Moon phases October 2025: Is there a full moon tonight?

For stargazers, tonight's sky viewing will be significantly enhanced by a rare astronomical phenomenon: the moon's arrival as a Supermoon, according to NASA. This exceptional alignment occurs because the moon is currently at perigee, its closest orbital point to Earth for the month. As a result, the lunar body will appear dramatically larger and brighter in the sky this evening, up to 14% larger and 30% brighter than an average full moon, making tonight a full moon night.

Full Moon tonight also carries the seasonal designation of the Harvest Moon, named for the full moon nearest the autumnal equinox. The moon will officially reach its maximum point of 100% illumination, the moment it sits precisely opposite the Sun, by midnight. The exact moment of fullness is set for October 7 at 3:48 a.m. UTC. For observers in North America, this translates to the late evening hours of Monday — 11:48 p.m. EDT or 8:48 p.m. PDT on October 6.
The Full Moon tonight will dominate the night sky, rising in the east exactly at sunset and remaining visible until it sets in the west at sunrise the following morning. This event marks the culmination of the cycle, with the Moon being precisely 14.9 days old since the previous New Moon, according to Moon Giant. The time elapsed between one Full Moon and the next, known as a Synodic month, is measured with extreme precision at 29.530587981 days.

The natural satellite of Earth that has completed 13.76 days since the last New Moon, is currently visibly bulging, a shape historically denoted by the term "Gibbous." The full disk will be easily observable across much of the night.

During the October Supermoon, observers can pinpoint numerous significant geographical features on the lunar surface across both hemispheres, as per NASA Moon. Even the unaided eye can distinguish several prominent landmarks, Mare Imbrium and Mare Tranquillitatis, alongside Tycho Crater. These features are readily visible from both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. For those using binoculars, the level of detail increases significantly, particularly allowing for closer views of the Mare Frigoris, the striking views of the Apennine Mountains, and the Grimaldi Basin. These regions are accessible to binocular users across the globe.
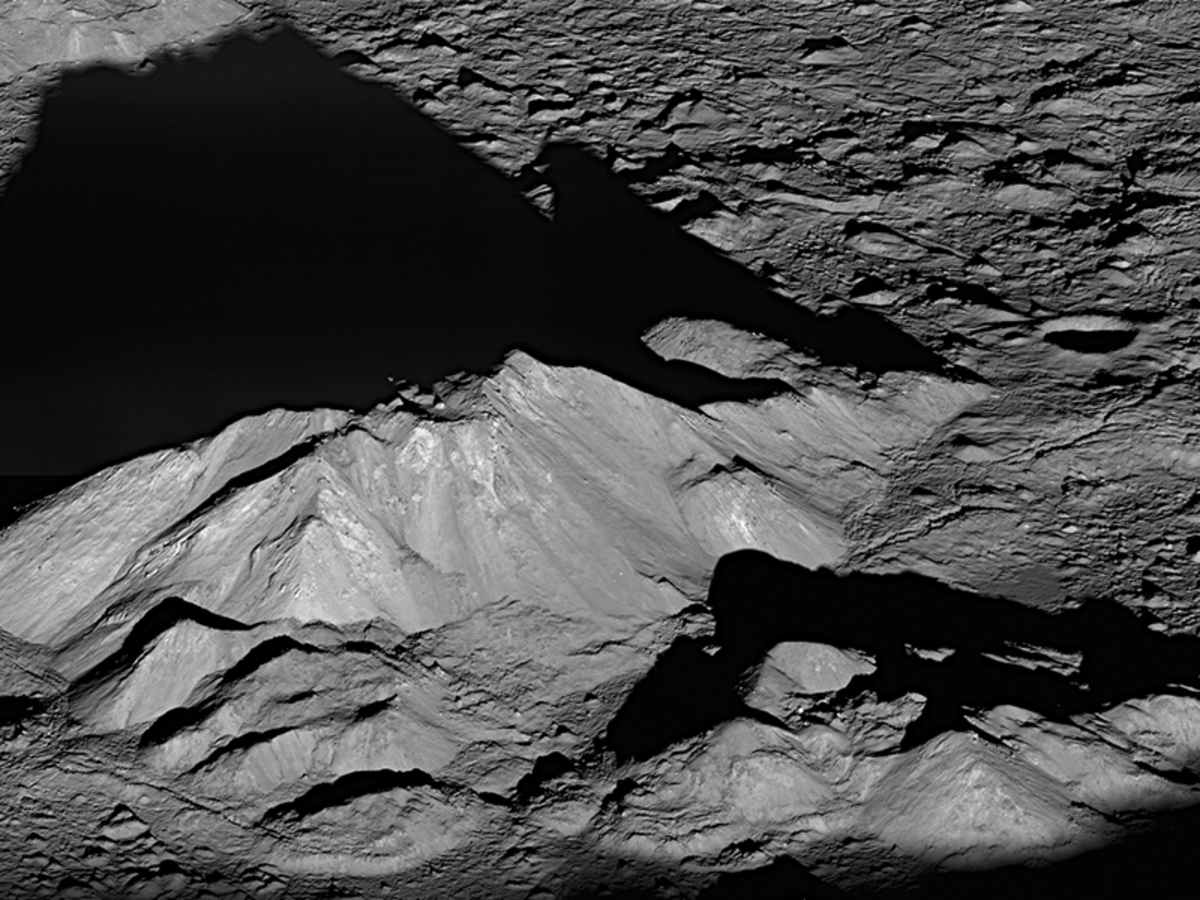

