Moon dust brought back 50 years ago is now revealing how the Sun changes the lunar surface

New analysis of lunar soil samples returned to Earth more than 50 years ago is providing critical insights into the relationship between space environment and the Moon's surface, according to Southwest Research Institute. Scientists from the Southwest Research Institute, in collaboration with those from UT San Antonio, are working together to understand how the continuous bombardment from solar winds and micrometeoroids over ages, the process known as space weathering, changes lunar dirt.
The principal investigator of the project, Dr. Ujjwal Raut of SwRI, examined just a few grains from soil collected during the Apollo 11, 16, and 17 missions. With the help of new, advanced instruments, they were able to derive fresh knowledge from these historic samples. “These Apollo-era samples continue to be a cornerstone of lunar science, providing the most direct link to the Moon’s surface processes and evolution, including space weathering,” Dr. Raut said.
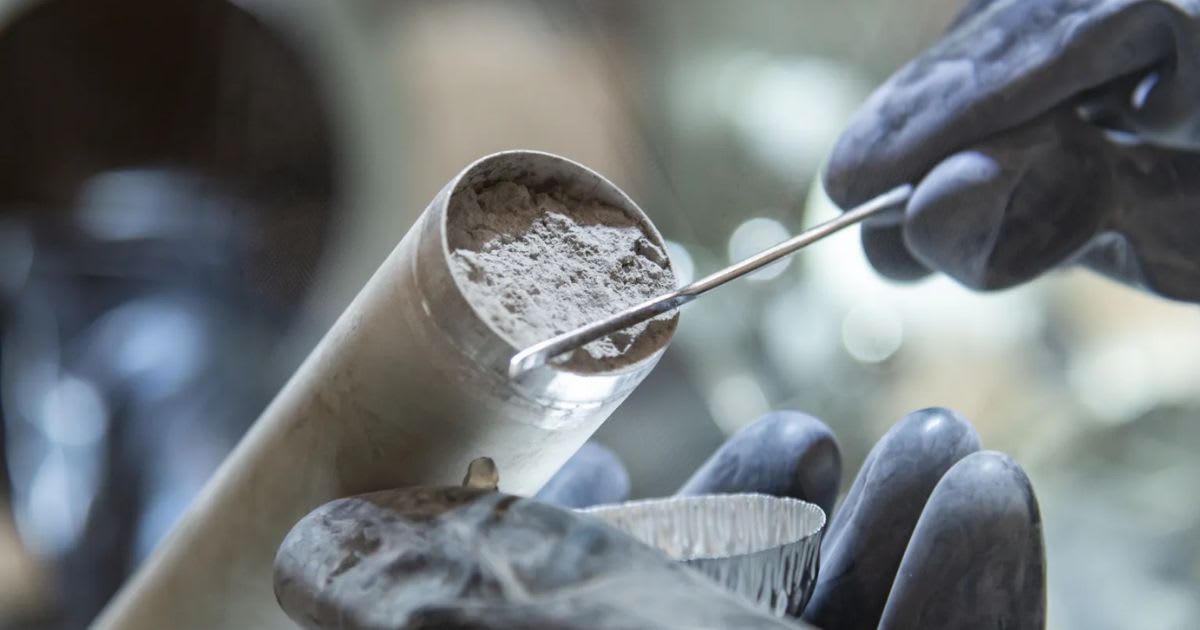

Caleb Gimar, who completed his doctoral degree in physics through the SwRI-UT San Antonio Joint Graduate Program, led the research. He explained that space weathering results in physical and chemical changes in lunar grains, which, in turn, influence their far-ultraviolet (FUV) reflectance. He added that this is the reason why "soils with different degrees of weathering vary in brightness and the way they scatter light in this spectral region."

