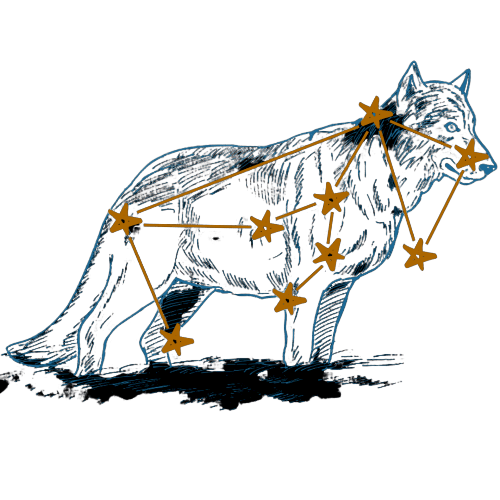

Lupus - The Wolf Constellation
The constellation of Lupus is a part of the southern hemisphere night sky in which a group of nearby stars together form the imaginary figure of a mythical wolf. The division of the sky by constellations has a historical basis, but the modern constellations are exactly separated from each other by a distinct boundary.
For centuries, constellations have been a means for humanity to understand and interpret the patterns of the night sky in order to navigate. And lupus, although it is made up of faint stars, is one of them.
Facts About The Lupus Constellation
Last updated: 22nd July 2020
- Lupus is ranked 46th among all existing constellations in terms of size.
- The Lupus constellation was part of the 48 constellations labelled in the astronomical manual “Almagest”, published in 150 AD.
- It was first thought that Lupus was part of a neighbouring constellation, a sacrifice made by the mythical centaur.
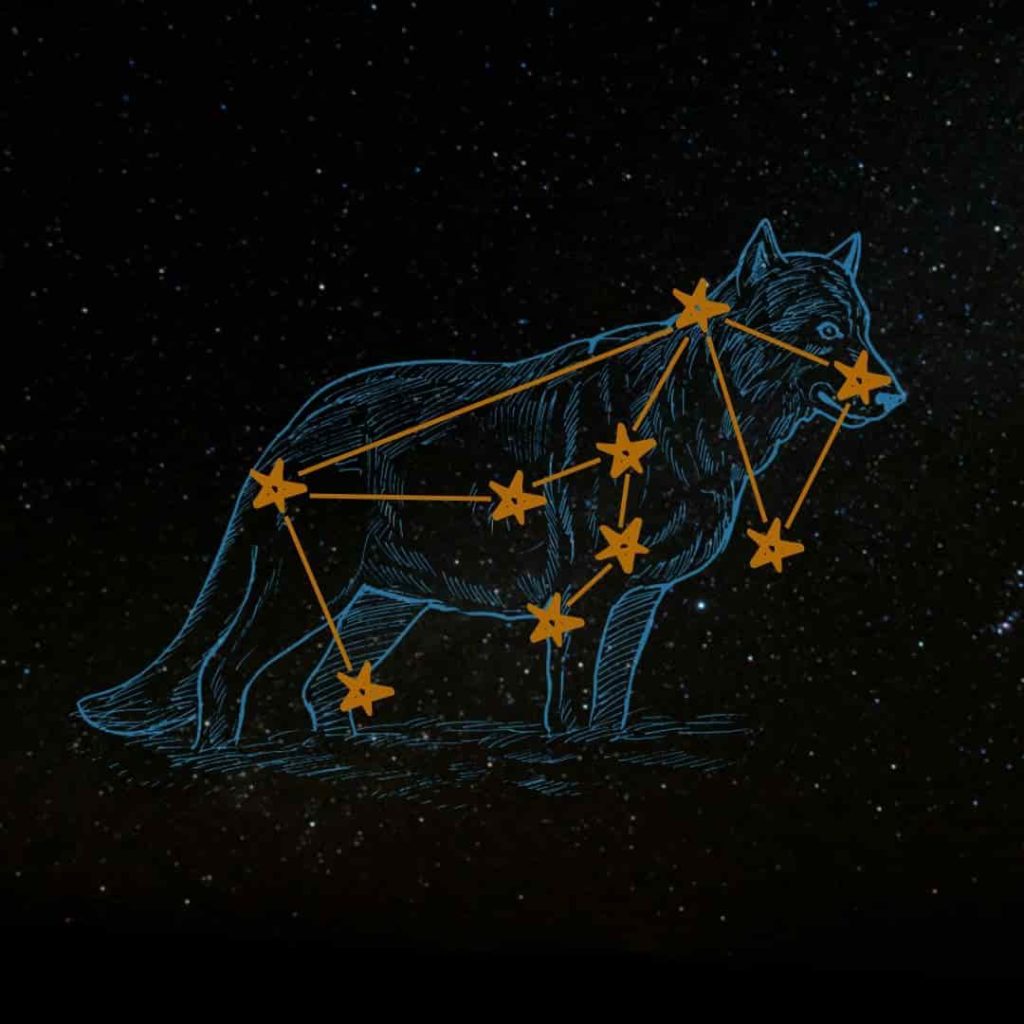
- The outline of the constellation is composed of 9 stars and contains 4 minor objects from the deep sky.
