Summer Triangle illuminates the night revealing three brilliant stars and hidden celestial gems

As June draws to a close, skywatchers are encouraged to turn their attention skyward for a prime viewing opportunity of the Summer Triangle, a prominent asterism now gracing the Northern Hemisphere's night sky. Following a month that has already delivered the Strawberry Moon, the summer solstice, and exceptional views of the Milky Way's core, the celestial show continues. The Summer Triangle, a distinctive three-star pattern, is currently reaching its peak visibility, according to IFL Science.

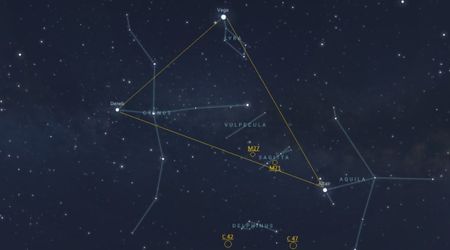
This astronomical formation comprises Altair, Deneb, and Vega, three of the brightest stars visible from Earth. Their increasing elevation in the night sky, combined with the recent new moon phase, creates optimal conditions for observation. The diminished lunar glow results in darker skies, enhancing the visibility of these brilliant stellar points. While still discernible during brighter moon phases, the current darkness offers an unparalleled viewing experience. To locate this stellar trio, observers should face the eastern sky. Vega, being the brightest of the three, will likely be the easiest to identify. Once Vega is pinpointed, Deneb can be found to its left, and Altair below. For those seeking assistance, various stargazing applications are readily available to guide identification.

It is important to note that the Summer Triangle is classified as an asterism, not a constellation. Unlike constellations, which are officially recognized star groupings with defined boundaries, asterisms are distinct, recognizable patterns of stars that lack formal designation. Other well-known asterisms include the Plough, Orion's Belt, and the Pleiades. Each star within the Summer Triangle belongs to a different constellation: Altair is part of Aquila, Deneb is in Cygnus, and Vega resides in Lyra.

Beyond the prominent Summer Triangle, the region offers astute observers the chance to spot several "hidden treasures," constellations that, once known, are surprisingly visible. These include Vulpecula the Fox, Sagitta the Arrow, and Delphinus the Dolphin, as mentioned by NASA. Vulpecula the Fox, a relatively small constellation, lies near the center of the Summer Triangle. Despite its modest size, it hosts one of the sky's most impressive planetary nebulae: M27, also known as the Dumbbell Nebula. Binoculars will reveal it as a fuzzy star, while larger telescopes will bring its distinctive dumbbell shape into clearer focus. Planetary Nebulae, so named for their planet-like appearance to early observers, are formed when stars similar to our Sun reach the end of their lives, expanding into red giants and shedding their outer gases. M27 showcases this stellar evolution, offering a glimpse into the distant future of our own Sun as it transitions into a white dwarf.

Even smaller is Sagitta the Arrow, the third smallest constellation. Situated between Vulpecula and Aquila the Eagle, its stars aptly form the shape of an arrow. Sagitta is home to M71, a unique and unusually young globular cluster. Its lack of a strong, concentrated core has historically puzzled astronomers, even leading to its misclassification as an open cluster until studies in the 1970s confirmed its globular nature. While your view may not match detailed astrophotography, binoculars will reveal this intriguing cluster, and a larger telescope will begin to resolve its stars, highlighting its open cluster-like appearance.

Finally, the delicate Delphinus the Dolphin appears to gracefully arc through the Milky Way, close to Aquila and Sagitta. Many stargazers consider Delphinus a harbinger of the "water constellations" that rise in the east as autumn approaches. This starry dolphin seems to leap from the celestial ocean, signaling more captivating sights to follow later in the evening. With a larger telescope and clear, dark skies, observers can even pinpoint the globular clusters Caldwell 42 and Caldwell 47 within its boundaries.