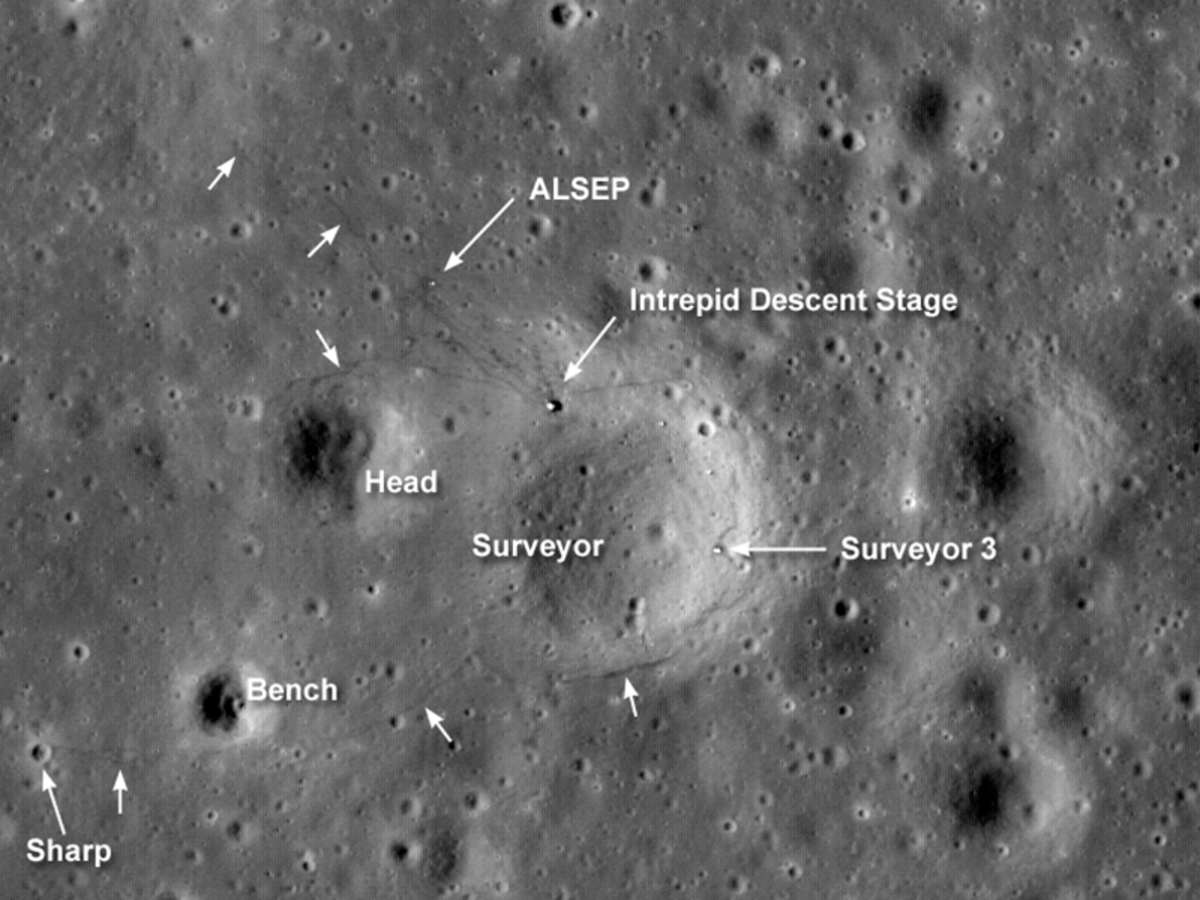
Finally, individuals with a telescope can examine even more subtle terrain. Recommended targets for tonight include the impressive Rupes Altai (the Altai Scarp), the historic landing site of Apollo 12, and the Schiller Crater. These high-magnification targets are observable from both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres.
More on Starlust
2025 Harvest Moon will make a rare October appearance—when and where to watch the spectacle
Earth's 'wind' is causing the Moon to rust—but how is this possible?