- It is a southern hemisphere constellation, which means it is not visible if you live in the north.
- A massive supernova occurred in the constellation of Lupus in 1006. The light from this cosmic explosion was visible in the night sky for many weeks.
- The best time to see this constellation is June.
- Lupus is a member of the Hercules family of constellations.
- The constellation of the wolf is one of 42 animal-shaped constellations
The Wolf Constellation
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) has compiled a list of 88 contemporary constellations, whose limits are well known so that each point in the sky belongs to only one constellation. Many constellations originate from ancient Greece and Mesopotamia and their names are mainly based on Greek mythology. One of those constellations is Lupus.

Discovery of the wolf constellation
In ancient times, the Lupus constellation was considered to be located within the asterism of the constellation Centaurus. It was originally thought that the star pattern represented a wolf about to be pierced by the Centaur. The first person who separated this constellation from the Centaur was Hipparchus of Bithynia and named it”Therion” in the 2nd century BC. It is not known when and exactly who invented the first names of the constellations, but a set of 48 constellations was already officially recognized in 150 AD. These constellations were listed in the Almagest, written by Ptolemy. One of the 48 constellations in Almagest was the constellation of the wolf.
Characteristics & Location
The International Astronomical Union has adopted a three-letter abbreviation for the constellation, Lup. Lupus ranks 46th among the 88 constellations in size and covers an area of 333.7 square degrees, equivalent to 0.81% of the night sky. The official constellation boundaries of Lupus are defined by a twelve-sided polygon. The lupus is a type of constellation that has the shape of an animal.
The wolf constellation is part of the Hercules constellation family and is located in the third quadrant of the southern hemisphere (SQ3). It is surrounded by the following constellations: Centaur, Hydra, Norma, Circinus, Scorpio and Libra.
For those who know how to use celestial coordinates: the limits of the Lupus constellation are between 14h 17m 48.0635s and 16h 08m 36.6735s, while its declination limits are between -29.83◦ and -55.58◦. It is best to observe it in June but, as it is a southern hemisphere constellation, it cannot be seen easily or at all from the northern hemisphere.
Meaning & Symbolism
Like most other constellations, the wolf constellation takes its name from a Latin word: Lupus (Pronunciation: Loo-puss), which means wolf. This is the modern name for this constellation because it looks like a wolf, but centuries ago astronomers didn’t know exactly what kind of animal this constellation was. That’s why the ancient Greeks gave it the name “Therion”, while the Romans called it Bestia, both names meaning “beast”. Both cultures first thought that Centaur, a nearby constellation, offered this animal as a sacrifice to Ara, the altar.
The ancient Hebrews and Arabs also recognized this constellation and gave it the names “Asedah” and “Asedaton”, which means “to be killed”. In the ancient carved Zodiac of Denderah, the constellation of Lupus is depicted as a small child with its finger on its lips and is called Sura.