The key finding involved extremely fine iron particles, called nanophase iron. Dr. Ana Stevanovic, head of UT San Antonio’s Kleberg Advanced Microscopy Center, said the group employed "a state-of-the-art transmission electron microscope — one that can actually image individual atoms." Those high-resolution images revealed that heavily weathered lunar grains are covered in thousands of specks of nanophase iron, each about one ten-thousandth the width of a human hair. Grains that had not been weathered as heavily contained much less of this iron and thus appeared far brighter in the FUV spectrum.
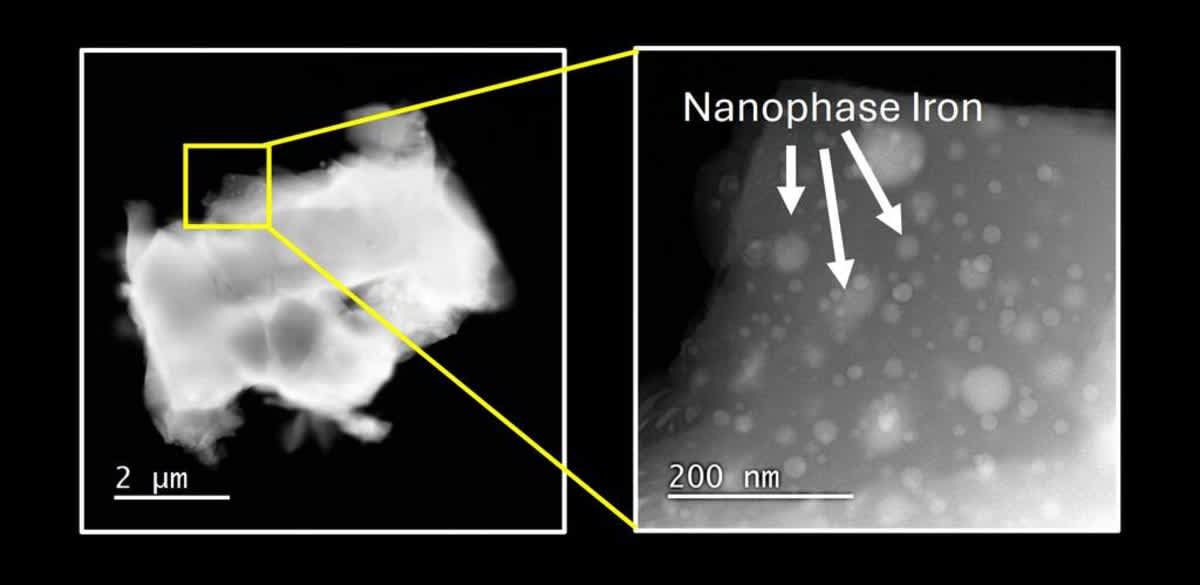
Understanding the FUV brightness difference aids in interpreting data taken from NASA's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Lyman-Alpha Mapping Project (LRO-LAMP). It has been orbiting the Moon since 2009. Using the FUV from stars, it has been looking for water ice that might be hidden in permanently shadowed craters on the lunar poles.
“Accurately identifying that ice and estimating its abundance depends on understanding the far-ultraviolet reflectance of the dry lunar soil — while accounting for any mineralogical differences caused by space weathering — to robustly isolate hydration signatures from the soil itself,” said Dr. Kurt D. Retherford, the principal investigator of the LAMP instrument. The full study detailing this nanoscale analysis was published in the Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets.
𝐋𝐮𝐧𝐚𝐫 𝐬𝐨𝐢𝐥 𝐚𝐧𝐚𝐥𝐲𝐬𝐞𝐬 𝐫𝐞𝐯𝐞𝐚𝐥 𝐡𝐨𝐰 𝐬𝐩𝐚𝐜𝐞 𝐰𝐞𝐚𝐭𝐡𝐞𝐫𝐢𝐧𝐠 𝐬𝐡𝐚𝐩𝐞𝐬 𝐭𝐡𝐞 𝐌𝐨𝐨𝐧’𝐬 𝐮𝐥𝐭𝐫𝐚𝐯𝐢𝐨𝐥𝐞𝐭 𝐫𝐞𝐟𝐥𝐞𝐜𝐭𝐚𝐧𝐜𝐞 https://t.co/mfwe73QriO pic.twitter.com/70vcK9cjJ7
— Southwest Research Institute (@SwRI) December 10, 2025
In a related development, recent research has indicated that lunar soil may be more than just barren rock; it may be a vital resource capable of sustaining future human outposts. Scientists are now proposing a new, efficient way of extracting water directly from the lunar soil, while concurrently converting carbon dioxide (CO2). This is a major step toward self-sufficiency in space. In fact, one of the main challenges for extended missions on the Moon has been the high cost and logistical nightmare associated with transporting water from Earth.
More on Starlust
Half-century-old Apollo 17 moon sample uncovers new clues to the origin of a lunar landslide
China is sharing precious moon samples globally — but one 2011 law prevents NASA from accessing them