October 2025 skywatching guide: Harvest Supermoon, Draconid meteor shower and more

October 2025 is poised to be an astronomical showcase, delivering a packed calendar of celestial events guaranteed to impress both casual and serious sky-watchers. Prepare your binoculars and telescopes; the autumn sky are ready for their close-up.

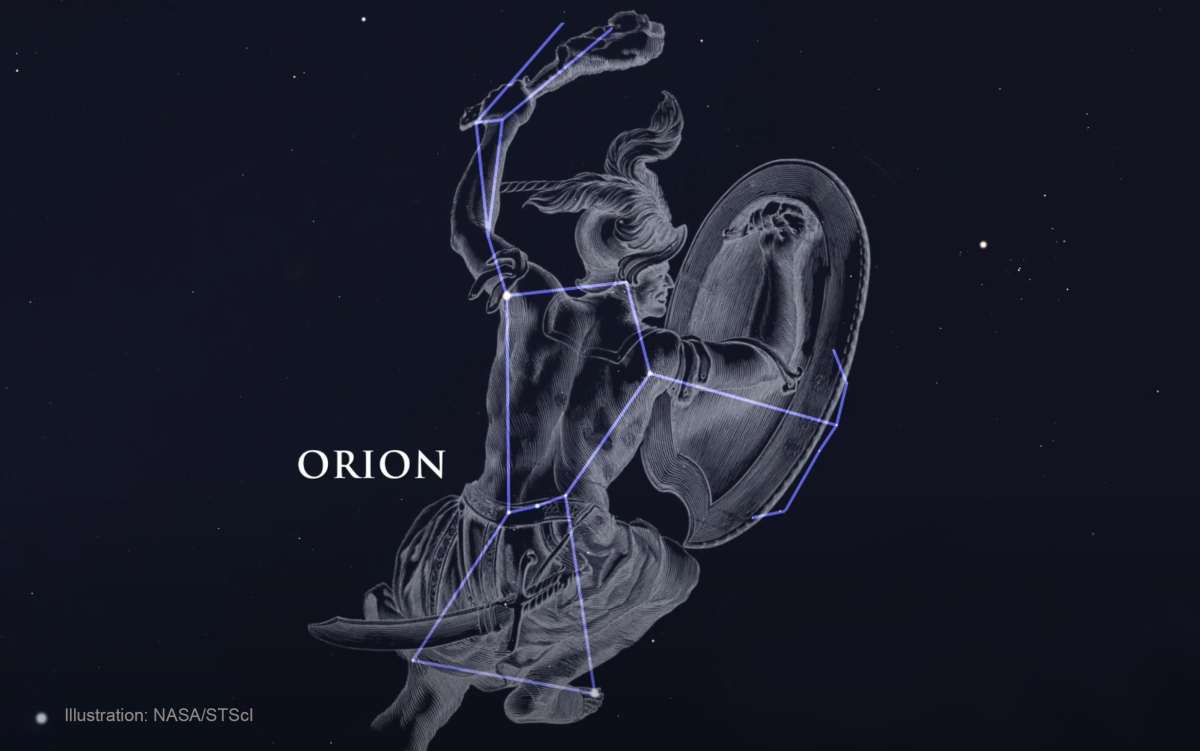
October 1: Orion the Hunter dominates pre-dawn skies
Look 50 degrees high in the south two hours before sunrise to find Orion the Hunter. Its bright stars, Rigel and Betelgeuse, frame the figure. Use optics to locate the Orion Nebula (M42), a luminous star-forming region below the three-star belt, which contains the young Trapezium Cluster. A scheduled close pass between the Moon and Pluto is not observable, per Astronomy.com.
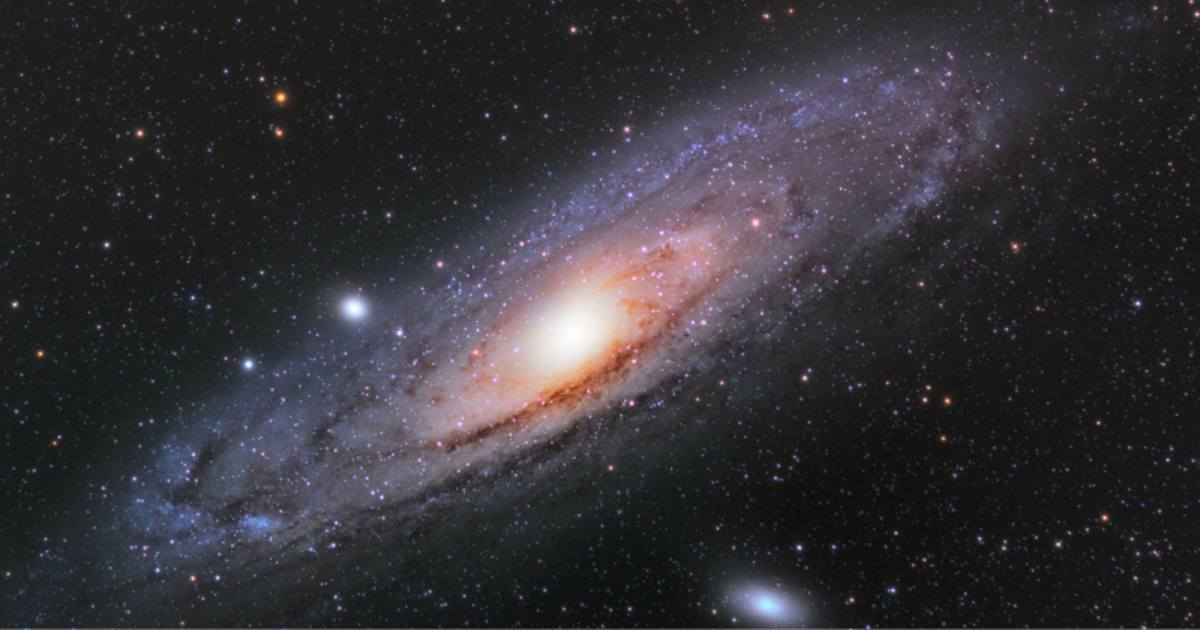
October 2: Andromeda and Ceres reach zenith
This night features two targets peaking around midnight: The Andromeda Galaxy (M31) reaches its highest point for optimal viewing, as mentioned on NAT GEO. Simultaneously, the dwarf planet Ceres, the main belt's largest object, hits opposition, shining at its peak brightness (magnitude 7.6), as per Astronomy.com. Separately, a conjunction between Mercury and Spica is unviewable due to the Sun's glare.

