Auroras from a moderate geomagnetic storm to brighten the skies of New York and Idaho on June 14

This weekend might bring a golden opportunity for aurora chasers. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's (NOAA) Space Weather Prediction Center (SWPC) released a warning about a geomagnetic storm. According to Space.com, the predicted G2-level storm will be caused by unruly space weather and will be accompanied by a display of northern lights, as far south as New York and Idaho, on June 14, 2025. However, with the northern hemisphere tuning in for the summer solstice, extended daytime hours reduce the window to catch the lights.

Geomagnetic storms are categorized on a G-scale, with intensity ranging from G1 (minor) to G5 (extreme). The surge in geomagnetic activity is primarily influenced by a co-rotating interaction region (CIR). This is a turbulent region in the solar wind when faster streams collide with the slower wind ahead. CIRs can generate shock waves that are similar to the ones produced by coronal mass ejections (CMEs). These can also trigger geomagnetic storms and increase the effects of space weather.
Moderate (G2) geomagnetic storm watch issued for June 14th when a coronal hole stream is predicted to reach Earth. https://t.co/aqK4Q6XLqw pic.twitter.com/X4Kdu9ZGUY
— SolarHam (@SolarHam) June 11, 2025
The upcoming CIR event festered from a colossal coronal hole that is now facing Earth. Coronal holes are areas where the magnetic field of the sun opens up and allows high-speed solar wind to escape into space. These regions are cooler as they are void of the typical hot gases trapped by the magnetic field. They are comparatively less dense and appear in darker tones in ultraviolet captures. The Kp index is a scale from 0 to 9 that measures global geomagnetic activity, and NOAA's SWPC forecasts the peak of the geomagnetic storm to be at a 5.67 on June 14.

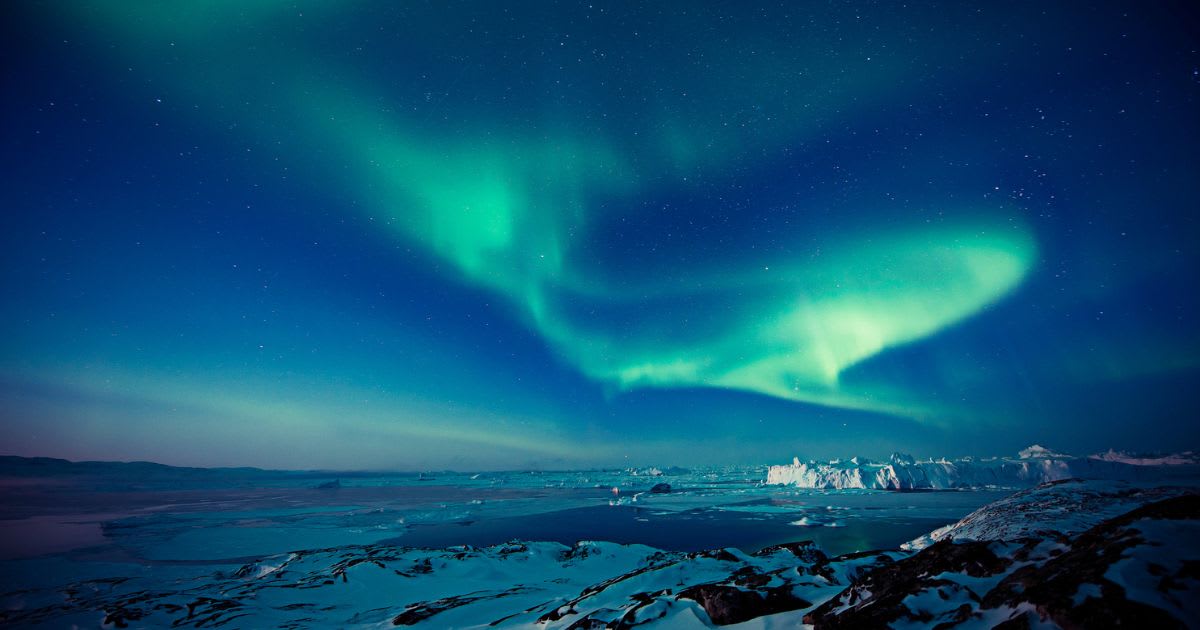
A climb in the value indicated can result in stronger geomagnetic storms, increasing the chances of witnessing auroras at lower latitudes. The mesmerizing natural phenomenon is also expected to be seen over some northern-tier and upper Midwest states, according to USA Today. The latest visual treat of the northern lights was earlier this month when people across 16 different states saw the green, red, and purple hues. However, several factors needed to be perfectly aligned for the lights to be visible, such as the location, weather, time of night, and the level of geomagnetic activity.
A G2 (Moderate) Geomagnetic Storm Watch has been issued for 14 June 2025 (UTC day) due to the arrival of a Coronal Hole High Speed Stream (CH HSS). The associated CH produced upper level G2 (Moderate) geomagnetic storming conditions last rotation. pic.twitter.com/SbUhMrFu2g
— NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center (@NWSSWPC) June 11, 2025
Around 10 states across the U.S might have the opportunity to witness the northern lights on Friday night, June 13, according to Forbes. Low chances are estimated for Washington, Idaho, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Wisconsin, Michigan, and Maine, while Alaska was forecast to have the highest. Though the forecast leading up to the weekend sight will not be as strong, people could still keep a lookout for them during hours after sunset and before sunrise. NOAA recommends a high, north-facing, and unobstructed vantage point away from light pollution.

To view the northern lights, one does not need advanced technology, as the colorful display was visible to the naked eye, as per People. As long as the weather and city lights don’t obstruct the view, one could easily watch, enjoy, and capture the phenomenon. Accurate information on the timings of the auroras is on the NOAA website, which details the viewing updates. NOAA also informed that if the Kp forecast increases to a six, the colors can be "quite bright and active." After the beautiful Strawberry Moon, the people get a glimpse of yet another wonderful natural phenomenon.