Organic compounds found on Enceladus suggest Saturn's moon may support alien life
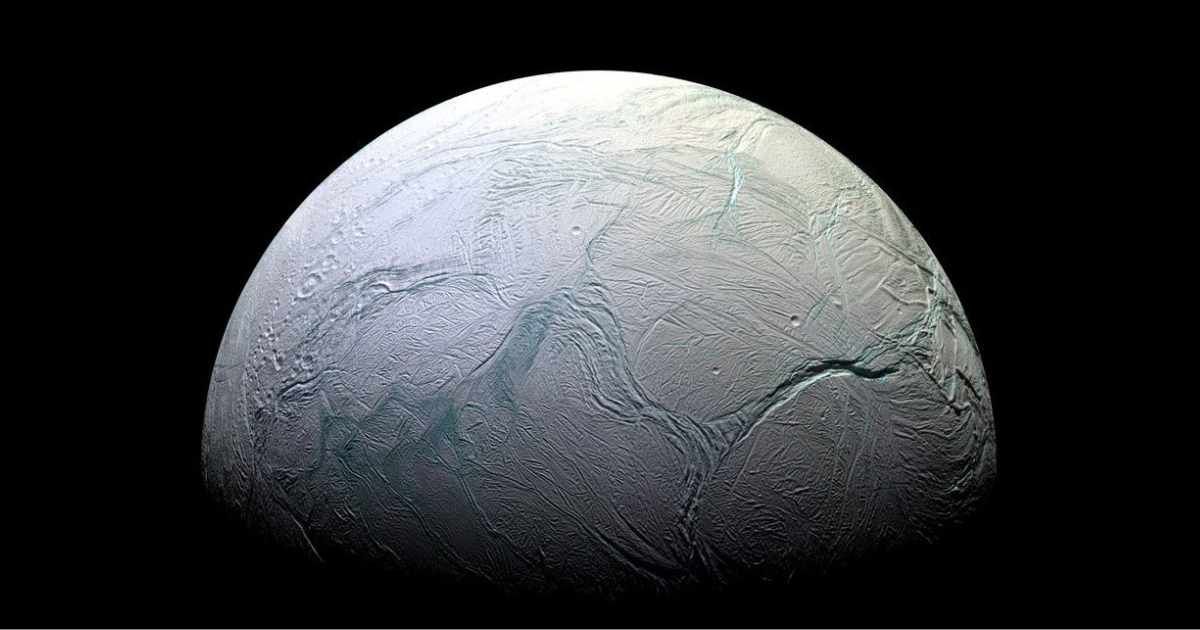

The tantalizing prospect of Enceladus harboring extraterrestrial life has received a significant boost following the identification of new organic compounds in material ejected from the icy Saturnian moon. The findings, detailed this month in the journal Nature Astronomy, stem from a re-analysis of data collected by the defunct Cassini probe, confirming a more chemically rich environment than previously understood within the satellite's subsurface ocean.

This evidence significantly advances the hypothesis that Enceladus contains all the fundamental ingredients necessary for biological life, as per WIRED. The key breakthrough stems from a fresh examination of data from a 2008 high-speed flyby. During that pass, the Cassini spacecraft was able to directly sample fresh ice fragments forcefully ejected into space by the moon's cryovolcanoes, giant geysers at its south pole.
Lead author Nozair Khawaja, a planetary scientist at Freie Universität Berlin, and his team confirmed the presence of known molecules while detecting several organic compounds that had never before been recorded on the moon. These compounds are believed to be potential precursors to more complex, biologically relevant molecules. "It is important to note, however, that these molecules can be formed abiotically as well,” Khawaja stated.

Enceladus, the sixth-largest of Saturn's moons, is notable for its constant geological activity. Plumes of water vapor and ice from its geysers can extend for thousands of kilometers, with much of this material supplying the planet's outermost E ring. Scientists believe this ejected material originates from a warm, saline ocean sealed beneath the icy crust, likely in contact with a rocky core where hydrothermal reactions under high pressure and heat are thought to occur. Crucially, the new organics were found in the freshly ejected material, suggesting they were generated within the hidden ocean or at the ocean-core interface, rather than being contaminants acquired during exposure to the harsh conditions of space.

Combined with prior research, scientists have now definitively confirmed the presence of five of the six essential elements for life, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur, in Enceladus’s output. This evidence confirms that the moon possesses the three essential conditions for life to form: liquid water, an energy source, and fundamental elements and organics. Khawaja asserted that this makes Enceladus the "prime target to explore habitability and search whether there is life, or not."
Despite its outwardly frigid, ice-covered appearance, Enceladus has been elevated to the forefront of the search for extraterrestrial life in the solar system. This shift began with a breakthrough discovery: a vast subterranean ocean of liquid water concealed beneath its frozen shell. For decades, scientists had largely dismissed the outer regions of the solar system as too cold and dark to support biological activity. That view was decisively challenged in 2005 when instruments aboard the Cassini spacecraft first detected enormous geysers erupting from deep fissures at Enceladus' south pole. This provided the initial, irrefutable evidence of the subsurface ocean, a finding hailed as a revolution in astrobiology.
More on Starlust
NASA observes peculiar red glowing formation floating on Saturn's biggest moon