October 3: Tracking dwarf planet Ceres
Following opposition, locate Ceres in the constellation Cetus. Shining at magnitude 7.6, the dwarf planet is positioned roughly 8 degrees north of the star Diphda. Identify a nearby chain of 5th- and 6th-magnitude stars (the Phi Ceti group) to help pinpoint and track Ceres' movement across the sky this month, per Astronomy.com.

October 5: Saturn and the Moon in close conjunction
The nearly full Moon and the planet Saturn will appear in a close conjunction, separated by only about 3.33 degrees, according to NAT GEO. They will be highest in the sky around midnight. Note that Saturn is currently exhibiting retrograde motion, temporarily shifting westward until late November.

October 6: The Harvest Supermoon arrives
October's full Moon is both the Harvest Moon and a Supermoon. This rare combination means the Moon is at its closest point to Earth (perigee), making it appear up to 14 percent larger and 30 percent brighter than average, as per NAT GEO. Expect brilliant moonlight for several nights.

October 8: Draconid meteor shower peak
The annual Draconid meteor shower peaks on October 8 as Earth passes through Comet 21P/Giacobini-Zinner's debris trail from October 6 to 10, according to NAT GEO. Unfortunately, the proximity to the full Moon means its intense glare will severely limit visibility, obscuring all but the brightest meteors.
October 10: The Moon meets the seven sisters (M45)
The waning gibbous Moon will pass within one degree of the Pleiades star cluster (M45). The Moon's glare (85% illumination) will obscure fainter members, but the brightest stars in this large cluster of over a thousand stars will still be visible, as per NAT GEO.