Myths and stories about the Lupus Constellation
Astronomers did not relate this constellation to a specific animal until the Renaissance when translating Ptolemy’s Almagest from Latin, scientists finally identified it as a wolf. As we already know, the ancient Greeks and Romans knew this constellation and called it “the beast”, but it could have been any beast.
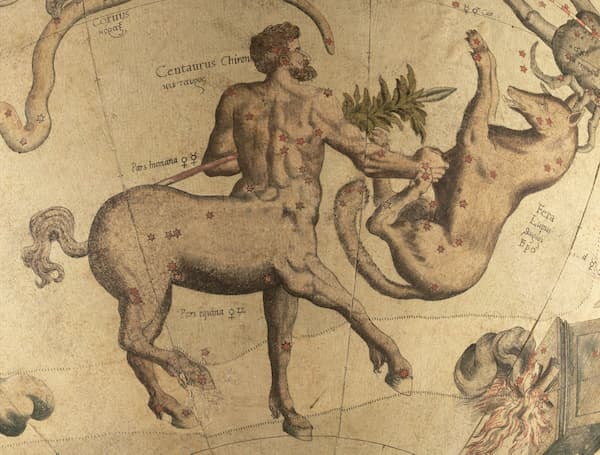

Greek Lore
Some mythologists believe that the constellation of Lupus could have a link with the story of Lycaon, the ancient king of Arcadia. This hypothesis is mainly based on a version of the story where the king is transformed into a wolf by Zeus himself.
Babylonian Lore
There is a theory that, in ancient Greek, this constellation is named after the Babylonian figure of the mad dog (Uridimmu). The mad dog was a hybrid creature with a human head and torso, while its paws and tail came from a lion. In addition, this mythical creature was often associated with the sun god and the buffalo man.
Chinese Lore
In chinse lore, the lupus constellation is not a wolf. Its stars are part of a larger constellation called “Qiguan”. Quigan represented the emperor’s army because of the fairly large number of stars that make up the shape of this ancient constellation. In modern astronomy, lupus is part of the eastern quadrant of the sky and is symbolized by the eastern azure dragon.
The main stars that outline the Lupus Constellation
Lupus contains about 1281 stars, 74 of which can be observed with the naked eye on a very clear night sky. However, 9 main stars make up the outline of the constellation of the wolf. These stars are quite faint but can be easily spotted if you know where to look using a stargazing application and an astronomy laser pointer. There are 3 main stars: they are all blue-white giants with a magnitude greater than 3.
