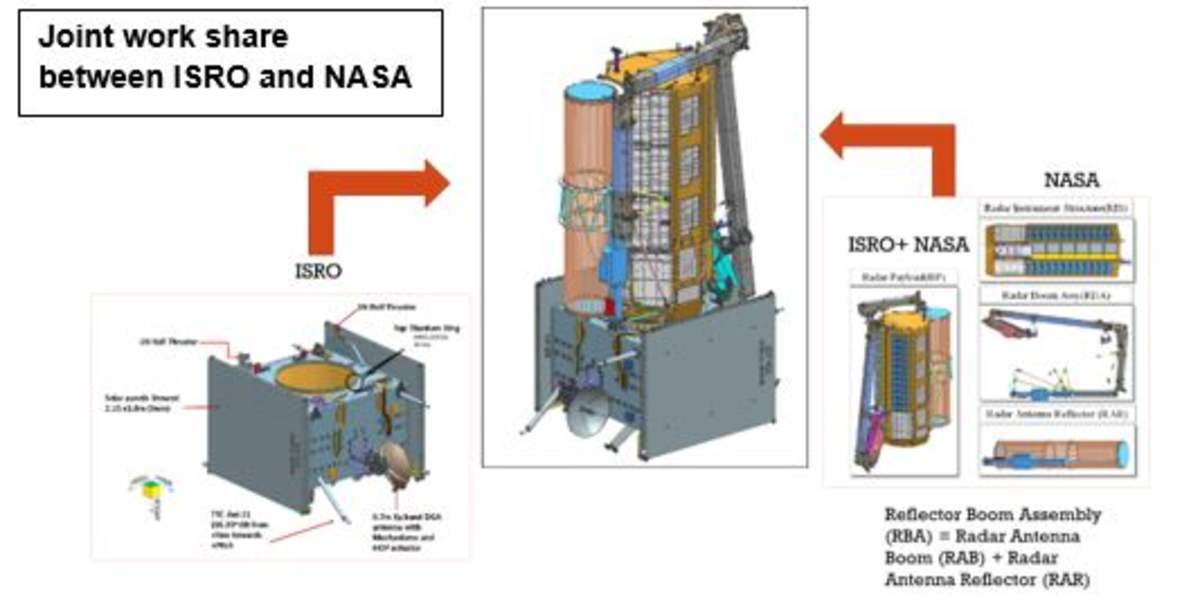
The mission itself is a powerful demonstration of international collaboration, with key responsibilities divided among prominent institutions. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL), managed by Caltech in Pasadena, led the United States' contribution. The invaluable L-band data collected by NISAR will be received and managed via NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, which oversees the Near Space Network.