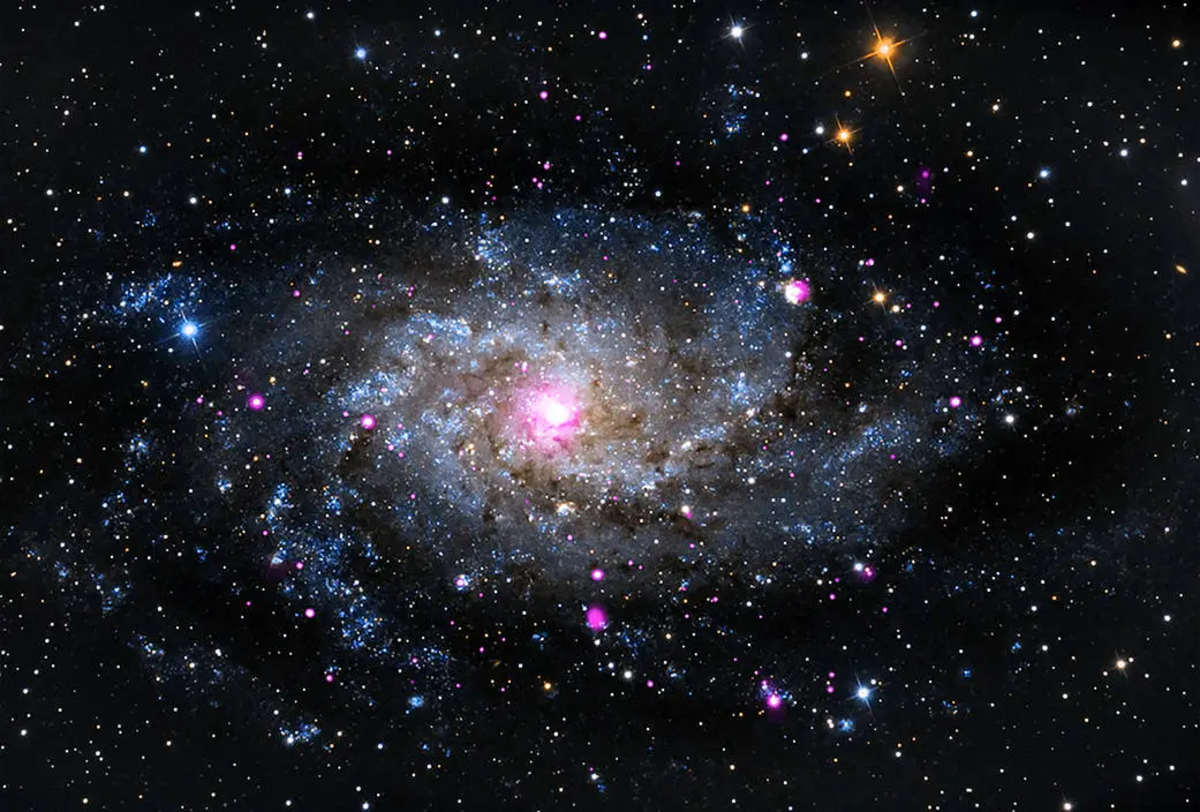
October 15: Triangulum Galaxy at peak altitude
The Triangulum Galaxy (M33), the third-largest spiral in our local group, rises to its highest point. While possibly visible to the naked eye under exceptionally dark conditions, a telescope or binoculars are highly recommended to discern its distinctive spiral structure, per NAT GEO.

October 19: Close approach of Venus and the Moon
Look toward the eastern horizon in the pre-dawn sky to see the Moon and the brilliant planet Venus paired closely together, separated by less than 4 degrees. Venus, appearing as the "morning star," is the third-brightest object in the sky, per NAT GEO.
October 21: Orionid meteor shower peaks under optimal darkness
The Orionid meteor shower peaks on October 21, coinciding perfectly with the New Moon. This guarantees optimal dark-sky conditions to view the quick, bright meteors originating from the debris of Halley's Comet, according to NAT GEO. The moonless sky is also ideal for observing other dim, deep-sky objects.
More on Starlust
Ceres, the only dwarf planet in the inner solar system, reaches opposition on October 2—how to watch
Here's how to spot Comet SWAN (C/2025 R2) in the night sky from now until October 20