Alpha Lupi
With a magnitude of 2.3, the brightest star in the wolf constellation is αLup (also called Men). This giant blue-white star is thought to be about 460 light-years away. It is about 10 times larger than our sun and 25,000 times brighter. In the outline of the constellation, you can find Alpha Lupi at the bottom, which is the shape of the wolf’s paw.
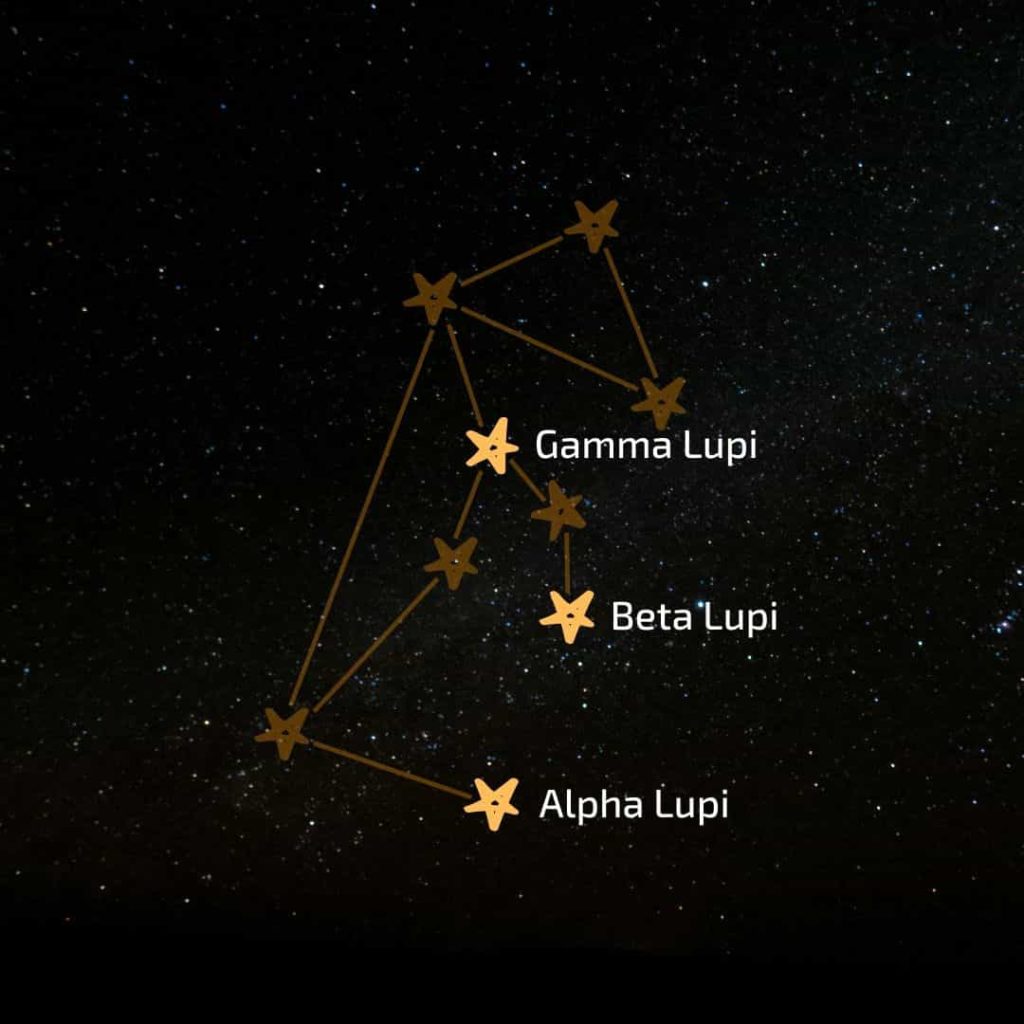
Beta Lupi
βLupi (Beta Lupi or Kekouan) is a little dimmer (magnitude 2.6) but is still observable with the naked eye on a clear night. It is also a blue-white giant and is located 383 light-years away from a supernova remnant. Beta Lupi is also much larger than our sun (8.8 times larger) and is at the end of the star configuration that resembles the forepaw of the wolf.
Gamma Lupi
The third brightest star in the wolf constellation is γLupi. Gamma Lupi is a blue-white subgiant star belonging to star class B2 IV. Its distance from Earth is about 420 light-years and its apparent visual magnitude is 2.77, which is just slightly smaller than Beta Lupi. You can find Gamma Lupi in the upper part of the constellation shape, below the wolf’s head.
Other less “impressive” stars in the constellation of Lupus are the blue-white subregions Delta Lupi, Eta Lupi, Iota Lupi, the yellow stars Zeta Lupi, 1 Lupi and the red giant star Phi-1 Lupi.
The major deep sky objects located in the Lupus Constellation
The constellation of the wolf does not contain any celestial objects that are part of the Messier catalog; unfortunately for astrophotographers, but it does have several interesting deep sky objects. The most famous ones are SN1006 (supernova remnant), NGC 5986 (globular cluster) and IC 4406 (the retina nebula).
