G1 Globular Cluster

Summer is the best time for astronomy. This is the season of clear nights with warm weather, and most of all, star parties. Hundreds of amateur astronomers gather under pristine skies to enjoy deep sky showpieces like the Lagoon Nebula or the bright globular star cluster M13. These are beautiful objects, which never fail to elicit a gasp when people see them for the first time. However, veteran observers might want to try something different…
How about a globular cluster located some 2.9 million light-years away, in the Andromeda Galaxy? Grab that telescope and prepare for some serious deep sky observing!
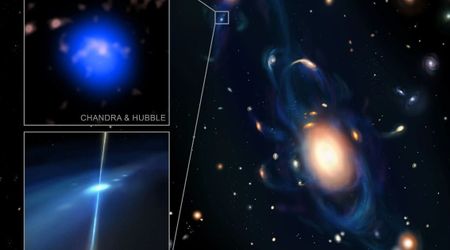
M31, the Andromeda Galaxy, contains numerous globular clusters, each closely packed together with up to a million stars. The brightest of these clusters is G1 (also known as Mayall II), and despite its visual magnitude of 13.7, it is the most luminous globular cluster in the entire Local Group of galaxies. G1 is located 170,000 light years from M31’s nucleus, and it has twice the mass of Omega Centauri. It’s estimated that the cluster consists of at least 300,000 old stars.
To locate G1, first center your telescope on the M32 galaxy, and from here move to the 5th-magnitude star 32 Andromedae. Star-hop another one and a half degrees to SAO 53986, the star marked on the coarse finder map. Once you have this star centered in the field, switch to the fine finder map and make your way to the cluster.
A 10-inch or slightly larger telescope should be enough to add G1 as a trophy in your observing log. At high magnification, the cluster appears as a tiny but obviously non-stellar patch, moderately brighter in the middle. A longer look will reveal two foreground stars on its southwestern edge.
Once you hone in on the correct location using the two charts below, switch to your highest power and sweep the field carefully. Remember that you are looking for a fuzzy patch only a few arcseconds wide, so give your eye plenty of time to dark-adapt and use averted vision.