James Webb Telescope directly images a Saturn-mass planet orbiting a distant young star

Astronomers utilizing the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) have uncovered compelling evidence of what could be the lightest exoplanet ever directly imaged. This potential discovery — a planet with a mass similar to Saturn — is orbiting the young star TWA 7, located approximately 111 light-years away, as mentioned by the ESA.
A never-before-seen planet! 🪐
— NASA Webb Telescope (@NASAWebb) June 25, 2025
This is Webb’s first discovery of a planet using direct imaging. With a mass similar to Saturn, it’s also the lightest exoplanet yet seen using this technique! https://t.co/ptWcXlFfmW pic.twitter.com/XTGwIqgH8n
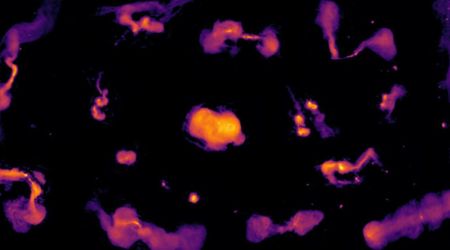
Should this finding be confirmed, it would mark a significant milestone for the Webb Telescope, representing its inaugural direct imaging discovery of a planet. The international research team, spearheaded by Dr. Anne-Marie Lagrange of the Observatoire de Paris-PSL and Université Grenoble Alpes, identified a faint infrared signal in the debris disc surrounding TWA 7.

This detection was made possible through Webb's Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI) and its coronagraph, employed on June 21, 2024. This specialized equipment allowed scientists to effectively block out the intense glare of the host stars, revealing the much fainter object. This high-contrast imaging technique is crucial for discerning exoplanets that would otherwise be obscured by their star's luminosity. Following advanced image processing to remove residual starlight, the infrared source became clearly distinguishable from background celestial bodies.
The star, TWA 7 is a young red dwarf, cooler and less massive than our own Sun, making planets easier to spot than if they were orbiting a much brighter star. MIRI’s coronagraph was used to suppress the glare of the star, revealing faint nearby objects - like this planet.
— NASA Webb Telescope (@NASAWebb) June 25, 2025
The suspected planet, tentatively named TWA 7b, is situated at roughly 50 times the Earth-Sun distance from its star. Its position aligns precisely with a prominent gap within one of three dust rings previously observed around TWA 7, as discovered by ground-based telescopes. Scientists suggest that the planets' gravitational influence is responsible for sculpting this gap in the debris disc. “Our observations reveal a strong candidate for a planet shaping the structure of the TWA 7 debris disc, and its position is exactly where we expected to find a planet of this mass,” stated Dr. Anne-Marie Lagrange.

Initial analyses indicate that TWA 7b is likely a young, cold planet with an estimated mass of about 0.3 times that of Jupiter (equivalent to approximately 100 Earth masses) and a temperature around 47 degrees Celsius. Its luminosity, color, and location within the ring system are all consistent with theoretical models for a young, cold planet with a Saturn-like mass actively interacting with its circumstellar environment.

Debris discs, composed of dust and rocky material, are common around young stars and often exhibit gaps or rings, which are theorized to be sculpted by orbiting planets. While these features strongly suggest the presence of planets, directly detecting the planet responsible has remained a challenge until now. This potential discovery could also offer the first observational hint of a "Trojan disc" — a collection of dust gravitationally trapped within a planet's orbit. TWA 7, also known as CE Antilae, is an M-type star approximately 6.4 million years old, with a nearly face-on disc, making it an ideal target for Webb's sensitive mid-infrared observations.

This preliminary result underscores Webb's unparalleled capability to explore previously undetected, low-mass planets around nearby stars. Continued observations are planned to refine the candidate's properties further, officially confirm its planetary status, and deepen our understanding of planet formation and disc evolution in nascent star systems.
The vast and diverse population of exoplanets continues to expand with such advancements in technology. While the majority of discovered exoplanets lie within the relatively confined region of our Milky Way galaxy, the sheer abundance of these celestial bodies is clear, with planets outnumbing stars. Even the nearest known exoplanet, Proxima Centauri b, is still located a considerable four light-years away, according to NASA.