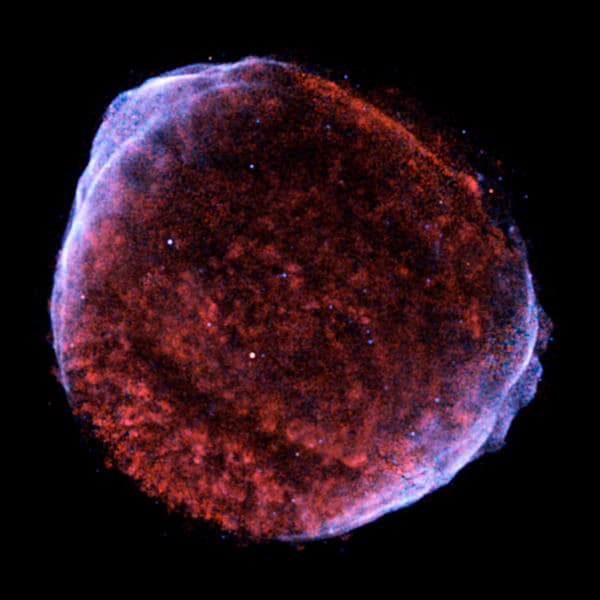
SN 1006
SN 1006 (image from the NASA library) is home to a supernova 7,200 light-years away that was visible from Earth in 1006. This celestial event has become as bright as -7.5 in apparent visual magnitude, making it brighter than any planet in the solar system. It was the brightest stellar event in history: it was observed between April 30 and May 1 of that year and was recorded by many observers from China, Egypt, Iraq, Japan, Switzerland and North America.
NGC 5986
NGC 5986 is a globular cluster located about 2.5 degrees northwest of the star Eta Lupi, about 33,900 light-years from our home planet. It contains thousands of individual stars and has an apparent visual magnitude of 7.52. This globular cluster is interesting because it has two very bright stars (class A-F) that are suspected to be in their last stage of evolution before becoming supernovae.
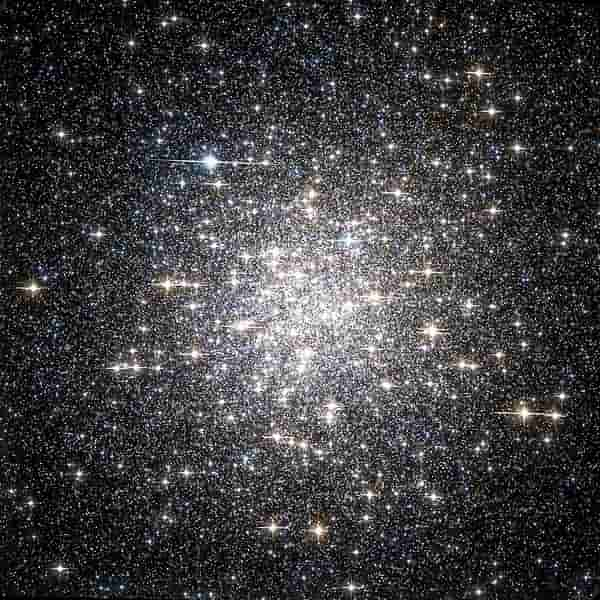

IC 4406
IC 4406 (Retina Nebula) is a planetary nebula located about 2,000 light-years away, near the western boundary of the lupus constellation. One of the main features of this nebula is that it resembles a doughnut when observed from the side. IC 4406 is classified as a bipolar nebula, which means that it looks like a bright spot of light with two lobes coming out on each side.

Trivia
During the conquest of England by William the Conqueror, it was believed that one of the bright stars in the lupus constellation was a divine sign in favour of the Duke of Normandy, who as in the process of conquering new lands.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the story behind the constellation Lupus?
Lupus is quite an old constellation and there are no clear story or myths for the wolf constellation. For a long time, it was considered a sacrifice made by the neighbouring constellation, Centaurus.
When can you see Lupus the constellation?
If you live in the southern hemisphere, you can see Lupus most of the year (the best month being June). If you are located in the North, it won’t be visible to you.
Where is the Lupus constellation?
The wolf constellation is located in the southern hemisphere, inside the third quadrant (SQ3).
Have you seen this constellation in the night sky? Let us know your experience in the comment section 🙂

I’ve been fascinated by space and astronomy from a very young age. When I’m not watching space-themed documentaries, movies or TV series, I spend most of my free time in my backyard admiring the planets and galaxies with my telescope.
Discover the neighboring constellations ✨
This constellation-related story is part of our collection of stargazing articles. If this piece sparked your interest, you’re sure to enjoy the fascinating insights offered in our subsequent articles.
Centaurus is a southern constellation composed of 17 stars that form the shape of the centaur: a mythical creature half man, half horse.

